DSPIC30F3012-30I/P Microchip Technology, DSPIC30F3012-30I/P Datasheet - Page 26

DSPIC30F3012-30I/P
Manufacturer Part Number
DSPIC30F3012-30I/P
Description
IC DSPIC MCU/DSP 24K 18DIP
Manufacturer
Microchip Technology
Series
dsPIC™ 30Fr
Datasheets
1.DSPIC30F2011-20ISO.pdf
(210 pages)
2.DSPIC30F2011-20ISO.pdf
(6 pages)
3.DSPIC30F2011-20IP.pdf
(26 pages)
4.DSPIC30F3012-20ISO.pdf
(14 pages)
5.DSPIC30F3012-20ISO.pdf
(20 pages)
6.DSPIC30F3014-30IP.pdf
(244 pages)
Specifications of DSPIC30F3012-30I/P
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Program Memory Size
24KB (8K x 24)
Package / Case
18-DIP (0.300", 7.62mm)
Core Processor
dsPIC
Core Size
16-Bit
Speed
30 MIPs
Connectivity
I²C, SPI, UART/USART
Peripherals
Brown-out Detect/Reset, POR, PWM, WDT
Number Of I /o
12
Eeprom Size
1K x 8
Ram Size
2K x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
2.5 V ~ 5.5 V
Data Converters
A/D 8x12b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Product
DSCs
Data Bus Width
16 bit
Processor Series
DSPIC30F
Core
dsPIC
Maximum Clock Frequency
30 MHz
Number Of Programmable I/os
12
Data Ram Size
2 KB
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 85 C
Mounting Style
Through Hole
3rd Party Development Tools
52713-733, 52714-737, 53276-922, EWDSPIC
Development Tools By Supplier
PG164130, DV164035, DV244005, DV164005, PG164120, ICE4000, DM240002, DM300018, DM330011
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
For Use With
AC30F005 - MODULE SCKT DSPIC30F 18DIP/SOICDV164005 - KIT ICD2 SIMPLE SUIT W/USB CABLEACICE0202 - ADAPTER MPLABICE 18P 300 MIL
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Other names
DSPIC30F3012-30IP
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
DSPIC30F3012-30I/P
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Quantity:
1 936
Company:
Part Number:
DSPIC30F3012-30I/P
Manufacturer:
TI
Quantity:
6
Part Number:
DSPIC30F3012-30I/P
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP/微芯
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
DSPIC30F3012-30I/PT
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP/微芯
Quantity:
20 000
dsPIC30F2011/2012/3012/3013
The SA and SB bits are modified each time data
passes through the adder/subtracter but can only be
cleared by the user. When set, they indicate that the
accumulator has overflowed its maximum range (bit 31
for 32-bit saturation or bit 39 for 40-bit saturation) and
will be saturated if saturation is enabled. When satura-
tion is not enabled, SA and SB default to bit 39 overflow
and thus indicate that a catastrophic overflow has
occurred. If the COVTE bit in the INTCON1 register is
set, SA and SB bits generate an arithmetic warning trap
when saturation is disabled.
The overflow and saturation Status bits can optionally
be viewed in the STATUS register (SR) as the logical
OR of OA and OB (in bit OAB) and the logical OR of SA
and SB (in bit SAB). This allows programmers to check
one bit in the STATUS register to determine if either
accumulator has overflowed, or one bit to determine if
either accumulator has saturated. This would be useful
for complex number arithmetic which typically uses
both the accumulators.
The device supports three saturation and overflow
modes:
1.
2.
3.
DS70139G-page 26
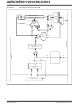
Bit 39 Overflow and Saturation:
When bit 39 overflow and saturation occurs, the
saturation logic loads the maximally positive 9.31
(0x7FFFFFFFFF) or maximally negative 9.31
value
accumulator. The SA or SB bit is set and remains
set until cleared by the user. This is referred to as
‘super saturation’ and provides protection against
erroneous
problems (e.g., gain calculations).
Bit 31 Overflow and Saturation:
When bit 31 overflow and saturation occurs, the
saturation logic then loads the maximally posi-
tive 1.31 value (0x007FFFFFFF) or maximally
negative 1.31 value (0x0080000000) into the
target accumulator. The SA or SB bit is set and
remains set until cleared by the user. When this
Saturation mode is in effect, the guard bits are
not used, so the OA, OB or OAB bits are never
set.
Bit 39 Catastrophic Overflow:
The bit 39 overflow Status bit from the adder is
used to set the SA or SB bit which remains set
until cleared by the user. No saturation operation
is performed and the accumulator is allowed to
overflow (destroying its sign). If the COVTE bit in
the INTCON1 register is set, a catastrophic
overflow can initiate a trap exception.
(0x8000000000)
data
or
unexpected
into
the
algorithm
target
2.4.2.2
The MAC class of instructions (with the exception of
MPY, MPY.N, ED and EDAC) can optionally write a
rounded version of the high word (bits 31 through 16)
of the accumulator that is not targeted by the instruction
into data space memory. The write is performed across
the X bus into combined X and Y address space. The
following addressing modes are supported:
1.
2.
2.4.2.3
The round logic is a combinational block which
performs a conventional (biased) or convergent
(unbiased) round function during an accumulator write
(store). The Round mode is determined by the state of
the RND bit in the CORCON register. It generates a
16-bit, 1.15 data value, which is passed to the data
space write saturation logic. If rounding is not indicated
by the instruction, a truncated 1.15 data value is stored
and the least significant word (lsw) is simply discarded.
Conventional rounding takes bit 15 of the accumulator,
zero-extends it and adds it to the ACCxH word (bits 16
through 31 of the accumulator). If the ACCxL word
(bits 0 through 15 of the accumulator) is between
0x8000 and 0xFFFF (0x8000 included), ACCxH is
incremented. If ACCxL is between 0x0000 and 0x7FFF,
ACCxH is left unchanged. A consequence of this
algorithm is that over a succession of random rounding
operations, the value tends to be biased slightly
positive.
Convergent (or unbiased) rounding operates in the
same manner as conventional rounding, except when
ACCxL equals 0x8000. If this is the case, the LSb
(bit 16 of the accumulator) of ACCxH is examined. If it
is ‘1’, ACCxH is incremented. If it is ‘0’, ACCxH is not
modified. Assuming that bit 16 is effectively random in
nature, this scheme will remove any rounding bias that
may accumulate.
The SAC and SAC.R instructions store either a
truncated (SAC) or rounded (SAC.R) version of the
contents of the target accumulator to data memory via
the
Section 2.4.2.4 “Data Space Write
Note that for the MAC class of instructions, the
accumulator write-back operation functions in the
same manner, addressing combined MCU (X and Y)
data space though the X bus. For this class of
instructions, the data is always subject to rounding.
W13, Register Direct:
The rounded contents of the non-target
accumulator are written into W13 as a 1.15
fraction.
[W13]+
Post-Increment:
The rounded contents of the non-target
accumulator are written into the address pointed
to by W13 as a 1.15 fraction. W13 is then
incremented by 2 (for a word write).
X
bus
Accumulator ‘Write-Back’
Round Logic
=
(subject
2,
© 2010 Microchip Technology Inc.
Register
to
data
Indirect
saturation,
Saturation”).
with
see