M30626FJPGP#U3C Renesas Electronics America, M30626FJPGP#U3C Datasheet - Page 131

M30626FJPGP#U3C
Manufacturer Part Number
M30626FJPGP#U3C
Description
IC M16C MCU FLASH 512K 100LQFP
Manufacturer
Renesas Electronics America
Series
M16C™ M16C/60r
Datasheets
1.QSK-62P_PLUS.pdf
(103 pages)
2.M30622SAFPU5.pdf
(308 pages)
3.M30620SPGPU3C.pdf
(423 pages)
Specifications of M30626FJPGP#U3C
Core Processor
M16C/60
Core Size
16-Bit
Speed
24MHz
Connectivity
I²C, IEBus, UART/USART
Peripherals
DMA, WDT
Number Of I /o
85
Program Memory Size
512KB (512K x 8)
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Ram Size
31K x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
2.7 V ~ 5.5 V
Data Converters
A/D 26x10b; D/A 2x8b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
100-LQFP
For Use With
867-1000 - KIT QUICK START RENESAS 62PR0K33062PS001BE - R0K33062P STARTER KITR0K33062PS000BE - KIT EVAL STARTER FOR M16C/62PM3062PT3-CPE-3 - EMULATOR COMPACT M16C/62P/30P
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Eeprom Size
-
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
- Current page: 131 of 423
- Download datasheet (5Mb)
M16C/62P Group (M16C/62P, M16C/62PT)
Rev.2.41
REJ09B0185-0241
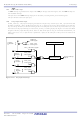
Figure 12.5
12.5.4
Address bus
CPU clock
Data bus
(1) The CPU obtains interrupt information (interrupt number and interrupt request level) by reading address
(2) The FLG register, prior to an interrupt sequence, is saved to a temporary register
(3) The I, D and U flags in the FLG register become as follows:
(4) The temporary register
(5) The PC is saved to the stack.
(6) The interrupt priority level of the acknowledged interrupt in IPL is set.
(7) The start address of the relevant interrupt routine set in the interrupt vector is stored in the PC.
An interrupt sequence − what are performed over a period from the instant an interrupt is accepted to the instant
the interrupt routine is executed − is described here.
If an interrupt occurs during execution of an instruction, the processor determines its priority when the
execution of the instruction is completed, and transfers control to the interrupt sequence from the next cycle. If
an interrupt occurs during execution of either the SMOVB, SMOVF, SSTR or RMPA instruction, the processor
temporarily suspends the instruction being executed, and transfers control to the interrupt sequence.
The CPU behavior during the interrupt sequence is described below. Figure 12.5 shows Time Required for
Executing Interrupt Sequence.
After the interrupt sequence is completed, an instruction is executed from the starting address of the interrupt
routine.
NOTES:
•
•
•
NOTES :
1.Temporary register cannot be modified by users.
Jan 10, 2006
000000h. Then, the IR bit applicable to the interrupt information is set to “0” (interrupt requested).
The I flag is set to “0” (interrupt disabled)
The D flag is set to “0” (single-step interrupt disabled)
The U flag is set to “0” (ISP selected)
However, the U flag does not change state if an INT instruction for software interrupt Nos. 32 to 63 is
executed.
WR
RD
Interrupt Sequence
1. The indeterminate state depends on the instruction queue buffer. A read cycle occurs when
2. The WR signal timing shown here is for the case where the stack is located in the internal RAM.
(2)
the instruction queue buffer is ready to accept instructions.
Time Required for Executing Interrupt Sequence
1
Address
0000h
information
2
Interrupt
Page 114 of 390
3
(1)
4
within the CPU is saved to the stack.
Indeterminate
Indeterminate
Indeterminate
5
6
(1)
(1)
7
(1)
8
SP-2
9
contents
SP-2
10
SP-4
11
contents
SP-4
12
13
vec
contents
vec
14
(1)
within the CPU.
vec+2
15
contents
vec+2
16
12. Interrupt
17
PC
18
Related parts for M30626FJPGP#U3C
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
KIT STARTER FOR M16C/29
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
KIT STARTER FOR R8C/2D
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
R0K33062P STARTER KIT
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
KIT STARTER FOR R8C/23 E8A
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
KIT STARTER FOR R8C/25
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
KIT STARTER H8S2456 SHARPE DSPLY
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
KIT STARTER FOR R8C38C
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
KIT STARTER FOR R8C35C
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
KIT STARTER FOR R8CL3AC+LCD APPS
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
KIT STARTER FOR RX610
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
KIT STARTER FOR R32C/118
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
KIT DEV RSK-R8C/26-29
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
KIT STARTER FOR SH7124
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
KIT STARTER FOR H8SX/1622
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
KIT DEV FOR SH7203
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Datasheet: