DSPIC30F4011-20E/PT Microchip Technology, DSPIC30F4011-20E/PT Datasheet - Page 17

DSPIC30F4011-20E/PT
Manufacturer Part Number
DSPIC30F4011-20E/PT
Description
IC DSPIC MCU/DSP 48K 44TQFP
Manufacturer
Microchip Technology
Series
dsPIC™ 30Fr
Datasheets
1.DSPIC30F4012-30ISO.pdf
(238 pages)
2.DSPIC30F4012-30ISO.pdf
(18 pages)
3.DSPIC30F4012-30ISO.pdf
(6 pages)
4.DSPIC30F4012-30ISO.pdf
(16 pages)
5.DSPIC30F4012-30ISO.pdf
(22 pages)
6.DSPIC30F4011-30IP.pdf
(228 pages)
Specifications of DSPIC30F4011-20E/PT
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Program Memory Size
48KB (16K x 24)
Package / Case
44-TQFP, 44-VQFP
Core Processor
dsPIC
Core Size
16-Bit
Speed
20 MIPS
Connectivity
CAN, I²C, SPI, UART/USART
Peripherals
Brown-out Detect/Reset, Motor Control PWM, QEI, POR, PWM, WDT
Number Of I /o
30
Eeprom Size
1K x 8
Ram Size
2K x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
2.5 V ~ 5.5 V
Data Converters
A/D 9x10b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 125°C
Data Bus Width
16 bit
Processor Series
DSPIC30F
Core
dsPIC
Maximum Clock Frequency
20 MHz
Number Of Programmable I/os
30
Data Ram Size
2 KB
Operating Supply Voltage
2.5 V to 5.5 V
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 125 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
3rd Party Development Tools
52713-733, 52714-737, 53276-922, EWDSPIC
Data Rom Size
1024 B
Development Tools By Supplier
PG164130, DV164035, DV244005, DV164005, PG164120, ICE4000, DM240002, DM300018, DM330011
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
Package
44TQFP
Device Core
dsPIC
Family Name
dsPIC30
Maximum Speed
20 MHz
Interface Type
CAN/I2C/SPI/UART
On-chip Adc
9-chx10-bit
Number Of Timers
5
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
For Use With
XLT44PT3 - SOCKET TRAN ICE 44MQFP/TQFPAC30F006 - MODULE SKT FOR DSPIC30F 44TQFP
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Other names
DSPIC30F401120EPT
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
DSPIC30F4011-20E/PT
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
DSPIC30F4011-20E/PT
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP/微芯
Quantity:
20 000
2.0
2.1
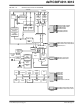
The core has a 24-bit instruction word. The Program
Counter (PC) is 23 bits wide with the Least Significant
bit (LSb) always clear (see
Address
is ignored during normal program execution, except for
certain specialized instructions. Thus, the PC can
address up to 4M instruction words of user program
space. An instruction prefetch mechanism is used to
help maintain throughput. Program loop constructs,
free from loop count management overhead, are
supported using the DO and REPEAT instructions, both
of which are interruptible at any point.
The working register array consists of 16x16-bit
registers, each of which can act as data, address or off-
set registers. One working register (W15) operates as
a software Stack Pointer for interrupts and calls.
The data space is 64 Kbytes (32K words) and is split into
two blocks, referred to as X and Y data memory. Each
block has its own independent Address Generation Unit
(AGU). Most instructions operate solely through the X
memory, AGU, which provides the appearance of a sin-
gle, unified data space. The Multiply-Accumulate (MAC)
class of dual source DSP instructions operate through
both the X and Y AGUs, splitting the data address space
into two parts (see
Space”). The X and Y data space boundary is device-
specific and cannot be altered by the user. Each data
word consists of 2 bytes, and most instructions can
address data either as words or bytes.
There are two methods of accessing data stored in
program memory:
• The upper 32 Kbytes of data space memory can be
© 2010 Microchip Technology Inc.
Note:
mapped into the lower half (user space) of program
space at any 16K program word boundary, defined
by the 8-bit Program Space Visibility Page (PSV-
PAG) register. This lets any instruction access pro-
gram space as if it were data space, with a
limitation that the access requires an additional
cycle. Moreover, only the lower 16 bits of each
instruction word can be accessed using this
method.
CPU ARCHITECTURE
OVERVIEW
Core Overview
Space”), and the Most Significant bit (MSb)
This data sheet summarizes features of
this group of dsPIC30F devices and is not
intended to be a complete reference
source. For more information on the CPU,
peripherals, register descriptions and
general device functionality, refer to the
“dsPIC30F Family Reference Manual”
(DS70046). For more information on the
device instruction set and programming,
refer to the “16-bit MCU and DSC
Reference Manual” (DS70157).
Section 3.2 “Data Address
Section 3.1 “Program
• SWWLinear indirect access of 32K word pages
Overhead-free circular buffers (Modulo Addressing)
are supported in both X and Y address spaces. This is
primarily intended to remove the loop overhead for
DSP algorithms.
The X AGU also supports Bit-Reversed Addressing on
destination effective addresses, to greatly simplify input
or output data reordering for radix-2 FFT algorithms.
Refer to
details on Modulo and Bit-Reversed Addressing.
The core supports Inherent (no operand), Relative, Lit-
eral, Memory Direct, Register Direct, Register Indirect,
Register Offset and Literal Offset Addressing modes.
Instructions are associated with predefined addressing
modes, depending upon their functional requirements.
For most instructions, the core is capable of executing
a data (or program data) memory read, a working reg-
ister (data) read, a data memory write and a program
(instruction) memory read per instruction cycle. As a
result, 3-operand instructions are supported, allowing
C = A + B operations to be executed in a single cycle.
A DSP engine has been included to significantly
enhance the core arithmetic capability and throughput.
It features a high-speed, 17-bit by 17-bit multiplier, a
40-bit ALU, two 40-bit saturating accumulators and a
40-bit bidirectional barrel shifter. Data in the accumula-
tor, or any working register, can be shifted up to 16 bits
right or 16 bits left in a single cycle. The DSP instruc-
tions operate seamlessly with all other instructions and
have been designed for optimal real-time performance.
The MAC class of instructions can concurrently fetch
two data operands from memory, while multiplying two
W registers. To enable this concurrent fetching of data
operands, the data space has been split for these
instructions and is linear for all others. This has been
achieved in a transparent and flexible manner by
dedicating certain working registers to each address
space for the MAC class of instructions.
The core does not support a multi-stage instruction
pipeline. However, a single-stage instruction prefetch
mechanism is used, which accesses and partially
decodes instructions a cycle ahead of execution in order
to maximize available execution time. Most instructions
execute in a single cycle with certain exceptions.
The core features a vectored exception processing
structure for traps and interrupts, with 62 independent
vectors. The exceptions consist of up to 8 traps (of
which 4 are reserved) and 54 interrupts. Each interrupt
is prioritized based on a user-assigned priority between
1 and 7 (1 being the lowest priority and 7 being the
highest) in conjunction with a predetermined ‘natural
order’. Traps have fixed priorities, ranging from 8 to 15.
within program space is also possible, using any
working register via table read and write instruc-
tions. Table read and write instructions can be
used to access all 24 bits of an instruction word.
dsPIC30F4011/4012
Section 4.0 “Address Generator Units”
DS70135G-page 17
for