C8051F018-GQR Silicon Laboratories Inc, C8051F018-GQR Datasheet
C8051F018-GQR
Specifications of C8051F018-GQR
Available stocks
Related parts for C8051F018-GQR
C8051F018-GQR Summary of contents
Page 1
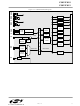
... Temperature Range: –40C to +85C DIGITAL I/O TEMP PCA SENSOR 10-Bit SMBus SAR SPI Bus ADC UART VREF Timer 0 Timer Timer 2 - VOLTAGE Timer 3 COMPARATORS CLOCK DEBUG JTAG CIRCUIT CIRCUITRY 1280 B 21 SANITY SRAM INTERRUPTS CONTROL C8051F018 C8051F019 (I2C Compatible), SPI , and UART ...
Page 2
... TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW ......................................................................................................... 7 Table 1.1. Product Selection Guide .....................................................................................................................7 Figure 1.1. C8051F018 Block Diagram ..............................................................................................................8 Figure 1.2. C8051F019 Block Diagram ..............................................................................................................9 TM 1.1. CIP-51 CPU .............................................................................................................................................10 Figure 1.3. Comparison of Peak MCU Execution Speeds.................................................................................10 Figure 1.4. On-Board Clock and Reset..............................................................................................................11 1.2. On-Board Memory ......................................................................................................................................12 Figure 1.5. On-Board Memory Map..................................................................................................................12 1 ...
Page 3
... C8051F018 C8051F019 Figure 6.3. CPT0CN: Comparator 0 Control Register ......................................................................................39 Figure 6.4. CPT1CN: Comparator 1 Control Register ......................................................................................40 Table 6.1. Comparator Electrical Characteristics ..............................................................................................41 7. VOLTAGE REFERENCE ................................................................................................. 42 Figure 7.1. Voltage Reference Functional Block Diagram ...............................................................................42 Figure 7.2. REF0CN: Reference Control Register ............................................................................................43 Table 7.1. Reference Electrical Characteristics .................................................................................................43 8. ...
Page 4
... Figure 14.8. SMB0STA: SMBus Status Register............................................................................................104 Table 14.1. SMBus Status Codes ....................................................................................................................105 15. SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE BUS.................................................................. 106 Figure 15.1. SPI Block Diagram .....................................................................................................................106 Figure 15.2. Typical SPI Interconnection........................................................................................................107 15.1. Signal Descriptions................................................................................................................................107 15.2. Operation ...............................................................................................................................................108 Figure 15.3. Full Duplex Operation.................................................................................................................108 Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 4 ...
Page 5
... C8051F018 C8051F019 15.3. Serial Clock Timing...............................................................................................................................109 Figure 15.4. Data/Clock Timing Diagram .......................................................................................................109 15.4. SPI Special Function Registers..............................................................................................................110 Figure 15.5. SPI0CFG: SPI Configuration Register........................................................................................110 Figure 15.6. SPI0CN: SPI Control Register ....................................................................................................111 Figure 15.7. SPI0CKR: SPI Clock Rate Register............................................................................................112 Figure 15 ...
Page 6
... Flash Programming Commands.............................................................................................................150 Figure 19.3. FLASHCON: JTAG Flash Control Register...............................................................................151 Figure 19.4. FLASHADR: JTAG Flash Address Register..............................................................................151 Figure 19.5. FLASHDAT: JTAG Flash Data Register....................................................................................152 Figure 19.6. FLASHSCL: JTAG Flash Scale Register ...................................................................................152 19.3. Debug Support.......................................................................................................................................153 Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 6 ...
Page 7
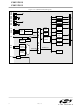
... Each MCU is specified for 2.8V-to-3.6V operation over the industrial temperature range (-45C to +85C). The Port I/Os, /RST, and JTAG pins are tolerant for input signals up to 5V. The C8051F018 is available in the 64-pin TQFP (see block diagram in Figure 1.1). The C8051F019 is available in the 48-pin TQFP (see block diagram in Figure 1.2). ...
Page 8
... Figure 1.1. C8051F018 Block Diagram VDD VDD VDD Digital Power DGND DGND DGND AV+ AV+ Analog Power AGND AGND TCK Boundary Scan JTAG TMS Logic TDI Debug HW TDO /RST VDD WDT Monitor External XTAL1 Oscillator XTAL2 Circuit Internal Oscillator VREF VREF 16kbyte ...
Page 9
... C8051F018 C8051F019 Figure 1.2. C8051F019 Block Diagram VDD VDD Digital Power DGND DGND DGND DGND AV+ AV+ Analog Power AGND AGND TCK Boundary Scan JTAG TMS Logic TDI Debug HW TDO /RST VDD WDT Monitor External XTAL1 Oscillator XTAL2 Circuit Internal Oscillator VREF ...
Page 10
... CIP-51 CPU 1.1.1. Fully 8051 Compatible The C8051F018/9 utilizes Silcon Labs’ proprietary CIP-51 microcontroller core. The CIP-51 is fully compatible TM with the MCS-51 instruction set. Standard 803x/805x assemblers and compilers can be used to develop software. The core has all the peripherals included with a standard 8052, including four 16-bit counter/timers, a full-duplex UART, 256 bytes of internal RAM space, 128 byte Special Function Register (SFR) address space, and four byte- wide I/O Ports ...
Page 11
... Additional Features The C8051F018/9 has several key enhancements both inside and outside the CIP-51 core to improve its overall performance and ease of use in the end applications. The extended interrupt handler provides 21 interrupt sources into the CIP-51 (as opposed to 7 for the standard 8051), allowing the numerous analog and digital peripherals to interrupt the controller ...
Page 12
... The same 1024 byte RAM 0x0BFF (same 1024 byte RAM block ) block can be addressed on 0x0800 1k boundaries throughout the 64k External Data 0x07FF (same 1024 byte RAM block ) Memory space. 0x0400 0x03FF RAM - 1024 Bytes (accessable using MOVX instruction) 0x0000 Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 12 ...
Page 13
... The C8051F015DK is a development kit with all the hardware and software necessary to develop application code and perform in-circuit debug with the C8051F018/9 MCUs. The kit includes software with a developer’s studio and debugger, an integrated 8051 assembler, and an RS-232 to JTAG protocol translator module referred to as the EC. ...
Page 14
... XBR0, XBR1, PRT0CF, PRT1CF, XBR2 Registers PRT2CF Registers 4 2 Priority Decoder I/O 2 Cells Digital Crossbar I/O Cells P2 8 I/O Cells PRT3CF Register P3 I/O Cells Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 External Pins P0.0 Highest Priority P0.7 P1.0 P1.7 P2.0 Lowest Priority P2.7 P3.0 P3.7 14 ...
Page 15
... C8051F019 1.5. Programmable Counter Array The C8051F018/9 have an on-board Programmable Counter/Timer Array (PCA) in addition to the four 16-bit general-purpose counter/timers. The PCA consists of a dedicated 16-bit counter/timer timebase with 5 programmable capture/compare modules. The timebase gets its clock from one of four sources: the system clock divided by 12, the system clock divided by 4, Timer 0 overflow External Clock Input (ECI) ...
Page 16
... Analog to Digital Converter The C8051F018/9 have an on-chip 10-bit SAR ADC with a 9-channel input multiplexer. With a maximum throughput of 100ksps, the ADC offers true 10-bit accuracy with an INL of 1LSB. The ADC has a maximum throughput of 100ksps. There is also an on-board 15ppm voltage reference external reference may be used via the VREF pin ...
Page 17
... Comparators The C8051F018/9 have two comparators on chip. The MCU data and control interface to each comparator is via the Special Function Registers. The MCU can individually place each comparator in low power shutdown mode. The comparators have software programmable hysteresis. Each comparator can generate an interrupt on its rising edge, falling edge, or both. The comparators’ ...
Page 18
... Frequency) Tsysl (SYSCLK Low Time) Tsysh (SYSCLK High Time) Note 1: Analog Supply AV+ must be greater than 1V for VDD monitor to operate. Note 2: SYSCLK must be at least 32 kHz to enable debugging. CONDITIONS MIN 2.8 2.8 - Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 TYP MAX UNITS 3.0 3 0 ...
Page 19
... C8051F018 C8051F019 4. PINOUT AND PACKAGE DEFINITIONS Type Description Name F018 F019 VDD 31, 23, Digital Voltage Supply. 40 DGND Digital Ground. 30, 22, 41, 33, 61 27, 19 AV+ 16, 13, Positive Analog Voltage Supply AGND Analog Ground TCK JTAG Test Clock with internal pull-up. TMS D In JTAG Test-Mode Select with internal pull-up ...
Page 20
... Port3 Bit5. (See the Port I/O Sub-System section for complete description). 57 P3.6 D I/O 46 Port3 Bit6. (See the Port I/O Sub-System section for complete description). P3.7 D I/O Port3 Bit7. (See the Port I/O Sub-System section for complete description). 45 Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 20 ...
Page 21
... Figure 4.1. TQFP-64 Pinout Diagram CP1 CP1+ CP0- 3 CP0+ 4 AGND 5 VRE F 6 AIN0 7 AIN1 8 AIN2 9 AIN3 10 AIN4 11 12 AIN5 AIN6 13 AIN7 14 AGND 15 AV C8051F018 Rev. 1.2 P0.3 P0.2 P3.6 P3.7 P2.6 P2.7 P0.1 DGND VD D P0.0 P1.0 P1.1 P1.2 P1.3 P1.4 P2.0 ...
Page 22
... Figure 4.2. TQFP-64 Package Drawing PIN 1 DESIGNATOR Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 MIN NOM (mm) ( 0.17 0. 12. 10. 0. ...
Page 23
... C8051F018 C8051F019 Figure 4.3. TQFP-48 Pinout Diagram CP0- 1 CP0+ 2 VREF 3 AIN0 4 AIN1 5 AIN2 6 AIN3 7 AIN4 8 AIN5 9 AIN6 10 AIN7 11 AGND 12 23 C8051F019 Rev. 1.2 P0.3 36 P0.2 35 P0.1 34 DGND 33 VDD 32 P0.0 31 P1.0 30 P1.1 29 P1.2 28 DGND 27 P1.3 26 P1.4 25 ...
Page 24
... Figure 4.4. TQFP-48 Package Drawing PIN 1 IDENTIFIER Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 MIN NOM MAX (mm) (mm) (mm 1.20 0.05 - 0.15 0.95 1.00 1.05 0.17 0.22 0. ...
Page 25
... C8051F018 C8051F019 5. ADC The ADC subsystem consists of a 9-channel configurable analog multiplexer (AMUX) and a 100ksps, 10-bit successive-approximation-register ADC with integrated track-and-hold and programmable window detector (see block diagram in Figure 5.1). The AMUX, PGA, Data Conversion Modes, and Window Detector are all configurable under software control via the Special Function Register’ ...
Page 26
... ADC is operated continuously. Mode 3 is used when the start of conversion is triggered by external hardware. In this case, the track-and-hold is in its low power mode at times when the CNVSTR input is high. Tracking can also be disabled (shutdown) when the entire chip is in low power standby or sleep modes. Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 26 ...
Page 27
... C8051F018 C8051F019 Figure 5.2. 10-Bit ADC Track and Conversion Example Timing A. ADC Timing for External Trigger Source CNVSTR (ADSTM[1:0]=10) SAR Clocks Low Power or ADCTM=1 Convert ADCTM=0 Track Or Convert B. ADC Timing for Internal Trigger Sources Timer2, Timer3 Overflow; Write 1 to ADBUSY (ADSTM[1:0]=00, 01, 11) ...
Page 28
... AIN0, AIN1 are (respectively differential input pair NOTE: The ADC Data Word is in 2’s complement format for channels configured as differential. R/W R/W R/W R/W - AIN67IC AIN45IC AIN23IC Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 R/W Reset Value AIN01IC 00000000 SFR Address: Bit1 Bit0 0xBA 28 ...
Page 29
... C8051F018 C8051F019 Figure 5.5. AMX0SL: AMUX Channel Select Register (C8051F01x) R/W R/W R Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bits7-4: UNUSED. Read = 0000b; Write = don’t care Bits3-0: AMXAD3-0: AMUX Address Bits 0000-1111: ADC Inputs selected per chart below 0000 0001 A 0000 AIN0 AIN1 M X +(AIN0) ...
Page 30
... SAR Conversion Clock = 16 Systems Clocks (Note: Conversion clock should be 2MHz.) Bits4-3: UNUSED. Read = 00b; Write = don’t care Bits2-0: Reserved: Must be = 000b R/W R/W R/W R AMPGN2 AMPGN1 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 R/W Reset Value AMPGN0 01100000 SFR Address: Bit1 Bit0 0xBC 30 ...
Page 31
... C8051F018 C8051F019 Figure 5.7. ADC0CN: ADC Control Register R/W R/W R/W ADCEN ADCTM ADCINT Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit7: ADCEN: ADC Enable Bit 0: ADC Disabled. ADC is in low power shutdown. 1: ADC Enabled. ADC is active and ready for data conversions. Bit6: ADCTM: ADC Track Mode Bit ...
Page 32
... R/W R/W Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 ADC0H:ADC0L (ADLJST = 1) 0xFFC0 0x8000 0x7FC0 0x0000 ADC0H:ADC0L (ADLJST = 1) 0x7FC0 0x0000 0xFFC0 0x8000 Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 R/W R/W Reset Value 00000000 SFR Address: Bit1 Bit0 0xBF R/W R/W Reset Value 00000000 SFR Address: Bit1 Bit0 0xBE ...
Page 33
... C8051F018 C8051F019 5.3. ADC Programmable Window Detector The ADC programmable window detector is very useful in many applications. It continuously compares the ADC output to user-programmed limits and notifies the system when an out-of-band condition is detected. This is especially effective in an interrupt-driven system, saving code space and CPU bandwidth while delivering faster system response times ...
Page 34
... ADC0LTH:ADC0LTH = 0xFFFF, ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL = 0x0100. An ADC End of Conversion will cause an ADC Window Compare Interrupt (ADWINT=1) if the resulting ADC (Two’s Data Word is < 0xFFFF or > 0x0100. (Two’s Complement math, 0xFFFF = -1.) Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 ADWINT=1 ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL ADWINT not affected ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL ADWINT=1 ...
Page 35
... C8051F018 C8051F019 Figure 5.15. 10-Bit ADC Window Interrupt Examples, Left Justified Data Input Voltage ADC Data (AD0 - AGND) Word REF x (1023/1024) 0xFFC0 ADWINT not affected 0x8040 REF x (512/1024) 0x8000 ADC0LTH:ADC0LTL 0x7FC0 ADWINT=1 0x4040 REF x (256/1024) 0x4000 ADC0GTH:ADC0GTL 0x3FC0 ADWINT not affected ...
Page 36
... Temp = 0C POWER SPECIFICATIONS Power Supply Current (AV+ Operating Mode, 100ksps supplied to ADC) Power Supply Rejection CONDITIONS MIN 59 th harmonic 16 1.5 0 AGND Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 TYP MAX UNITS 10 bits ½ 1 LSB ½ 1 LSB 0.5 LSB -1.5 ...
Page 37
... C8051F019 6. COMPARATORS The C8051F018/9 have two on-chip analog voltage comparators as shown in Figure 6.1. The inputs of each Comparator are available at the package pins. The output of each comparator is optionally available at the package pins via the I/O crossbar (see Section 13.1). When assigned to package pins, each comparator output can be programmed to operate in open drain or push-pull modes (see section 13 ...
Page 38
... VIN+ + CP0 CP0- _ VIN- CIRCUIT CONFIGURATION Positive Hysteresis Voltage (Programmed with CP0HYSP Bits) VIN- INPUTS VIN OUTPUT V OL Positive Hysteresis Disabled OUT Negative Hysteresis Disabled Maximum Positive Hysteresis Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 Negative Hysteresis Voltage (Programmed by CP0HYSN Bits) Maximum Negative Hysteresis 38 ...
Page 39
... C8051F018 C8051F019 Figure 6.3. CPT0CN: Comparator 0 Control Register R/W R R/W CP0EN CP0OUT CP0RIF Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit7: CP0EN: Comparator 0 Enable Bit 0: Comparator 0 Disabled. 1: Comparator 0 Enabled. Bit6: CP0OUT: Comparator 0 Output State Flag 0: Voltage on CP0+ < CP0- 1: Voltage on CP0+ > CP0- Bit5: CP0RIF: Comparator 0 Rising-Edge Interrupt Flag ...
Page 40
... Bit1-0: CP1HYN1-0: Comparator 1 Negative Hysteresis Control Bits 00: Negative Hysteresis Disabled 01: Negative Hysteresis = 2mV 10: Negative Hysteresis = 4mV 11: Negative Hysteresis = 10mV R/W R/W R/W CP1FIF CP1HYP1 CP1HYP0 CP1HYN1 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 R/W R/W Reset Value CP1HYN0 00000000 SFR Address: Bit1 Bit0 0x9F 40 ...
Page 41
... C8051F018 C8051F019 Table 6.1. Comparator Electrical Characteristics VDD = 3.0V, AV+ = 3.0V, -40C to +85C unless otherwise specified. PARAMETER Response Time1 (CP+) – (CP-) = 100mV (Note 1) Response Time2 (CP+) – (CP-) = 10mV (Note 1) Common Mode Rejection Ratio Positive Hysteresis1 CPnHYP1 Positive Hysteresis2 CPnHYP1 Positive Hysteresis3 CPnHYP1 Positive Hysteresis4 ...
Page 42
... A/D measurements performed on the sensor while disabled result in meaningless data. Figure 7.1. Voltage Reference Functional Block Diagram AV+ External Voltage Reference Circuit R1 AGND VREF External Equivalent Load Circuit RLOAD AGND Temp EN Sensor Bias EN TEMPE BIASE Generator REFBE AGND 2.4V EN Reference AGND Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 (to Analog Mux) (Bias to ADC) (to ADC) 42 ...
Page 43
... C8051F018 C8051F019 Figure 7.2. REF0CN: Reference Control Register R/W R/W R Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bits7-3: UNUSED. Read = 00000b; Write = don’t care Bit2: TEMPE: Temperature Sensor Enable Bit 0: Internal Temperature Sensor Off. 1: Internal Temperature Sensor On. Bit1: BIASE: Bias Enable Bit for ADC 0: Internal Bias Off ...
Page 44
... TMP1 TMP2 SRAM ADDRESS ALU REGISTER DATA BUS BUFFER D8 SFR BUS D8 SFR_WRITE_DATA D8 INTERFACE D8 MEMORY MEM_WRITE_DATA A16 INTERFACE MEM_READ_DATA PIPELINE D8 INTERRUPT INTERFACE D8 D8 REGISTER Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 TM instruction set. STACK POINTER SRAM (256 X 8) SFR_ADDRESS SFR_CONTROL SFR_READ_DATA MEM_ADDRESS MEM_CONTROL SYSTEM_IRQs EMULATION_IRQ 44 ...
Page 45
... C8051F018 C8051F019 Performance The CIP-51 employs a pipelined architecture that greatly increases its instruction throughput over the standard 8051 architecture standard 8051, all instructions except for MUL and DIV take system clock cycles to execute, and usually have a maximum system clock of 12MHz. By contrast, the CIP-51 core executes 70% of its instructions in one or two system clock cycles, with no instructions taking more than eight system clock cycles. With the CIP-51’ ...
Page 46
... XRL A,@Ri Exclusive-OR indirect RAM to A XRL A,#data Exclusive-OR immediate to A XRL direct,A Exclusive- direct byte XRL direct,#data Exclusive-OR immediate to direct byte CLR A Clear A CPL A Complement Rotate A left RLC A Rotate A left through carry Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 Clock Bytes Cycles ...
Page 47
... C8051F018 C8051F019 Mnemonic Description RR A Rotate A right RRC A Rotate A right through carry SWAP A Swap nibbles of A MOV A,Rn Move register to A MOV A,direct Move direct byte to A MOV A,@Ri Move indirect RAM to A MOV A,#data Move immediate to A MOV Rn,A Move A to register ...
Page 48
... LCALL and LJMP. The destination may be anywhere within the 64K-byte program memory space. There is one unused opcode (0xA5) that performs the same function as NOP. All mnemonics copyrighted © Intel Corporation 1980. Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 Clock Bytes Cycles ...
Page 49
... Instructions using indirect addressing above 0x7F will access the upper 128 bytes of data memory. Figure 8.2 illustrates the data memory organization of the CIP-51. The C8051F018/9 also have 1024 bytes of RAM in the external data memory space of the CIP-51, accessible using the MOVX instruction. Refer to Section 10 (External RAM) for details. ...
Page 50
... The MCS-51™ assembly language allows an alternate notation for bit addressing of the form XX.B where XX is the byte address and B is the bit position within the byte. For example, the instruction: MOV C, 22h.3 moves the Boolean value at 0x13 (bit 3 of the byte at location 0x22) into the user Carry flag. Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 50 ...
Page 51
... C8051F018 C8051F019 PROGRAM MEMORY 0x807F FLASH (In-System Programmable) 0x8000 0x7FFF RESERVED 0x3E00 0x3DFF FLASH (In-System Programmable in 512 Byte Sectors) 0x0000 8.2.5. Stack A programmer’s stack can be located anywhere in the 256-byte data memory. The stack area is designated using the Stack Pointer (SP, 0x81) SFR. The SP will point to the last location used. The next value pushed on the stack is placed at SP+1 and then SP is incremented ...
Page 52
... ADC0GTL ADC0GTH AMX0SL ADC0CF PRT1IF PRT0CF PRT1CF SPI0DAT SPI0CKR TMR3RLH TMR3L TMR3H TL1 TH0 TH1 DPH 2(A) 3(B) 4(C) Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 PCA0CPH4 WDTCN EIP1 EIP2 PCA0CPL4 RSTSRC EIE1 EIE2 PCA0CPM4 SMB0CR ADC0LTL ADC0LTH ADC0L ADC0H FLSCL FLACL EMI0CN PRT2CF ...
Page 53
... C8051F018 C8051F019 Address Register Description 0xBA AMX0CF ADC MUX Configuration 0xBB AMX0SL ADC MUX Channel Selection 0xF0 B B Register 0x8E CKCON Clock Control 0x9E CPT0CN Comparator 0 Control 0x9F CPT1CN Comparator 1 Control 0x83 DPH Data Pointer (High Byte) 0x82 DPL Data Pointer (Low Byte) ...
Page 54
... TMR3H Timer 3 High 0x94 TMR3L Timer 3 Low 0x93 TMR3RLH Timer 3 Reload High 0x92 TMR3RLL Timer 3 Reload Low 0xFF WDTCN Watchdog Timer Control 0xE1 XBR0 Port I/O Crossbar Configuration 1 Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 Page No. 144 134 134 43 79 119 120 103 ...
Page 55
... C8051F018 C8051F019 Address Register Description 0xE2 XBR1 Port I/O Crossbar Configuration 2 0xE3 XBR2 Port I/O Crossbar Configuration 3 0x84-86, 0x96-97, 0x9C, 0xA1-A3, 0xA9-AC, 0xAE, 0xB3-B5, 0xB9, Reserved 0xBD, 0xC9, 0xCE, 0xDF, 0xE4-E5, 0xF1-F5 55 Rev. 1.2 Page No ...
Page 56
... R/W R/W Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 R/W R/W R/W Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 R/W R/W R/W Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 R/W R/W Reset Value 00000111 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address: 0x81 R/W R/W Reset Value 00000000 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address: 0x82 ...
Page 57
... C8051F018 C8051F019 Figure 8.6. PSW: Program Status Word R/W R/W R Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit7: CY: Carry Flag. This bit is set when the last arithmetic operation results in a carry (addition borrow (subtraction cleared all other arithmetic operations. Bit6: AC: Auxiliary Carry Flag. This bit is set when the last arithmetic operation results in a carry into (addition borrow from (subtraction) the high order nibble ...
Page 58
... ACC.4 ACC.3 ACC.2 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Figure 8. Register R/W R/W R/W B.4 B.3 B.2 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 R/W R/W Reset Value ACC.1 ACC.0 00000000 SFR Address: Bit1 Bit0 0xE0 (bit addressable) R/W R/W Reset Value B.1 B.0 ...
Page 59
... C8051F018 C8051F019 8.4. INTERRUPT HANDLER The CIP-51 includes an extended interrupt system supporting a total of 22 interrupt sources with two priority levels. The allocation of interrupt sources between on-chip peripherals and external inputs pins varies according to the specific version of the device. Each interrupt source has one or more associated interrupt-pending flag(s) located in an SFR ...
Page 60
... ADCINT (ADC0CN.5) 16 IE4 (PRT1IF.4) 17 IE5 (PRT1IF.5) 18 IE6 (PRT1IF.6) 19 IE7 (PRT1IF.7) 20 None 21 XTLVLD (OSCXCN.7) Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 Enable Always enabled EX0 (IE.0) ET0 (IE.1) EX1 (IE.2) ET1 (IE.3) ES (IE.4) ET2 (IE.5) ESPI0 (EIE1.0) ESMB0 (EIE1.1) EWADC0 (EIE1.2) EPCA0 (EIE1.3) ECP0F (EIE1.4) ECP0R (EIE1 ...
Page 61
... C8051F018 C8051F019 8.4.5. Interrupt Register Descriptions The SFRs used to enable the interrupt sources and set their priority level are described below. Refer to the datasheet section associated with a particular on-chip peripheral for information regarding valid interrupt conditions for the peripheral and the behavior of its interrupt-pending flag(s). ...
Page 62
... This bit sets the priority of the External Interrupt 0 interrupts. 0: External Interrupt 0 set to low priority level. 1: External Interrupt 0 set to high priority level. R/W R/W R/W PS PT1 PX1 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 R/W R/W Reset Value PT0 PX0 00000000 SFR Address: Bit1 Bit0 0xB8 (bit addressable) ...
Page 63
... C8051F018 C8051F019 Figure 8.11. EIE1: Extended Interrupt Enable 1 R/W R/W R/W ECP1R ECP1F ECP0R Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit7: ECP1R: Enable Comparator 1 (CP1) Rising Edge Interrupt. This bit sets the masking of the CP1 interrupt. 0: Disable CP1 Rising Edge interrupt. 1: Enable interrupt requests generated by the CP1RIF flag (CPT1CN.5). ...
Page 64
... This bit sets the masking of the Timer 3 interrupt. 0: Disable all Timer 3 interrupts. 1: Enable interrupt requests generated by the TF3 flag (TMR3CN.7) R/W R/W R/W EX6 EX5 EX4 EADC0 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 R/W R/W Reset Value ET3 00000000 SFR Address: Bit1 Bit0 0xE7 64 ...
Page 65
... C8051F018 C8051F019 Figure 8.13. EIP1: Extended Interrupt Priority 1 R/W R/W R/W PCP1R PCP1F PCP0R Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit7: PCP1R: Comparator 1 (CP1) Rising Interrupt Priority Control. This bit sets the priority of the CP1 interrupt. 0: CP1 rising interrupt set to low priority level. 1: CP1 rising interrupt set to high priority level. ...
Page 66
... This bit sets the priority of the Timer 3 interrupts. 0: Timer 3 interrupt set to low priority level. 1: Timer 3 interrupt set to high priority level. R/W R/W R/W PX6 PX5 PX4 PADC0 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 R/W R/W Reset Value PT3 00000000 SFR Address: Bit1 Bit0 0xF7 66 ...
Page 67
... C8051F018 C8051F019 8.5. Power Management Modes The CIP-51 core has two software programmable power management modes: Idle and Stop. Idle mode halts the CPU while leaving the external peripherals and internal clocks active. In Stop mode, the CPU is halted, all interrupts and timers (except the Missing Clock Detector) are inactive, and the system clock is stopped. Since clocks are running in Idle mode, power consumption is dependent upon the system clock frequency and the number of peripherals left in active mode before entering Idle ...
Page 68
... Goes into idle mode. (Shuts off clock to CPU, but clock to Timers, Interrupts, Serial Ports, and Analog Peripherals are still active.) R/W R/W R/W GF2 GF1 GF0 STOP Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 R/W R/W Reset Value IDLE 00000000 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address: 0x87 68 ...
Page 69
... C8051F018 C8051F019 9. FLASH MEMORY These devices include 16k + 128 bytes of on-chip, reprogrammable Flash memory for program code and non- volatile data storage. The Flash memory can be programmed in-system, a single byte at a time, through the JTAG interface or by software using the MOVX instruction. Once cleared Flash bit must be erased to set it back to 1 ...
Page 70
... MOVX instruction. The location must be erased before writing data. 0: Write to Flash program memory disabled. 1: Write to Flash program memory enabled. The Program Store Write Enable R/W R/W R PSEE Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 R/W R/W Reset Value PSWE 00000000 SFR Address: Bit1 Bit0 0x8F 70 ...
Page 71
... The Flash Access Limit security feature (see Figure 9.3) protects proprietary program code and data from being read by software running on the C8051F018/9 MCUs. This feature provides support for OEMs that wish to program the MCU with proprietary value-added firmware before distribution. The value-added firmware can be protected while allowing additional code to be programmed in remaining program memory space later ...
Page 72
... FLACL. A write to this register sets the Flash Access Limit. This register can only be written once after any reset. Any subsequent writes are ignored until the next reset. R/W R/W R/W Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 R/W R/W Reset Value 00000000 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address: 0xB7 ...
Page 73
... Reserved Values 1111: Flash Memory Write/Erase Disabled The prescaler value is the smallest value satisfying the following equation: FLASCL > log (System Clock / 50kHz For test purposes. The C8051F018/9 is not guaranteed for operation over 25MHz. 73 R/W R/W R/W - FLASCL ...
Page 74
... EXTERNAL RAM The C8051F018/9 includes 1024 bytes of RAM mapped into the external data memory space. All of these address locations may be accessed using the external move instruction (MOVX) and the data pointer (DPTR), or using MOVX indirect addressing mode. If the MOVX instruction is used with an 8-bit address operand (such as @R1), then the high byte of the 16-bit address is provided by the External Memory Interface Control Register (EMI0CN as shown in Figure 10 ...
Page 75
... C8051F018 C8051F019 11. RESET SOURCES The reset circuitry of the MCUs allows the controller to be easily placed in a predefined default condition. On entry to this reset state, the CIP-51 halts program execution, forces the external port pins to a known state and initializes the SFRs to their defined reset values. Interrupts and timers are disabled. On exit, the program counter (PC) is reset, and program execution starts at location 0x0000 ...
Page 76
... Power-on Reset The C8051F018/9 incorporates a power supply monitor that holds the MCU in the reset state until VDD rises above the V level during power-up. (See Figure 11.2 for timing diagram, and refer to Table 11.1 for the Electrical RST Characteristics of the power supply monitor circuit.) The /RST pin is asserted (low) until the end of the 100ms VDD Monitor timeout in order to allow the VDD supply to become stable ...
Page 77
... C8051F018 C8051F019 11.4. External Reset The external /RST pin provides a means for external circuitry to force the MCU into a reset state. Asserting an active-low signal on the /RST pin will cause the MCU to enter the reset state. Although there is a weak internal pullup, it may be desirable to provide an external pull-up and/or decoupling of the /RST pin to avoid erroneous noise-induced resets ...
Page 78
... The WDTCN.[2:0] bits set the Watchdog Timeout Interval. When writing these bits, WDTCN.7 must be set the system clock period). SYSCLK R/W R/W R/W Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 R/W R/W Reset Value xxxxx111 SFR Address: Bit1 Bit0 0xFF 78 ...
Page 79
... C8051F018 C8051F019 Figure 11.4. RSTSRC: Reset Source Register R R/W R/W JTAGRST CNVRSEF C0RSEF Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 (Note: Do not use read-modify-write operations on this register.) Bit7: JTAGRST. JTAG Reset Flag. 0: JTAG is not currently in reset state. 1: JTAG is in reset state. Bit6: CNVRSEF: Convert Start Reset Source Enable and Flag ...
Page 80
... Reset Time Delay /RST rising edge after crossing reset threshold Missing Clock Detector Time from last system clock to reset Timeout generation CONDITIONS MIN 0.7 x VDD 1.0 1.0 2.40 80 100 Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 TYP MAX UNITS 0 0 VDD 2.55 2.80 ...
Page 81
... C8051F018 C8051F019 12. OSCILLATOR Each MCU includes an internal oscillator and an external oscillator drive circuit, either of which can generate the system clock. The MCUs boot from the internal oscillator after any reset. The internal oscillator starts up instantly. It can be enabled/disabled and its frequency can be changed using the Internal Oscillator Control Register (OSCICN) as shown in Figure 12.2. The internal oscillator’ ...
Page 82
... Internal Oscillator Power Supply (VDD) Stability R R/W R/W IFRDY CLKSL IOSCEN Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 CONDITIONS MIN 1.5 3.1 6.2 12.3 Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 R/W R/W Reset Value IFCN1 IFCN0 00000100 SFR Address: Bit1 Bit0 0xB2 TYP MAX UNITS 2 2.4 MHz 4 4 ...
Page 83
... C8051F018 C8051F019 Figure 12.3. OSCXCN: External Oscillator Control Register R R/W R/W XTLVLD XOSCMD2 XOSCMD1 Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit7: XTLVLD: Crystal Oscillator Valid Flag (Valid only when XOSCMD = 1xx.) 0: Crystal Oscillator is unused or not yet stable 1: Crystal Oscillator is running and stable (should read 1ms after Crystal Oscillator is enabled to avoid transient condition) ...
Page 84
... Frequency Control value (XFCN) in the OSCXCN Register, select the capacitor to be used and find the frequency of oscillation from the equations below. Assume AV+ = 3.0V and C = 50pF VDD ( 150 If a frequency of roughly 90kHz is desired, select the K Factor from the table in Figure 12 13 /150 = 0.087MHz, or 87kHz Therefore, the XFCN value to use in this example is 011. (4) 2 Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 84 ...
Page 85
... Figure 13.1. The designer has complete control over which functions are assigned, limited only by the number of physical I/O pins available on the selected package (the C8051F018 has all four ports pinned out, and the C8051F019 has P0 and P1). This resource assignment flexibility is achieved through the use of a Priority CrossBar Decoder ...
Page 86
... PRT0CF, PRT1CF, XBR2 Registers PRT2CF Registers Priority Decoder P0 8 I/O Cells Digital Crossbar P1 8 I/O Cells P2 8 I/O Cells PRT3CF Register P3 I/O Cells Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 External Pins P0.0 Highest Priority P0.7 P1.0 P1.7 P2.0 Lowest Priority P2.7 P3.0 P3.7 86 ...
Page 87
... C8051F018 C8051F019 Figure 13.2. Port I/O Cell Block Diagram WEAKPUD PUSH-PULL /PORT-OUTENABLE PORT-OUTPUT PORT-INPUT 87 VDD VDD (WEAK) VDD DGND Rev. 1.2 PORT PAD ...
Page 88
... In the Priority Decode Table, a dot () is used to show the external Port I/O pin (column) to which each signal (row) can be assigned by the user application code via programming registers XBR2, XBR1, and XBR0 Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 ...
Page 89
... C8051F018 C8051F019 Figure 13.3. XBR0: Port I/O CrossBar Register 0 R/W R/W R/W CP0OEN ECIE Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit7: CP0OEN: Comparator 0 Output Enable Bit 0: CP0 unavailable at Port pin. 1: CP0 routed to Port Pin. Bit6: ECIE: PCA0 Counter Input Enable Bit 0: ECI unavailable at Port pin. ...
Page 90
... T0 routed to Port Pin. Bit0: CP1OEN: Comparator 1 Output Enable Bit 0: CP1 unavailable at Port pin. 1: CP1 routed to Port Pin. R/W R/W R/W INT1E T1E INT0E Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 R/W R/W Reset Value T0E CP1OEN 00000000 SFR Address: Bit1 Bit0 0xE2 90 ...
Page 91
... I/O or one of the internal digital resources assigned as shown in Figure 13.1. The designer has complete control over which functions are assigned, limited only by the number of physical I/O pins available on the selected package (the C8051F018 has all four ports pinned out, and the C8051F019 has P0 and P1). This resource assignment flexibility is achieved through the use of a Priority CrossBar Decoder ...
Page 92
... Figure 13.6. P0: Port0 Register R/W R/W R/W P0.4 P0.3 P0.2 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 R/W R/W R/W Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 R/W R/W Reset Value P0.1 P0.0 11111111 SFR Address: Bit1 Bit0 0x80 (bit addressable) R/W R/W Reset Value 00000000 ...
Page 93
... C8051F018 C8051F019 R/W R/W R/W P1.7 P1.6 P1.5 Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bits7-0: P1.[7:0] (Write – Output appears on I/O pins per XBR0, XBR1, and XBR2 registers) 0: Logic Low Output. 1: Logic High Output (high-impedance if corresponding PRT1CF.n bit = 0) (Read – Regardless of XBR0, XBR1, and XBR2 Register settings). ...
Page 94
... Corresponding P2.n Output mode is Push-Pull. R/W R/W R/W P2.4 P2.3 P2.2 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 R/W R/W R/W Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 R/W R/W Reset Value P2.1 P2.0 11111111 SFR Address: Bit1 Bit0 0xA0 (bit addressable) R/W R/W Reset Value 00000000 ...
Page 95
... C8051F018 C8051F019 R/W R/W R/W P3.7 P3.6 P3.5 Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bits7-0: P3.[7:0] (Write) 0: Logic Low Output. 1: Logic High Output (high-impedance if corresponding PRT3CF.n bit = 0) (Read) 0: P3.n is logic low. 1: P3.n is logic high. Figure 13.14. PRT3CF: Port3 Configuration Register R/W R/W R/W Bit7 ...
Page 96
... C serial bus. Reads and writes to the th of the system clock if desired (this can be faster than SMB0CR Clock Divide SYSCLK Logic FILTER SCL Control SDA Data Path Control Control 8 SMB0DAT FILTER Read Write to SMB0DAT SMB0DAT Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 SCL Port I SDA N 96 ...
Page 97
... C8051F018 C8051F019 Figure 14.2 shows a typical SMBus configuration. The SMBus interface will work at any voltage between 3.0V and 5.0V and different devices on the bus may operate at different voltage levels. The SCL (serial clock) and SDA (serial data) lines are bi-directional. They must be connected to a positive power supply voltage through a pull-up resistor or similar circuit ...
Page 98
... After each byte is received, an acknowledge bit is transmitted by the master. The master outputs START and STOP conditions to indicate the beginning and end of the serial transfer. Figure 14.3. SMBus Transaction DATA ACK Time Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 The master DATA NACK STOP 98 ...
Page 99
... C8051F018 C8051F019 14.2.4. Slave Receiver Mode Serial data is received on SDA while the serial clock is received on SCL. First, a byte is received that contains an address and data direction bit. In this case the data direction bit (R/W) will be logic 0 to indicate a “WRITE” operation. If the received address matches the slave’s assigned address (or a general call address is received) one or more bytes of serial data are received from the master ...
Page 100
... Setting the SMBus timeout enable bit (TOE, SMB0CN.0) to logic 1 enables Timer 3 to count up when the SCL line is low and Timer 3 is enabled. If Timer 3 overflows, a Timer 3 interrupt will be generated, which will alert the CPU that a SMBus SCL low timeout has occurred. Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 100 ...
Page 101
... C8051F018 C8051F019 Figure 14.4. SMB0CN: SMBus Control Register R R/W R/W BUSY ENSMB STA Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit7: BUSY: Busy Status Flag. 0: SMBus is free 1: SMBus is busy Bit6: ENSMB: SMBus Enable. This bit enables/disables the SMBus serial interface. 0: SMBus disabled. 1: SMBus enabled. Bit5: STA: SMBus Start Flag ...
Page 102
... Using the same value of SMB0CR from above, the Bus Free Timeout period is given in the following equation: T BFT R/W R/W R/W Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 (256 – SMB0CR) / SYSCLK (258 – SMB0CR) / SYSCLK + 625 ns [(256 – SMB0CR SYSCLK Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 R/W R/W Reset Value 00000000 SFR Address: Bit1 Bit0 0xCF 102 ...
Page 103
... C8051F018 C8051F019 14.6.3. Data Register The SMBus Data register SMB0DAT holds a byte of serial data to be transmitted or one that has just been received. Data remains stable in the register as long set to logic 1. Software can safely read or write to the data register when the SI flag is set. Software should not attempt to access the SMB0DAT register when the SMBus is enabled and the SI flag is cleared to logic 0 since the hardware may be in the process of shifting a byte of data in or out of the register ...
Page 104
... Bits2-0: STA2-STA0: The three least significant bits of SMB0STA are always read as logic 0 when the SI flag is logic 1. R/W R/W R/W STA4 STA3 STA2 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 R/W R/W Reset Value STA1 STA0 11111000 SFR Address: Bit1 Bit0 0xC1 ...
Page 105
... C8051F018 C8051F019 Status Code Mode (SMB0STA) 0x00 All 0x08 Master Transmitter/Receiver 0x10 Master Transmitter/Receiver 0x18 Master Transmitter 0x20 Master Transmitter 0x28 Master Transmitter 0x30 Master Transmitter 0x38 Master Transmitter 0x40 Master Receiver 0x48 Master Receiver 0x50 Master Receiver 0x58 Master Receiver ...
Page 106
... Figure 15.1. SPI Block Diagram SFR Bus SPI0CFG SPI0CN Bit Count Logic SPI CONTROL LOGIC SPI Clock Pin Control (Master Mode) Interface SCK MOSI Tx Data Pin SPI0DAT Control Logic Shift Register MISO Rx Data NSS Read SPI0DAT Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 SPI IRQ Port I 106 ...
Page 107
... C8051F018 C8051F019 Figure 15.2. Typical SPI Interconnection NSS Slave Device Master Device 15.1. Signal Descriptions The four signals used by the SPI (MOSI, MISO, SCK, NSS) are described below. 15.1.1. Master Out, Slave In The master-out, slave-in (MOSI) signal is an output from a master device and an input to slave devices used to serially transfer data from the master to the slave ...
Page 108
... MSTEN and SPIEN bits of the SPI control register are cleared by hardware, thereby placing the SPI module Figure 15.3. Full Duplex Operation SLAVE DEVICE MOSI MOSI SPI SHIFT REGISTER MISO MISO 0 7 VDD NSS NSS SCK SCK Px.y Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 Receive Buffer 108 ...
Page 109
... C8051F018 C8051F019 in an “off-line” state multiple-master environment, the system controller should check the state of the SLVSEL flag (SPI0CN.2) to ensure the bus is free before setting the MSTEN bit and initiating a data transfer. 15.3. Serial Clock Timing As shown in Figure 15.4, four combinations of serial clock phase and polarity can be selected using the clock control bits in the SPI Configuration Register (SPI0CFG) ...
Page 110
... They are ignored in slave mode. SPIFRS R/W BC1 BC0 SPIFRS2 SPIFRS1 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit Transmitted Bit 0 (LSB) Bit 1 Bit 2 Bit 3 Bit 4 Bit 5 Bit 6 Bit 7 (MSB) Bits Shifted Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 R/W R/W Reset Value SPIFRS0 00000111 SFR Address: Bit1 Bit0 0x9A 110 ...
Page 111
... C8051F018 C8051F019 Figure 15.6. SPI0CN: SPI Control Register R/W R/W R/W SPIF WCOL MODF Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit7: SPIF: SPI Interrupt Flag. This bit is set to logic 1 by hardware at the end of a data transfer. If interrupts are enabled, setting this bit causes the CPU to vector to the SPI0 interrupt service routine. This bit is not automatically cleared by hardware ...
Page 112
... R/W R/W SCR4 SCR3 SCR2 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 for 0 SPI0CKR 255, R/W R/W R/W Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 R/W R/W Reset Value SCR1 SCR0 00000000 SFR Address: Bit1 Bit0 0x9D R/W R/W Reset Value 00000000 SFR Address: ...
Page 113
... C8051F018 C8051F019 16. UART The UART is a serial port capable of asynchronous transmission. The UART can function in full duplex mode. In all modes, receive data is buffered in a holding register. This allows the UART to start reception of a second incoming data byte before software has finished reading the previous data byte. ...
Page 114
... Baud Clock Data Bits SYSCLK/12 Timer 1 or Timer 2 Overflow SYSCLK/32 or SYSCLK/64 Timer 1 or Timer 2 Overflow TX CLK RX DATA 8 Extra Outputs MODE 0 TRANSMIT MODE 0 RECEIVE Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 Start/Stop Bits 8 None 8 1 Start, 1 Stop 9 1 Start, 1 Stop 9 1 Start, 1 Stop Shift Reg 114 ...
Page 115
... C8051F018 C8051F019 16.1.2. Mode 1: 8-Bit UART, Variable Baud Rate Mode 1 provides standard asynchronous, full duplex communication using a total of 10 bits per data byte: one start bit, eight data bits (LSB first), and one stop bit (see the timing diagram in Figure 16.4). Data are transmitted from the TX pin and received at the RX pin (see the interconnection diagram in Figure 16 ...
Page 116
... C/T2 bit (T2CON.1) to logic 1 will allow Timer clocked from the external input pin T2. See the Timers section for complete timer configuration details. Figure 16.5. UART Modes 1, 2, and 3 Interconnect Diagram RS-232 TX RS-232 C8051Fxxx LEVEL RX XLTR MCU C8051Fxxx RX RX Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 116 ...
Page 117
... C8051F018 C8051F019 16.1.3. Mode 2: 9-Bit UART, Fixed Baud Rate Mode 2 provides asynchronous, full-duplex communication using a total of eleven bits per data byte: a start bit, 8 data bits (LSB first), a programmable ninth data bit, and a stop bit (see timing diagram in Figure 16.6). On transmit, the ninth data bit is determined by the value in TB8 (SCON.3). It can be assigned the value of the parity flag P in the PSW or used in multiprocessor communications ...
Page 118
... Figure 16.7. UART Multi-Processor Mode Interconnect Diagram Master Slave Device Device Slave Device Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 Slave Device VDD RX TX 118 ...
Page 119
... C8051F018 C8051F019 Table 16.2. Oscillator Frequencies for Standard Baud Rates Oscillator Frequency (MHz) 24.0 23.592 22.1184 18.432 16.5888 14.7456 12.9024 11.0592 9.216 7.3728 5.5296 3.6864 1.8432 24.576 25.0 25.0 24.576 24.0 23.592 22.1184 18.432 16.5888 14.7456 12.9024 11.0592 9.216 7.3728 5.5296 3 ...
Page 120
... UART interrupt is enabled, setting this bit causes the CPU to vector to the UART interrupt service routine. This bit must be cleared manually by software. R/W R/W R/W REN TB8 RB8 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 R/W R/W Reset Value TI RI 00000000 SFR Address: Bit1 Bit0 0x98 ...
Page 121
... C8051F018 C8051F019 17. TIMERS Each MCU implements four counter/timers: three are 16-bit counter/timers compatible with those found in the standard 8051, and one is a 16-bit timer for use with the ADC, SMBus, or for general purpose use. These can be used to measure time intervals, count external events and generate periodic interrupt requests. Timer 0 and Timer 1 are nearly identical and have four primary modes of operation ...
Page 122
... Mode 1 in the same manner as for Mode 0. GATE0 /INT0 Counter/Timer X X Disabled 0 X Enabled 1 0 Disabled 1 1 Enabled TMOD TCLK TL0 (5 bits) Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 TF1 TR1 TF0 Interrupt TH0 TR0 (8 bits) IE1 IT1 IE0 IT0 122 ...
Page 123
... C8051F018 C8051F019 17.1.3. Mode 2: 8-bit Counter/Timer with Auto-Reload Mode 2 configures Timer 0 and Timer 1 to operate as 8-bit counter/timers with automatic reload of the start value. The TL0 holds the count and TH0 holds the reload value. When the count in TL0 overflows from all ones to 0x00, the timer overflow flag TF0 (TCON ...
Page 124
... Refer to Section 16 (UART) for information on configuring Timer 1 for baud rate generation. Figure 17.3. T0 Mode 3 Block Diagram CKCON TR1 12 0 SYSCLK 1 T0 Crossbar TR0 GATE0 /INT0 Crossbar TMOD TH0 (8 bits) C/ TL0 (8 bits) Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 TF1 Interrupt TR1 TF0 Interrupt TR0 IE1 IT1 IE0 IT0 124 ...
Page 125
... C8051F018 C8051F019 Figure 17.4. TCON: Timer Control Register R/W R/W R/W TF1 TR1 TF0 Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit7: TF1: Timer 1 Overflow Flag. Set by hardware when Timer 1 overflows. This flag can be cleared by software but is automatically cleared when the CPU vectors to the Timer 1 interrupt service routine. ...
Page 126
... Mode 1: 16-bit counter/timer 1 0 Mode 2: 8-bit counter/timer with auto-reload 1 1 Mode 3: Two 8-bit counter/timers R/W R/W R/W T1M0 GATE0 C/T0 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 R/W R/W Reset Value T0M1 T0M0 00000000 SFR Address: Bit1 Bit0 0x89 126 ...
Page 127
... C8051F018 C8051F019 Figure 17.6. CKCON: Clock Control Register R/W R/W R T2M Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bits7-6: UNUSED. Read = 00b, Write = don’t care. Bit5: T2M: Timer 2 Clock Select. This bit controls the division of the system clock supplied to Timer 2. This bit is ignored when the timer is in baud rate generator mode or counter mode (i.e. C/T2 = 1). ...
Page 128
... R/W R/W Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 R/W R/W R/W Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 R/W R/W R/W Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 R/W R/W Reset Value 00000000 SFR Address: Bit1 Bit0 0x8A R/W R/W Reset Value 00000000 SFR Address: Bit1 Bit0 0x8B ...
Page 129
... C8051F018 C8051F019 17.2. Timer 2 Timer 16-bit counter/timer formed by the two 8-bit SFRs: TL2 (low byte) and TH2 (high byte). As with Timers 0 and 1, Timer 2 can use either the system clock or transitions on an external input pin as its clock source. The Counter/Timer Select bit C/T2 bit (T2CON.1) selects the clock source for Timer 2. Clearing C/T2 selects the system clock as the input for the timer (divided by either one or twelve as specified by the Timer Clock Select bit T2M in CKCON) ...
Page 130
... If EXEN2 is cleared, transitions on T2EX will be ignored. Figure 17.11. T2 Mode 0 Block Diagram 12 0 SYSCLK Crossbar 1 TR2 EXEN2 T2EX Crossbar CKCON TCLK TL2 TH2 Capture RCAP2L RCAP2H Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 CP/RL2 C/T2 TR2 EXEN2 TCLK RCLK Interrupt EXF2 TF2 130 ...
Page 131
... C8051F018 C8051F019 17.2.2. Mode 1: 16-bit Counter/Timer with Auto-Reload The Counter/Timer with Auto-Reload mode sets the TF2 timer overflow flag when the counter/timer register overflows from 0xFFFF to 0x0000. An interrupt is generated if enabled. On overflow, the 16-bit value held in the two capture registers (RCAP2H, RCAP2L) is automatically loaded into the counter/timer register and the timer is restarted ...
Page 132
... Figure 17.13. T2 Mode 2 Block Diagram SYSCLK 2 C/ Crossbar TR2 Timer 1 Overflow 1 EXEN2 Crossbar T2EX Timer 2 Overflow TL2 TH2 TCLK Reload PCON RCAP2L RCAP2H CP/RL2 C/T2 TR2 EXEN2 TCLK RCLK Interrupt EXF2 TF2 Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 Clock 0 RCLK Clock 0 TCLK 132 ...
Page 133
... C8051F018 C8051F019 Figure 17.14. T2CON: Timer 2 Control Register R/W R/W R/W TF2 EXF2 RCLK Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit7: TF2: Timer 2 Overflow Flag. Set by hardware when Timer 2 overflows from 0xFFFF to 0x0000 or reload value. When the Timer 2 interrupt is enabled, setting this bit causes the CPU to vector to the Timer 2 interrupt service routine ...
Page 134
... R/W R/W Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 R/W R/W R/W Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 R/W R/W R/W Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 R/W R/W Reset Value 00000000 SFR Address: Bit1 Bit0 0xCA R/W R/W Reset Value 00000000 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address: 0xCB ...
Page 135
... C8051F018 C8051F019 17.3. Timer 3 Timer 16-bit timer formed by the two 8-bit SFRs, TMR3L (low byte) and TMR3H (high byte). The input for Timer 3 is the system clock (divided by either one or twelve as specified by the Timer 3 Clock Select bit T3M in the Timer 3 Control Register TMR3CN). Timer 3 is always configured as an auto-reload timer, with the reload value held in the TMR3RLL (low byte) and TMR3RLH (high byte) registers ...
Page 136
... R/W R/W Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 R/W R/W R/W Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 R/W R/W R/W Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 R/W R/W Reset Value 00000000 SFR Address: Bit1 Bit0 0x92 R/W R/W Reset Value 00000000 Bit1 Bit0 SFR Address: 0x93 ...
Page 137
... C8051F018 C8051F019 18. PROGRAMMABLE COUNTER ARRAY The Programmable Counter Array (PCA) provides enhanced timer functionality while requiring less CPU intervention than the standard 8051 counter/timers. The PCA consists of a dedicated 16-bit counter/timer and five 16-bit capture/compare modules. Each capture/compare module has its own associated I/O line (CEXn) which is routed through the Crossbar to Port I/O when enabled (see Section 13 ...
Page 138
... PCA Module 4 TOG PWM ECCF Operation Mode Capture triggered by positive edge on CEXn Capture triggered by negative edge on CEXn Capture triggered by transition on CEXn Software Timer High Speed Output Pulse Width Modulator Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 EPCA0 EA (EIE1.3) (IE.7) Interrupt 0 0 Priority 1 1 Decoder 138 ...
Page 139
... C8051F018 C8051F019 18.1.1. Edge-triggered Capture Mode In this mode, a valid transition on the CEXn pin causes the PCA to capture the value of the PCA counter/timer and load it into the corresponding module’s 16-bit capture/compare register (PCA0CPLn and PCA0CPHn). The CAPPn and CAPNn bits in the PCA0CPMn register are used to select the type of transition that triggers the capture: low-to- high transition (positive edge), high-to-low transition (negative edge), or either transition (positive or negative edge) ...
Page 140
... Write to PCA0CPHn ENB PCA0CPLn Enable PCA Timebase PCA0CPLn PCA0CPHn Enable 16-bit Comparator PCA PCA0L PCA0H Timebase PCA0CPMn PCA0CN PCA0CPHn Match 16-bit Comparator 1 TOGn Toggle PCA0L PCA0H Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 PCA Interrupt PCA0CN Match 1 PCA Interrupt CEXn Crossbar Port I/O 1 140 ...
Page 141
... C8051F018 C8051F019 18.1.4. Pulse Width Modulator Mode All of the modules can be used independently to generate pulse width modulated (PWM) outputs on their respective CEXn pin. The frequency of the output is dependent on the timebase for the PCA counter/timer. The duty cycle of the PWM output signal is varied using the module’s PCA0CPLn capture/compare register. When the value in the low byte of the PCA counter/timer (PCA0L) is equal to the value in PCA0CPLn, the output on the CEXn pin will be set ...
Page 142
... Figure 18.7. PCA Counter/Timer Block Diagram IDLE PCA0MD PCA0CN SYSCLK/12 00 SYSCLK/4 01 Timer 0 Overflow 10 ECI 11 Reading PCA0L automatically latches the value PCA0L read write Snapshot Register 0 PCA0H PCA0L 1 Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 To SFR Bus Overflow To PCA Interrupt System CF To PCA Modules 142 ...
Page 143
... C8051F018 C8051F019 18.3. Register Descriptions for PCA The system device may implement one or more Programmable Counter Arrays. Following are detailed descriptions of the special function registers related to the operation of the PCA. The CIP-51 System Controller section of the datasheet provides additional information on the SFRs and their use. ...
Page 144
... This bit sets the masking of the PCA Counter/Timer Overflow (CF) interrupt. 0: Disable the CF interrupt. 1: Enable a PCA Counter/Timer Overflow interrupt request when CF (PCA0CN.7) is set. R/W R/W R CPS1 CPS0 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 R/W R/W Reset Value ECF 00000000 SFR Address: Bit1 Bit0 0xD9 144 ...
Page 145
... C8051F018 C8051F019 Figure 18.10. PCA0CPMn: PCA Capture/Compare Registers R/W R/W R/W - ECOMn CAPPn Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 PCA0CPMn Address: PCA0CPM0 = 0xDA ( PCA0CPM1 = 0xDB ( PCA0CPM2 = 0xDC ( PCA0CPM3 = 0xDD ( PCA0CPM4 = 0xDE ( Bit7: UNUSED. Read = 0, Write = don’t care. Bit6: ECOMn: Comparator Function Enable. This bit enables/disables the comparator function for PCA module n. ...
Page 146
... R/W R/W Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 R/W R/W R/W Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 R/W R/W R/W Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 R/W R/W Reset Value 00000000 SFR Address: Bit1 Bit0 0xE9 R/W R/W Reset Value 00000000 SFR Address: Bit1 Bit0 0xF9 ...
Page 147
... C8051F018 C8051F019 19. JTAG (IEEE 1149.1) Each MCU has an on-chip JTAG interface and logic to support boundary scan for production and in-system testing, Flash read and write operations, and non-intrusive in-circuit debug. The JTAG interface is fully compliant with the IEEE 1149.1 specification. Refer to this specification for detailed descriptions of the Test Interface and Boundary- Scan Architecture ...
Page 148
... P3.n output enable from MCU (e.g. Bit71=P3.0, Bit73=P3.1, etc.) 71,73,75,77, 79,81,83,85 Update P3.n output enable to pin (e.g. Bit71=P3.0oe, Bit73=P3.1oe, etc.) Capture P3.n input from pin (e.g. Bit72=P3.0, Bit74=P3.1, etc.) 72,74,76,78, 80,82,84,86 Update P3.n output to pin (e.g. Bit72=P3.0, Bit74=P3.1, etc.) Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 148 ...
Page 149
... The IDCODE instruction is accessed via the IR. It provides access to the 32-bit Device ID register. Figure 19.2. DEVICEID: JTAG Device ID Register Version Part Number Bit31 Bit28 Bit27 Version = 0000b (Revision A) = 0001b (Revision B) Part Number = 0000 0000 0000 0010b (C8051F018/9) Manufacturer ID = 0010 0100 001b (Silicon Laboratories) 149 Manufacturer ID Bit12 Bit11 Rev. 1.2 Reset Value 1 ...
Page 150
... Busy is 0, the following 18 bits can be shifted out to obtain the resulting data. ReadData is always right-justified. This allows registers shorter than 18 bits to be read using a reduced number of shifts. For example, the result from a byte-read requires 9 bit shifts (Busy + 8 bits). 17:0 WriteData Operation 0x Poll 10 Read 11 Write 18:1 ReadData Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 0 Busy 150 ...
Page 151
... C8051F018 C8051F019 Figure 19.3. FLASHCON: JTAG Flash Control Register WRMD3 WRMD2 WRMD1 Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 This register determines how the Flash interface logic will respond to reads and writes to the FLASHDAT Register. Bits7-4: WRMD3-0: Write Mode Select Bits. The Write Mode Select Bits control how the interface logic responds to writes to the ...
Page 152
... All Flash read/write/erase operations are SYSCLK disallowed when FLSCL[3:0] = 1111b. DATA3 DATA2 DATA1 DATA0 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 - FLSCL3 FLSCL2 FLSCL1 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 / 50kHz) SYSCLK Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 Reset Value FAIL FBUSY 0000000000 Bit1 Bit0 Reset Value FLSCL0 00000000 Bit1 Bit0 152 ...
Page 153
... The WDT is disabled when the MCU is halted during single stepping breakpoint. The C8051F015DK is a development kit with all the hardware and software necessary to develop application code and perform in-circuit debugging with the C8051F018/9. Environment (IDE) which has a debugger and integrated 8051 assembler. It has an RS-232 to JTAG protocol translator module referred to as the EC ...
Page 154
... Silicon Laboratories products for any such unintended or unauthorized application, Buyer shall indemnify and hold Silicon Laboratories harmless against all claims and damages. Silicon Laboratories and Silicon Labs are trademarks of Silicon Laboratories Inc. Other products or brandnames mentioned herein are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders Rev. 1.2 C8051F018 C8051F019 154 ...