LH7A404N0F092B3,55 NXP Semiconductors, LH7A404N0F092B3,55 Datasheet

LH7A404N0F092B3,55
Specifications of LH7A404N0F092B3,55
935285071551
LH7A404N0F092B3-S
Available stocks
Related parts for LH7A404N0F092B3,55
LH7A404N0F092B3,55 Summary of contents
Page 1
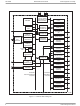
Preliminary data sheet FEATURES • 32-bit ARM9TDMI™ RISC Core – Cache Instruction and 8 kB Data Cache – MMU (Windows CE™ Enabled) – 266 MHz; See Table 1 for speed options • ...
Page 2
... INTERFACE SYNCHRONOUS MEMORY CONTROLLER LCD AHB BUS COLOR LCD CONTROLLER ADVANCED INTERFACE (ALI) USB HOST INTERFACE HIGH-PERFORMANCE 2 NXP Semiconductors 14.7456 MHz 32.768 kHz OSCILLATOR, PLL1 and PLL2, POWER MANAGEMENT, and RESET CONTROL VECTORED BOOT INTERRUPT ROM CONTROLLER BOOT CONTROLLER ADVANCED PERIPHERAL ...
Page 3
... K12 L9 VSS I/O Ring Ground L10 L11 L12 M9 M10 M11 M12 T18 E7 E9 E14 G5 G16 VDDC Core Power P5 P16 T7 T12 T14 Preliminary data sheet NXP Semiconductors Table 2. LH7A404 Functional Pin List DESCRIPTION LH7A404 RESET STANDBY OUTPUT I/O NOTES STATE STATE DRIVE 3 ...
Page 4
... E4 MEDCHG and WIDTHx pins to determine boot device. When LOW, boot device is selected according to the Y20 INTBOOT MEDCHG bit. When HIGH, the lower 64 kB address- es are mapped to the internal Boot ROM. 4 NXP Semiconductors RESET DESCRIPTION STATE Input Input Input Input Input LOW ...
Page 5
... D24 A20 D25 B18 D26 C16 D27 B17 D28 A18 D29 A17 D30 B15 D31 P17 A0 Asynchronous Address Bus N16 A1 Preliminary data sheet NXP Semiconductors RESET DESCRIPTION STATE LOW HIGH LH7A404 STANDBY OUTPUT I/O NOTES STATE DRIVE LOW 12 mA I/O LOW ...
Page 6
... E16 nSCS3 Synchronous Memory Chip Select 3 B16 nSWE Synchronous Memory Write Enable A14 SCKE0 Clock Enable 0 for Synchronous Memory B13 SCKE1_2 Clock Enable for Synchronous Memory 6 NXP Semiconductors RESET DESCRIPTION STATE LOW LOW LOW LOW LOW LOW HIGH HIGH HIGH HIGH ...
Page 7
... PC0/UARTTX1 • UART1 Transmit Data Output T1 PC1 T2 PC2 T3 PC3 GPIO Port C[5:1] R4 PC4 U1 PC5 U2 PC6 GPIO Port C6 Preliminary data sheet NXP Semiconductors RESET DESCRIPTION STATE Depends on MEDCHG LOW HIGH HIGH HIGH HIGH HIGH HIGH HIGH PA0: Input PA1: Input PAx: Input ...
Page 8
... Output Enable for PC Card (PCMCIA or CompactFlash) in Single or Dual Card mode • GPIO Port G1 W4 PG1/nPCWE • Write Enable for PC Card (PCMCIA or CompactFlash) in Single or Dual Card mode 8 NXP Semiconductors RESET DESCRIPTION STATE PC7: LOW PDx: LOW PEx: Output PE4: Output PE5: Output ...
Page 9
... Address Bit 24 for PC Card (PCMCIA) in Single nPCWAIT2 Card mode • WAIT Signal for Card 2 for PC Card (PCMCIA or CompactFlash) in Dual Card mode • GPIO Port H6 V7 PH6/nAC97RESET • AC97 Reset Preliminary data sheet NXP Semiconductors RESET DESCRIPTION STATE LOW LOW LOW LOW LOW LOW ...
Page 10
... DC-DC Converter 0 Output (Pulse Width Modulated) C10 PWM1 DC-DC Converter 1 Output (Pulse Width Modulated) B9 PWM2 PWM Output 2 D10 PWM3 PWM Output 3 C9 PWMSYNC PWM Synchronizing Input for PWM2 10 NXP Semiconductors RESET DESCRIPTION STATE PHx: Input LOW LOW LOW LOW LOW LOW HIGH LOW HIGH ...
Page 11
... AN1/UR/X- • Touch Screen Controller Upper Right • Touch Screen Controller X-minus • ADC channel 2 W14 AN2/LL/Y+ • Touch Screen Controller Lower Left • Touch Screen Controller Y-plus Preliminary data sheet NXP Semiconductors RESET DESCRIPTION STATE Input LOW LOW Input LOW ...
Page 12
... Chapter of the User’s Guide for more information. 5. The nWAIT pin must be pulled HIGH with a 33 kΩ resistor to avoid the possibility of the SMC inadvertently going into WAIT. 6. The internal pullup and pulldown resistance on all digital I/O pins Ω is 50K . 12 NXP Semiconductors RESET DESCRIPTION STATE Input Input Input Input ...
Page 13
... The Intensity bit is identically generated for all three colors. 2. MUSTN = Monochrome Upper Panel MLSTN = Monochrome Lower Panel CUSTN = Color Upper Panel CLSTN = Color Lower Panel Preliminary data sheet NXP Semiconductors Table 4. LCD Controller Pins STN MONO 4-BIT MONO 8-BIT DUAL SINGLE ...
Page 14
... B18 D26 95 mV/ns B19 A24 95 mV/ns B20 D23 95 mV/ns C1 nEXTPWR C2 TCK C3 PE5/SCCLKEN 95 mV/ns C4 DEOT0 95 mV/ns C5 nRESETOUT 14 NXP Semiconductors Table 5. LFBGA Numerical Pin List (Cont’d) SLEW OUTPUT LFBGA RATE DRIVE MMCDATA ACBITCLK C8 PF3/INT3 PWMSYNC 8 mA C10 PWM1 8 mA C11 PWM0 ...
Page 15
... A13/SA11 95 mV/ns H19 D12 95 mV/ns H20 A11/SA9 95 mV/ns J1 COL3 100 mV/ns J2 COL0 100 mV/ns J3 COL4 100 mV/ns Preliminary data sheet NXP Semiconductors Table 5. LFBGA Numerical Pin List (Cont’d) SLEW OUTPUT LFBGA RATE DRIVE J4 COL5 COL6 VSS J10 VSS J11 VSS ...
Page 16
... R4 PC4 95 mV/ns R5 VSSC R16 VSSC R17 nCS7 95 mV/ns R18 nCS2 95 mV/ns R19 nCS1 95 mV/ns R20 nCS6 95 mV/ns T1 PC1 95 mV/ns 16 NXP Semiconductors Table 5. LFBGA Numerical Pin List (Cont’d) SLEW OUTPUT LFBGA RATE DRIVE PC2 PC3 T4 LCDFP/LCDSPS T5 PG4/nPCREG T6 VSSC T7 VDDC T8 LCDVD1 12 mA ...
Page 17
... W8 PH4/nPCWAIT1 110 mV/ns W9 LCDVD2 95 mV/ns W10 PE1/LCDVD5 95 mV/ns W11 PD4/LCDVD12 95 mV/ns W12 PD2/LCDVD10 95 mV/ns Preliminary data sheet NXP Semiconductors Table 5. LFBGA Numerical Pin List (Cont’d) SLEW OUTPUT LFBGA RATE DRIVE 8 mA W13 WIDTH1 8 mA W14 AN2/LL/ W15 AN7 12 mA ...
Page 18
... The clock and state controller provides the clock gating and frequency division necessary, and then supplies the clocks to the processor and rest of the system. The amount of clock gating that actually takes place depends on the power saving mode selected. 18 NXP Semiconductors ...
Page 19
... DIVIDE BY MAINDIV1+2 RTC OSC Figure 3. Clock and State Controller Block Diagram Preliminary data sheet NXP Semiconductors Data Paths The data paths in the LH7A404 are: • The AMBA AHB bus • The AMBA APB bus • The External Bus Interface • ...
Page 20
... ARM922T core. 20 NXP Semiconductors USB HOST CONTROLLER DMA BUS The USB Host Controller has its own DMA control- ler. It acts as another bus master on the AHB bus. It does not interact with the non-USB DMA controller except in bus arbitration ...
Page 21
... SynchFlash (Initializes device MODE Register) 16-bit SROM (Initializes device MODE Register) 32-bit SynchFlash (Initializes device MODE Register) 32-bit SROM (Initializes device MODE Register) Boot from internal Boot ROM; see Table 6 Preliminary data sheet NXP Semiconductors Table 6. Internal Boot Modes GPIO LATCHED LATCHED PA7 ...
Page 22
... LCD MMU/DMA LCD AHB BUS Figure 4. External Bus Interface Block Diagram 22 NXP Semiconductors After a power-on reset, all mask register bits are cleared, masking all interrupts. They must be set by software after power-on reset to enable interrupts. A vectored interrupt has improved latency as it pro- ...
Page 23
... Byte lane write control • External bus interface • CompactFlash or PCMCIA interfacing. Preliminary data sheet NXP Semiconductors SDRAM (Synchronous) Memory Controller The SDRAM (Synchronous) Memory Controller pro- vides a high speed memory interface to a wide variety of synchronous memory devices, including Synchronous DRAM, Synchronous Flash and Synchronous ROMs ...
Page 24
... Software-initiated card deactivation sequence on transaction complete • Limited support for synchronous smart cards via reg- istered input/output. 24 NXP Semiconductors PROGRAMMABLE PARAMETERS • Smart Card clock frequency • Communication baud rate • Protocol convention • Card activation/deactivation time • ...
Page 25
... DMA channels (three transmit and three receive) to allow different sample frequency data queues to be handled with low software overhead. Preliminary data sheet NXP Semiconductors The DMA controller includes an M2M transfer fea- ture allowing block moves of data from one memory address space to another with minimum of program effort and time ...
Page 26
... All the necessary clocks and timing pulses to per- form serialization or de-serialization of the data stream to, or from the codec device. 26 NXP Semiconductors The interface supports full duplex operation and the transmit and receive paths are buffered with internal FIFO memories allowing bytes to be stored independently in both transmit and receive modes ...
Page 27
... MHz clock after the data register has been updated. Preliminary data sheet NXP Semiconductors FREE-RUNNING MODE In free-running mode, the timer wraps around to 0xFFFF when it underflows and continues counting down. ...
Page 28
... SMBus provides an arbitration mechanism by relying on the wired-AND connection of all SMBus interfaces to the SMBus. 28 NXP Semiconductors DC-to-DC Converter The features of the DC-DC Converter interface are: • Dual-drive PWM outputs with independent closed loop feedback • ...
Page 29
... Core Voltage should never exceed I/O Voltage after initial power up. See “Power Supply Sequencing” on page 31. 2. Many of the peripherals do not operate properly at clock speeds other than 14.7456 MHz. Some (such as USB) function only at 14.7456 MHz. Preliminary data sheet NXP Semiconductors MINIMUM MAXIMUM −0.3 V 2.4 V − ...
Page 30
... Guaranteed values are in the Recommended Operating Conditions table. 255 250 245 240 235 230 225 220 215 210 205 200 25 35 Figure 5. Temperature/Voltage/Speed Chart (LH7A404-N0E-000-xx and LH7A404-N0F-000-xx Only) 30 NXP Semiconductors MINIMUM TYPICAL MAXIMUM NOTES 2.0 V 2.1 V 2.2 V 3.14 V 3.3 V 3.6 V 2.2 V 2.0 V 2.1 V 3.0 V 3 MHz ...
Page 31
... See ’Current Consumption by Operating Mode’, page 34 for operating conditions. 4. Both oscillators running, LCD Active; all other peripherals stopped kHz oscillator running; all other peripherals stopped. Preliminary data sheet NXP Semiconductors To avoid a potential latchup condition, voltage should be applied to input pins only after the device is powered-on as described above. ...
Page 32
... Trying to pull the analog input pins above or below the power supply rails will cause protection diodes to be forward-biased, resulting in large current source/sink and possible damage to the ADC. 8. Bandgap and other low-bandwidth circuitry operating. All other ADC blocks shut down. 32 NXP Semiconductors MIN. TYP. MAX. ...
Page 33
... LSB OFFSET ERROR DNL AC Test Conditions PARAMETER DC I/O Supply Voltage (VDD) DC Core Supply Voltage (VDDC) Input Pulse Levels Input Rise and Fall Times Input and Output Timing Reference Levels Preliminary data sheet NXP Semiconductors IDEAL TRANSFER CURVE TRANSFER CURVE INTEGRAL NON-LINEARITY ...
Page 34
... I/O Current NOTES: 1. FCLK = 200 MHZ pertains to LH7A404-N0E-000-xx and LH7A404-N0F-000-xx 2. FCLK = 266 MHz pertains to LH7A404-N0E-092-xx and LH7A404-N0F-092-xx. 34 NXP Semiconductors PERIPHERAL CURRENT CONSUMPTION In addition to the modal current consumption, Table 10 shows the typical current consumption for each of the on-board peripheral blocks. The values were determined with the peripheral clock running at 200 MHz, typical conditions, and no I/O loads ...
Page 35
... OUTPUT SIGNAL (O) INPUT SIGNAL (I) Preliminary data sheet NXP Semiconductors For outputs from the LH7A404, tOVXXX (e.g. tOVA) represents the amount of time for the output to become valid from the rising edge of the reference clock signal. Maximum requirements for tOVXXX are shown in Table 12. ...
Page 36
... PCMCIA INTERFACE SIGNALS (+ [wait states × HCLK period]) tOVDREG nPCREG Output 50 pF tOHDREG 36 NXP Semiconductors Table 12. AC Signal Characteristics MIN. MAX. 4 × tHCLK – 7 × tHCLK + 7.5 ns Read Cycle Time 4 × tHCLK – 7 × tHCLK + 7.5 ns Write Cycle Time tHCLK ns tHCLK ns tHCLK – ...
Page 37
... MMC Clock 4. ‘tcyc’ is the period of one AC97 Clock 5. ‘nC’ in the MIN./MAX. columns indicates the number of system clock (HCLK) periods after valid address 6. For Output Drive strength specifications, refer to Table 2 Preliminary data sheet NXP Semiconductors MIN. MAX. — tHCLK + 5 ns Data Valid 4 × ...
Page 38
... Write. Figure 10 and Figure 11 show the waveforms and timing for an external asynchronous memory Read. 0 HCLK A[27:0] D[31:0] nCSx nWE nBLE Figure 8. External Asynchronous Memory Write, Zero Wait States (BCRx:WST1 = 0b000) 38 NXP Semiconductors tWC VALID ADDRESS tDVWE, tDHWE, tDVBE tDHBE VALID DATA tAVCS ...
Page 39
... System-on-Chip 0 1 HCLK A[27:0] D[31:0] nCSx nWE nBLE 0 WAIT STATE Figure 9. External Asynchronous Memory Write, Four Wait States (BCRx:WST1 = 0b100) Preliminary data sheet NXP Semiconductors VALID ADDRESS VALID DATA nCSx Valid nWE Valid nBLE Valid WAIT WAIT WAIT WAIT STATE 1 ...
Page 40
... LH7A404 0 HCLK A[27:0] D[31:0] nCSx nOE nBLE Figure 10. External Asynchronous Memory Read, Zero Wait States (BCRx:WST1 = 0b000) 40 NXP Semiconductors tRC tAHOE, tAHBE VALID ADDRESS VALID DATA tDSCS tAVCS tCS nCS Valid tDSOE tAVOE tOE nOE Valid tDSBE tAVBE tBER nBLE Valid ...
Page 41
... HCLK A[27:0] nCS[3:0, CS[7:6] nOE nBLE D[31:0] 0 WAIT STATE, DATA WOULD BE LATCHED HERE Figure 11. External Asynchronous Memory Read, Four Wait States (BCRx:WST1 = 0b100) Preliminary data sheet NXP Semiconductors VALID ADDRESS nCSx Valid nOE Valid nBLE Valid VALID DATA WAIT WAIT WAIT ...
Page 42
... HCLK periods, the minimum setting of BCRx:WST1 total the minimum value for BCRx:WST1. 42 NXP Semiconductors is released, allowing slow memory or memory-mapped peripherals time to complete the action. Figure 12 through Figure 17 illustrate nWAIT timing using different WST register settings and circumstances ...
Page 43
... HCLK WSD-4 Transaction Sequence DELAY NOTES: SQ: nWAIT Sampled and Queued SI: nWAIT Sampled and Ignored Figure 14. nWAIT Read Sequence (BCRx:WST1 = 4); nWAIT Has No Effect On Current Transaction Preliminary data sheet NXP Semiconductors tA_nWAIT SQ-3 SQ-2 SQ-1 SQ-0 SQ-4 SQ-3 SQ-2 nWAIT nWAIT nWAIT ...
Page 44
... Once nWAIT is sampled HIGH (de-asserted), the current memory transaction is queued to complete. 7. Since static and dynamic memory cannot be accessed at the same time, prolonged extension of an SMC transaction by either Wait States or nWAIT delays can cause refresh failure for the SDRAM, and may cause SDRAM data loss. 44 NXP Semiconductors tDD_nWAIT_nCS(x) tDD_nWAIT_nWE tA_nWAIT SQ-2 ...
Page 45
... WSD-3 WSD2 Sequence DELAY DELAY DELAY NOTES: SQ: nWAIT Sampled and Queued SI: nWAIT Sampled and Ignored Figure 16. nWAIT Write Sequence (BCRx:WST1 = 4); Ignored and Queued nWAIT Delays Preliminary data sheet NXP Semiconductors tA_nWAIT SQ-3 SQ-2 SQ-1 SQ-0 SQ-4 SQ-3 SQ-2 nWAIT nWAIT nWAIT ...
Page 46
... HCLK WSD-4 Transaction Sequence DELAY NOTES: SQ: nWAIT Sampled and Queued SI: nWAIT Sampled and Ignored Figure 17. nWAIT Write Sequence (BCRx:WST1 = 4); nWAIT Has No Effect On Current Transaction 46 NXP Semiconductors tA_nWAIT SI SI WSD-3 WSD-2 WSD-1 WSD-0 DELAY DELAY DELAY DELAY CYCLE 32-Bit System-on-Chip ...
Page 47
... LOW. 5. SDCKE is static HIGH. SSPCLK SSPFRM SSPTXD/ SSPRXD Figure 19. Synchronous Bank Activate and Write Preliminary data sheet NXP Semiconductors t OHXXX READ t OVB t OVXXX BANK, tISD tIHD COLUMN tOVA DATA n DATA Figure 18 ...
Page 48
... SSPFRM SSPTXD/ SSPRXD Figure 21. Texas Instruments Synchronous Serial Frame Format (Continuous Transfer) 48 NXP Semiconductors SSPFRM signal marks the beginning and end of a frame. Figure 20 and Figure 21 show Texas Instruments synchronous serial frame format, Figure 22 through Figure 29 show the Motorola SPI format, and Figure 30 and Figure 31 show National Semiconductor’ ...
Page 49
... Figure 23. Motorola SPI Frame Format (Continuous Transfer) with SPO = 0 and SPH = 0 SSPCLK nSSPFRM SSPRXD Q MSB SSPTXD MSB NOTE undefined. Figure 24. Motorola SPI Frame Format (Single Transfer) with SPO = 0 and SPH = 1 Preliminary data sheet NXP Semiconductors in single and continuous modes. See Figures 22 through 29 BITS LSB MSB BITS BITS LH7A404 LSB Q ...
Page 50
... Figure 26. Motorola SPI Frame Format (Continuous Transfer) with SPO = 1 and SPH = 1 SSPCLK nSSPFRM SSPRXD MSB SSPTXD MSB NOTE undefined. Figure 27. Motorola SPI Frame Format (Single Transfer) with SPO = 1 and SPH = 0 50 NXP Semiconductors LSB MSB BITS LSB MSB BITS BITS 32-Bit System-on-Chip LSB ...
Page 51
... Figure 28. Motorola SPI Frame Format (Continuous Transfer) with SPO = 1 and SPH = 0 SSPCLK nSSPFRM SSPRXD Q MSB SSPTXD MSB NOTE undefined. Figure 29. Motorola SPI Frame Format (Single Transfer) with SPO = 1 and SPH = 1 Preliminary data sheet NXP Semiconductors MSB LSB BITS BITS LH7A404 MSB LH7A404-32 LSB Q LSB ...
Page 52
... MSB BITS OUTPUT DATA Figure 31. MICROWIRE Frame Format (Continuous Transfers) 52 NXP Semiconductors an 8-bit control message is transmitted to the off-chip slave. During this transmission no incoming data is received by the SSP. After the message has been sent, the external slave device decodes the message. After ...
Page 53
... System-on-Chip SSPCLK (Programmable CLOCK phase) SSPTX SSPRX SSPFRM (Programmable FRAME phase and duration) Preliminary data sheet NXP Semiconductors tCLK CLOCK CLOCK PHASE 1 PHASE 2 tOVTX tOHTX BITn BITn-1 OUTPUT OUTPUT tISRX tIHRX BITn BITn-1 INPUT INPUT tOHFRM tOVFRM Figure 32. General SSP Timing ...
Page 54
... Precharge time, access time, and hold time are programmable wait-state times. 2. nPCCE1 nPCCE2 TRANSFER TYPE 0 0 Common Memory 0 1 Attribute Memory None 54 NXP Semiconductors PRECHARGE ACCESS TIME TIME (See Note 1) (See Note 1) (See Note 1) ADDRESS tOVDREG tOHDREG tOVCEx tOHCEx tOVPCD tOHPCD DATA tISD tIHD tOVOE tOHOE Figure 33 ...
Page 55
... Common Memory 0 1 Attribute Memory None nPCWE, nPCOE, nPCIOW, nPCIOR nCSx Figure 35. PCMCIA Precharge, Access, and Hold Waveform Preliminary data sheet NXP Semiconductors PRECHARGE ACCESS TIME TIME (See Note 1) (See Note 1) (See Note 1) ADDRESS tOVDREG tOHDREG tOVCEx tOHCEx tOVPCD DATA tOVD ...
Page 56
... MMC command or data Read. MMCCLK MMCCMD MMCDATA MMCCLK MMCCMD MMCDATA ACBITCLK ACOUT/ACSYNC ACIN 56 NXP Semiconductors AC97 Interface Waveforms Figure 38 shows the waveforms and timing for the AC97 interface Data Setup and Hold. tMMCCLK tOVCMD tOHCMD tOVDAT tOHDAT Figure 36. MMC Command/Data Write tISCMD ...
Page 57
... ACBITCLK ACSYNC BIT ACIN LCDDCLK LCDVD (SoC Output) Preliminary data sheet NXP Semiconductors Color LCD Controller Waveforms Figure 41 shows the Valid Output Setup Time for LCD data. Timing diagrams for each CLCDC mode are represented in Figure 42 through Figure 47. tOVD tOHD ACIN ...
Page 58
... LH7A404 58 NXP Semiconductors Figure 42. STN Horizontal Timing 32-Bit System-on-Chip Preliminary data sheet ...
Page 59
... System-on-Chip Preliminary data sheet NXP Semiconductors Figure 43. STN Vertical Timing LH7A404 59 ...
Page 60
... LH7A404 60 NXP Semiconductors Figure 44. TFT Horizontal Timing 32-Bit System-on-Chip Preliminary data sheet ...
Page 61
... System-on-Chip Preliminary data sheet NXP Semiconductors Figure 45. TFT Vertical Timing LH7A404 61 ...
Page 62
... Figure 46. AD-TFT and HR-TFT Horizontal Timing LCDSPS T4 (Vertical Sync) LCDHRLP V2 (Horizontal Sync) LCDVD (LCD Data) V3 LCDSPL 62 NXP Semiconductors 1 AD-TFT or HR-TFT HORIZONTAL LINE TIMING0:HSW 001 002 003 004 005 006 007 008 PIXEL DATA TIMING0:HSW + TIMING0:HBP 001 002 003 004 005 006 1 LCDDCLK ALITIMING2:SPLDEL ...
Page 63
... NOTE: *The timing relationship is specified as a cycle-based timing. Due to variations in crystal input clock jitter, power rail noise and I/O conditioning these timings will vary marginally recommended that designers Preliminary data sheet NXP Semiconductors Hz clock periods after assertion of nPOR to allow time for sampling BATOK and nEXTPWR. The delay prevents a false ‘ ...
Page 64
... NOTE: *The timing relationship is specified as a cycle-based timing. Due to variations in crystal input clock jitter, power rail noise and I/O conditioning these timings will vary marginally recommended that designers 64 NXP Semiconductors tDD_nPOR_WKUP tDD_nPOR_nRSTO TYP. ...
Page 65
... NOTE: *The timing relationship is specified as a cycle-based timing. Due to variations in crystal input clock jitter, power rail noise and I/O conditioning these timings will vary marginally recommended that designers Preliminary data sheet NXP Semiconductors tDD_nURESET_WKUP tDD_nURESET_nRSTO MAX. ...
Page 66
... NXP Semiconductors tDD_nPWRFL_WKUP tA_nPWRFL tA_nRSTO MAX. UNITS* 4 XTAL32 Periods nPWRFL to nRESETOUT assertion delay XTAL32 Periods nRESETOUT assertion time XTAL32 Periods nPWRFL assertion time 1 Hz Periods ...
Page 67
... Tolerance for R1, C1 ≤ 5%. Figure 52. 32.768 kHz External Oscillator Components and Schematic Preliminary data sheet NXP Semiconductors Increased switching noise generated by faster switch- ing circuits could affect the overall system stability. The amount of switching noise is directly affected by the application executed on the SoC ...
Page 68
... R1 must be in the circuit. 5. Ground connections should be short and return to the ground plane which is connected to the processor's core ground pins. 6. Tolerance for R1, C1 ≤ 5%. Figure 53. 14.7456 MHz External Oscillator Components and Schematic 68 NXP Semiconductors ENABLE XTALIN XTALOUT Y1 14.7456 MHz R1 1 MΩ ...
Page 69
... Figure 54. VDDA, VSSA Filter Circuit Preliminary data sheet NXP Semiconductors UNUSED INPUT SIGNAL CONDITIONING Floating input signals can cause excessive power consumption. Unused inputs without internal pull-up or pull-down resistors should be pulled up or down exter- nally, to tie the signal to its inactive state. NXP recom- mends using no larger than 33 kΩ ...
Page 70
... ball index area DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions) A UNIT max 0.4 1.35 0.5 17.1 mm 1.7 0.3 1.15 0.4 16.9 OUTLINE VERSION IEC SOT1021-1 Figure 55. Package outline SOT1021-1 (LFBGA324) 70 NXP Semiconductors ∅ 1/2 e ∅ 1 scale 17.1 0.8 15.2 15.2 0.15 0.08 0.12 16 ...
Page 71
... System-on-Chip REVISION HISTORY Document ID Release date Data sheet status LH7A404_N_1 20070716 Preliminary data sheet Modifications: • First NXP version based on the LH7A404 data sheet of 20061201 Preliminary data sheet NXP Semiconductors Table 17. Revision history Change notice Supersedes - LH7A404 V1-5 12-1-2006 LH7A404 71 ...
Page 72
... NXP Semiconductors. In case of any inconsistency or conflict between information in this document and such terms and conditions, the latter will prevail. ...
Page 73
... Dear customer from June 1 , 2007 NXP Semiconductors has acquired the LH7xxx ARM Microcontrollers from Sharp Microelectronics. The following changes are applicable to the attached data sheet. In data sheets where the previous Sharp or Sharp Corporation references remain, please use the new links as shown below. ...
Page 74
... Terms and conditions of sale (DS) Terms and conditions of sale — NXP Semiconductors products are sold subject to the general terms and conditions of commercial sale, as published at http://www.nxp.com/profile/terms, including those pertaining to warranty, intellectual property rights infringement and limitation of liability, unless explicitly otherwise agreed to in writing by NXP Semiconductors ...
Page 75
... The product is not designed, authorized or warranted to be suitable for any other use, including medical, military, aircraft, space or life support equipment, nor in applications where failure or malfunction of an NXP Semiconductors product can reasonably be expected to result in personal injury, death or severe property or environmental damage ...