MC68HC705C9ACFN Freescale Semiconductor, MC68HC705C9ACFN Datasheet - Page 34

MC68HC705C9ACFN
Manufacturer Part Number
MC68HC705C9ACFN
Description
IC MCU 2.1MHZ 16K OTP 44-PLCC
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor
Series
HC05r
Datasheet
1.MC705C9ACPE.pdf
(118 pages)
Specifications of MC68HC705C9ACFN
Core Processor
HC05
Core Size
8-Bit
Speed
2.1MHz
Connectivity
SCI, SPI
Peripherals
POR, WDT
Number Of I /o
24
Program Memory Size
16KB (16K x 8)
Program Memory Type
OTP
Ram Size
352 x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
3 V ~ 5.5 V
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
44-PLCC
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Eeprom Size
-
Data Converters
-
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
MC68HC705C9ACFN
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
MC68HC705C9ACFNE
Manufacturer:
RFMD
Quantity:
8 729
Company:
Part Number:
MC68HC705C9ACFNE
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
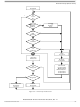
Central Processor Unit (CPU)
3.2.1 Accumulator (A)
The accumulator is a general-purpose 8-bit register used to hold operands and results of arithmetic
calculations or data manipulations.
3.2.2 Index Register (X)
The index register is an 8-bit register used for the indexed addressing value to create an effective
address. The index register may also be used as a temporary storage area.
3.2.3 Program Counter (PC)
The program counter is a 16-bit register that contains the address of the next byte to be fetched.
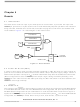
3.2.4 Stack Pointer (SP)
The stack pointer contains the address of the next free location on the stack. During an MCU reset or the
reset stack pointer (RSP) instruction, the stack pointer is set to location $0FF. The stack pointer is then
decremented as data is pushed onto the stack and incremented as data is pulled from the stack.
When accessing memory, the eight most significant bits are permanently set to 00000011. These eight
bits are appended to the six least significant register bits to produce an address within the range of $00FF
to $00C0. Subroutines and interrupts may use up to 64 (decimal) locations. If 64 locations are exceeded,
the stack pointer wraps around and loses the previously stored information. A subroutine call occupies
two locations on the stack; an interrupt uses five locations.
3.2.5 Condition Code Register (CCR)
The CCR is a 5-bit register in which four bits are used to indicate the results of the instruction just
executed, and the fifth bit indicates whether interrupts are masked. These bits can be individually tested
by a program, and specific actions can be taken as a result of their state. Each bit is explained in the
following paragraphs.
Half Carry (H)
Interrupt (I)
Negative (N)
Zero (Z)
Carry/Borrow (C)
34
This bit is set during ADD and ADC operations to indicate that a carry occurred between bits 3 and 4.
When this bit is set, the timer, SCI, SPI, and external interrupt are masked (disabled). If an interrupt
occurs while this bit is set, the interrupt is latched and processed as soon as the interrupt bit is cleared.
When set, this bit indicates that the result of the last arithmetic, logical, or data manipulation was
negative.
When set, this bit indicates that the result of the last arithmetic, logical, or data manipulation was zero.
When set, this bit indicates that a carry or borrow out of the arithmetic logical unit (ALU) occurred
during the last arithmetic operation. This bit is also affected during bit test and branch instructions and
during shifts and rotates.
MC68HC05C9A Advance Information Data Sheet, Rev. 4.1
Freescale Semiconductor