MC68HC705B16CFN Freescale Semiconductor, MC68HC705B16CFN Datasheet - Page 78
MC68HC705B16CFN
Manufacturer Part Number
MC68HC705B16CFN
Description
IC MCU 2.1MHZ 15K OTP 52-PLCC
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor
Series
HC05r
Datasheet
1.MC68HC705B16CFN.pdf
(302 pages)
Specifications of MC68HC705B16CFN
Core Processor
HC05
Core Size
8-Bit
Speed
2.1MHz
Connectivity
SCI
Peripherals
POR, WDT
Number Of I /o
32
Program Memory Size
15KB (15K x 8)
Program Memory Type
OTP
Eeprom Size
256 x 8
Ram Size
352 x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
4.5 V ~ 5.5 V
Data Converters
A/D 8x8b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
52-PLCC
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
MC68HC705B16CFN
Manufacturer:
MOT
Quantity:
5 510
Part Number:
MC68HC705B16CFN
Manufacturer:
FREESCALE
Quantity:
20 000
- Current page: 78 of 302
- Download datasheet (4Mb)
6
6.6.1
In idle line wake-up mode, a dormant receiver wakes up as soon as the RDI line becomes idle.
Idle is defined as a continuous logic high level on the RDI line for ten (or eleven) full bit times.
Systems using this type of wake-up must provide at least one character time of idle between
messages to wake up sleeping receivers, but must not allow any idle time between characters
within a message.
6.6.2
In address mark wake-up, the most significant bit (MSB) in a character is used to indicate whether
it is an address (1) or data (0) character. Sleeping receivers will wake up whenever an address
character is received. Systems using this method for wake-up would set the MSB of the first
character of each message and leave it clear for all other characters in the message. Idle periods
may be present within messages and no idle time is required between messages for this wake-up
method.
6.7
Receive data is the serial data that is applied through the input line and the SCI to the internal bus.
The receiver circuitry clocks the input at a rate equal to 16 times the baud rate. This time is referred
to as the RT rate in
The receiver clock generator is controlled by the baud rate register, as shown in
Figure
Once a valid start bit is detected, the start bit, each data bit and the stop bit are sampled three
times at RT intervals 8 RT, 9 RT and 10 RT (1 RT is the position where the bit is expected to start),
as shown in
the majority of the samples. A noise flag is set when all three samples on a valid start bit or data
bit or the stop bit do not agree.
6.8
When the input (idle) line is detected low, it is tested for three more sample times (referred to as
the start edge verification samples in
detect a logic zero, a valid start bit has been detected, otherwise the line is assumed to be idle. A
noise flag is set if one of the three verification samples detect a logic one, thus a valid start bit
could be assumed with a set noise flag present.
Freescale
6-6
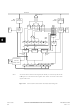
6-2; however, the SCI is synchronized by the start bit, independent of the transmitter.
Figure
Idle line wake-up
Address mark wake-up
Receive data in (RDI)
Start bit detection
6-5. The value of the bit is determined by voting logic which takes the value of
Figure 6-4
SERIAL COMMUNICATIONS INTERFACE
and as the receiver clock in
Figure
6-4). If at least two of these three verification samples
Figure
6-2.
Figure 6-1
MC68HC05B6
Rev. 4.1
and
Related parts for MC68HC705B16CFN
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet: