MC68HC908QY4CP Freescale Semiconductor, MC68HC908QY4CP Datasheet - Page 44
MC68HC908QY4CP
Manufacturer Part Number
MC68HC908QY4CP
Description
IC MCU 4K FLASH W/ADC 16-DIP
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor
Series
HC08r
Datasheet
1.MC908QY4MDWER.pdf
(184 pages)
Specifications of MC68HC908QY4CP
Core Processor
HC08
Core Size
8-Bit
Speed
8MHz
Peripherals
LVD, POR, PWM
Number Of I /o
13
Program Memory Size
4KB (4K x 8)
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Ram Size
128 x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
2.7 V ~ 5.5 V
Data Converters
A/D 4x8b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
16-DIP (0.300", 7.62mm)
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Eeprom Size
-
Connectivity
-
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
MC68HC908QY4CP
Manufacturer:
FREESCALE
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
MC68HC908QY4CPE
Manufacturer:
KEMET
Quantity:
12 000
Company:
Part Number:
MC68HC908QY4CPE
Manufacturer:
FREESCAL
Quantity:
943
Part Number:
MC68HC908QY4CPE
Manufacturer:
FREESCALE
Quantity:
20 000
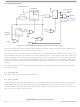
Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
3.3.2 Voltage Conversion
When the input voltage to the ADC equals V
, the ADC converts the signal to $FF (full scale). If the input
DD
voltage equals V
the ADC converts it to $00. Input voltages between V
and V
are a straight-line
SS,
DD
SS
linear conversion. All other input voltages will result in $FF if greater than V
and $00 if less than V
.
DD
SS
NOTE
Input voltage should not exceed the analog supply voltages.
3.3.3 Conversion Time
Sixteen ADC internal clocks are required to perform one conversion. The ADC starts a conversion on the
first rising edge of the ADC internal clock immediately following a write to the ADSCR. If the ADC internal
clock is selected to run at 1 MHz, then one conversion will take 16 μs to complete. With a 1-MHz ADC
internal clock the maximum sample rate is 62.5 kHz.
16 ADC Clock Cycles
Conversion Time =
ADC Clock Frequency
Number of Bus Cycles = Conversion Time × Bus Frequency
3.3.4 Continuous Conversion
In the continuous conversion mode (ADCO = 1), the ADC continuously converts the selected channel
filling the ADC data register (ADR) with new data after each conversion. Data from the previous
conversion will be overwritten whether that data has been read or not. Conversions will continue until the
ADCO bit is cleared. The COCO bit (ADSCR, $003C) is set after each conversion and will stay set until
the next read of the ADC data register.
When a conversion is in process and the ADSCR is written, the current conversion data should be
discarded to prevent an incorrect reading.
3.3.5 Accuracy and Precision
The conversion process is monotonic and has no missing codes.
3.4 Interrupts
When the AIEN bit is set, the ADC module is capable of generating a central processor unit (CPU)
interrupt after each ADC conversion. A CPU interrupt is generated if the COCO bit is at 0. The COCO bit
is not used as a conversion complete flag when interrupts are enabled.
3.5 Low-Power Modes
The following subsections describe the ADC in low-power modes.
3.5.1 Wait Mode
The ADC continues normal operation during wait mode. Any enabled CPU interrupt request from the ADC
can bring the microcontroller unit (MCU) out of wait mode. If the ADC is not required to bring the MCU out
of wait mode, power down the ADC by setting the CH[4:0] bits in ADSCR to 1s before executing the WAIT
instruction.
MC68HC908QY/QT Family Data Sheet, Rev. 6
44
Freescale Semiconductor