LTC1992-2CMS8 Linear Technology, LTC1992-2CMS8 Datasheet - Page 25

LTC1992-2CMS8
Manufacturer Part Number
LTC1992-2CMS8
Description
IC AMP/DVR I/O GAIN OF 2 8MSOP
Manufacturer
Linear Technology
Datasheet
1.LTC1992CMS8PBF.pdf
(42 pages)
Specifications of LTC1992-2CMS8
Amplifier Type
Differential
Number Of Circuits
1
Output Type
Differential, Rail-to-Rail
Slew Rate
1.5 V/µs
Gain Bandwidth Product
3.2MHz
Current - Input Bias
2pA
Voltage - Input Offset
250µV
Current - Supply
700µA
Current - Output / Channel
30mA
Voltage - Supply, Single/dual (±)
2.7 V ~ 11 V, ±1.35 V ~ 5.5 V
Operating Temperature
0°C ~ 70°C
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
8-MSOP, Micro8™, 8-uMAX, 8-uSOP,
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
-3db Bandwidth
-
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
LTC1992-2CMS8
Manufacturer:
LT
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
LTC1992-2CMS8
Manufacturer:
LINEAR/凌特
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
LTC1992-2CMS8#PBF
Manufacturer:
LT
Quantity:
759
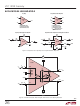
block DiagraMs
applicaTions inForMaTion
Theory of Operation
The LTC1992 family consists of five fully differential, low
power amplifiers. The LTC1992 is an unconstrained fully
differential amplifier. The LTC1992-1, LTC1992-2, LTC1992-
5 and LTC1992-10 are fixed gain blocks (with gains of
1, 2, 5 and 10 respectively) featuring precision on-chip
resistors for accurate and ultra stable gain.
In many ways, a fully differential amplifier functions much
like the familiar, ubiquitous op amp. However, there are
several key areas where the two differ. Referring to Figure 1,
an op amp has a differential input, a high open-loop gain
and utilizes negative feedback (through resistors) to set
the closed-loop gain and thus control the amplifier’s gain
with great precision. A fully differential amplifier has all of
these features plus an additional input and a complemen-
tary output. The complementary output reacts to the input
signal in the same manner as the other output, but in the
opposite direction. Two outputs changing in an equal but
opposite manner require a common reference point (i.e.,
opposite relative to what?). The additional input, the V
pin, sets this reference point. The voltage on the V
directly sets the output signal’s common mode voltage and
LTC1992-10
LTC1992-1
LTC1992-2
LTC1992-5
PART
R
30k
30k
30k
15k
IN
150k
150k
(1992-X)
R
30k
60k
FB
V
–IN
MID
+IN
1
7
8
–V
+V
OCM
6
3
S
S
200k
200k
input
V
OCM
OCM
2
+V
–V
+V
–V
S
S
S
S
allows the output signal’s common mode voltage to be
set completely independent of the input signal’s common
mode voltage. Uncoupling the input and output common
mode voltages makes signal level shifting easy.
For a better understanding of the operation of a fully dif-
ferential amplifier, refer to Figure 2. Here, the LTC1992
functional block diagram adds external resistors to real-
ize a basic gain block. Note that the LTC1992 functional
block diagram is not an exact replica of the LTC1992
circuitry. However, the Block Diagram is correct and is
a very good tool for understanding the operation of fully
differential amplifier circuits. Basic op amp fundamentals
together with this block diagram provide all of the tools
needed for understanding fully differential amplifier circuit
applications.
The LTC1992 Block Diagram has two op amps, two sum-
ming blocks (pay close attention the signs) and four resis-
tors. Two resistors, R
the V
reference. Its use is optional and it is not involved in the
operation of the LTC1992’s amplifier. The LTC1992 functions
through the use of two servo networks each employing
R
R
IN
IN
MID
pin and simply provide a convenient mid-supply
–
+
+
–
R
R
FB
FB
MID1
LTC1992 Family
and R
1992-X BD
4
5
MID2
+OUT
–OUT
, connect directly to
1992fa