LP3856ES-1.8/NOPB National Semiconductor, LP3856ES-1.8/NOPB Datasheet - Page 11
LP3856ES-1.8/NOPB
Manufacturer Part Number
LP3856ES-1.8/NOPB
Description
IC REG LDO 3.0A 1.8V TO-263-5
Manufacturer
National Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.LP3856ES-3.3NOPB.pdf
(18 pages)
Specifications of LP3856ES-1.8/NOPB
Regulator Topology
Positive Fixed
Voltage - Output
1.8V
Voltage - Input
2.5 ~ 7 V
Number Of Regulators
1
Current - Output
3A (Max)
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 125°C
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
TO-263-5, D²Pak (5 leads + Tab), TO-263BA
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Voltage - Dropout (typical)
-
Current - Limit (min)
-
Other names
*LP3856ES-1.8
*LP3856ES-1.8/NOPB
LP3856ES-1.8
*LP3856ES-1.8/NOPB
LP3856ES-1.8
Application Hints
EXTERNAL CAPACITORS
Like any low-dropout regulator, external capacitors are re-
quired to assure stability. These capacitors must be correctly
selected for proper performance.
INPUT CAPACITOR: An input capacitor of at least 10µF is
required. Ceramic or Tantalum may be used, and capacitance
may be increased without limit
OUTPUT CAPACITOR: An output capacitor is required for
loop stability. It must be located less than 1 cm from the device
and connected directly to the output and ground pins using
traces which have no other currents flowing through them
(see PCB Layout section).
The minimum amount of output capacitance that can be used
for stable operation is 10µF. For general usage across all load
currents and operating conditions, the part was characterized
using a 10µF Tantalum input capacitor. The minimum and
maximum stable ESR range for the output capacitor was then
measured which kept the device stable, assuming any output
capacitor whose value is greater than 10µF (see
low).
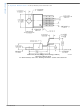
FIGURE 1. ESR Curve for C
It should be noted that it is possible to operate the part with
an output capacitor whose ESR is below these limits, assum-
ing that sufficient ceramic input capacitance is provided. This
will allow stable operation using ceramic output capacitors
(see next section).
OPERATION WITH CERAMIC OUTPUT CAPACITORS
LP385X voltage regulators can operate with ceramic output
capacitors if the values of input and output capacitors are se-
lected appropriately. The total ceramic output capacitance
must be equal to or less than a specified maximum value in
order for the regulator to remain stable over all operating con-
ditions. This maximum amount of ceramic output capacitance
is dependent upon the amount of ceramic input capacitance
used as well as the load current of the application. This rela-
tionship is shown in
stable value of ceramic output capacitance as a function of
ceramic input capacitance for load currents of 1A, 2A, and 3A.
For example, if the maximum load current is 1A, a 10µF ce-
ramic input capacitor will allow stable operation for values of
ceramic output capacitance from 10µF up to about 500µF.
Figure
Capacitor)
OUT
2, which graphs the maximum
(with 10µF Tantalum Input
20030970
Figure 1
be-
11
If the maximum load current is 2A and a 10µF ceramic input
capacitor is used, the regulator will be stable with ceramic
output capacitor values from 10µF up to about 50µF. At 3A of
load current, the ratio of input to output capacitance required
approaches 1:1, meaning that whatever amount of ceramic
output capacitance is used must also be provided at the input
for stable operation. For load currents between 1A, 2A, and
3A, interpolation may be used to approximate values on the
graph. When calculating the total ceramic output capacitance
present in an application, it is necessary to include any ce-
ramic bypass capacitors connected to the regulator output.
SELECTING A CAPACITOR
It is important to note that capacitance tolerance and variation
with temperature must be taken into consideration when se-
lecting a capacitor so that the minimum required amount of
capacitance is provided over the full operating temperature
range. In general, a good Tantalum capacitor will show very
little capacitance variation with temperature, but a ceramic
may not be as good (depending on dielectric type). Aluminum
electrolytics also typically have large temperature variation of
capacitance value.
Equally important to consider is a capacitor's ESR change
with temperature: this is not an issue with ceramics, as their
ESR is extremely low. However, it is very important in Tanta-
lum and aluminum electrolytic capacitors. Both show increas-
ing ESR at colder temperatures, but the increase in aluminum
electrolytic capacitors is so severe they may not be feasible
for some applications (see Capacitor Characteristics Sec-
tion).
CAPACITOR CHARACTERISTICS
CERAMIC: For values of capacitance in the 10 to 100 µF
range, ceramics are usually larger and more costly than tan-
talums but give superior AC performance for bypassing high
frequency noise because of very low ESR (typically less than
10 mΩ). However, some dielectric types do not have good
capacitance characteristics as a function of voltage and tem-
perature.
Z5U and Y5V dielectric ceramics have capacitance that drops
severely with applied voltage. A typical Z5U or Y5V capacitor
can lose 60% of its rated capacitance with half of the rated
FIGURE 2. Maximum Ceramic Output Capacitance vs
Ceramic Input Capacitance
20030985
www.national.com