RFPIC12F675F-I/SS Microchip Technology, RFPIC12F675F-I/SS Datasheet - Page 73

RFPIC12F675F-I/SS
Manufacturer Part Number
RFPIC12F675F-I/SS
Description
IC MCU 1KX14 RF FSK/ASK 20SSOP
Manufacturer
Microchip Technology
Series
PIC®r
Specifications of RFPIC12F675F-I/SS
Package / Case
20-SSOP
Frequency
380MHz ~ 450MHz
Applications
RKE, Security Systems
Modulation Or Protocol
ASK, FSK
Data Rate - Maximum
40 kbps
Power - Output
10dBm
Current - Transmitting
14mA
Data Interface
PCB, Surface Mount
Antenna Connector
PCB, Surface Mount
Memory Size
1024 x 14 words Flash, 128 x 8 Byte EEPROM, 64 x 8 Byte SRAM
Voltage - Supply
2V ~ 5.5V
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 125°C
Processor Series
RFPIC12F
Core
PIC
Data Bus Width
8 bit
Data Ram Size
64 B
Interface Type
USB
Maximum Clock Frequency
20 MHz
Number Of Programmable I/os
6
Number Of Timers
2
Operating Supply Voltage
2 V to 5.5 V
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 85 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
Development Tools By Supplier
ICE2000, DV164102, AC164101, AC164103
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
On-chip Adc
4-ch x 10-bit
Program Memory Type
Flash
Program Memory Size
1.75 KB
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
For Use With
XLT20SS-1 - SOCKET TRANSITION 18DIP 20SSOPAC164103 - MODULE RCVR RFPIC 433MHZAC164101 - MODULE TRANSMITTER RFPIC 433MHZDV164102 - KIT DEV RFPICKIT KIT 1AC124002 - MOD SKT PROMATEII 18SOIC/20SSOP
Features
-
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Other names
Q3188156
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
RFPIC12F675F-I/SS
Manufacturer:
MCP
Quantity:
181
Company:
Part Number:
RFPIC12F675F-I/SS
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP
Quantity:
12 000
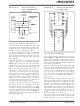
FIGURE 10-14:
10.10 In-Circuit Serial Programming
The rfPIC12F675 microcontrollers can be serially
programmed while in the end application circuit. This is
done with two lines for clock and data, and three lines
for power, ground, and programming voltage.
This allows customers to manufacture boards with
unprogrammed devices, and then program the
microcontroller before shipping the product. This also
allows the most recent firmware or custom firmware to
be programmed.
The device is placed into a Program/Verify mode by
holding the GP0 and GP1 pins low, while raising the
MCLR (V
Specification). GP0 becomes the programming data
and GP1 becomes the programming clock. Both GP0
and GP1 are Schmitt Trigger inputs in this mode.
After RESET, to place the device into Programming/
Verify mode, the program counter (PC) is at location
00h. A 6-bit command is then supplied to the device.
Depending on the command, 14-bits of program data
are then supplied to or from the device, depending on
whether the command was a load or a read. For
complete details of serial programming, please refer to
the Programming Specifications document.
A typical In-Circuit Serial Programming connection is
shown in Figure 10-14. The programming connections
are isolated from conflicting outputs and capacitive
loads by the 3 resistors. The V
may not be required if the pin is configured as GP3. Do
not place sensitive circuitry on the GP3/MCLR pin
without protection since the V
V
2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
DD
External
Connector
Signals
during programming.
Data I/O
CLK
+5V
V
0V
PP
PP
) pin from V
To Normal
Connections
To Normal
Connections
TYPICAL IN-CIRCUIT
SERIAL PROGRAMMING
CONNECTION
IL
to V
PP
DD
IHH
signal goes well above
connection on MCLR
(see Programming
V
V
GP3/MCLR/V
GP1
GP0
V
rfPIC12F675
DD
SS
DD
PP
Preliminary
FIGURE 10-15:
10.11 In-Circuit Debugging
Since in-circuit debugging requires the loss of clock,
data and MCLR pins, MPLAB
an 8-pin microcontroller is not practical. Since the
MPLAB ICE 2000 emulation module leads would be
too long for the RF signals the following debug/emula-
tion strategy is recommended.
Build a prototype board with all your digital, analog, and
RF circuitry. Add an 8 pin DIP socket for the PIC12F675
debugging. Connect the socket as shown in Figure 10-
15. When soldering the rfPIC12F675 down bend up
pins 1-4 and 17-20 so that they do not contact the
board. A PIC12F675 or emulation/debugging develop-
ment tool can be plugged into the socket as in
Figure 10-16.
This test method encourages RF development to start
early, as soon as the firmware can toggle the RF enable
and data lines. The socket can even be left in the final
layout for in-circuit production programming. A simple
method for programming is to solder all the
rfPIC12F675 pins to the board and move the 8-pin DIP
socket to the back side of the board. Then use the 8-pin
standoff from the MPLAB ICE 2000 emulator to
connect the PCB to a programmer such as the Pro
Mate
There is an ICD 2 header inteface board for the
PIC12F675, part number AC162050. This special ICD
module is mounted on the top of a header and its
®
II or PICkit™ 1 as in Figure 10-17.
V
GP5
GP4
GP3
1
2
3
4
DD
rfPIC12F675
PARALLEL DIP SOCKET
FOR EMULATION
®
GP0
GP1
GP2
V
ICD 2 development with
SS
8
7
6
5
DS70091A-page 71