DS1822+ Maxim Integrated Products, DS1822+ Datasheet - Page 5

DS1822+
Manufacturer Part Number
DS1822+
Description
Board Mount Temperature Sensors IC THERMOMETER ECONO DIG
Manufacturer
Maxim Integrated Products
Datasheet
1.DS1822Z.pdf
(21 pages)
Specifications of DS1822+
Temperature Threshold
Programmable
Full Temp Accuracy
+/- 2 C
Package / Case
TO-92
Digital Output - Bus Interface
1-Wire
Digital Output - Number Of Bits
9 bit to 12 bit
Supply Voltage (max)
5.5 V
Supply Voltage (min)
3 V
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 125 C
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 55 C
Output Type
Digital
Supply Current
1.5 mA
Ic Output Type
Digital
Sensing Accuracy Range
± 2°C
Supply Voltage Range
3V To 5.5V
Resolution (bits)
12bit
Sensor Case Style
TO-92
No. Of Pins
3
Accuracy %
2°C
Rohs Compliant
Yes
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
DS1822
OPERATION—ALARM SIGNALING
After the DS1822 performs a temperature conversion, the temperature value is compared to the user-
defined two’s complement alarm trigger values stored in the 1-byte T
and T
registers (see Figure 3).
H
L
The sign bit (S) indicates if the value is positive or negative: for positive numbers S = 0 and for negative
numbers S = 1. The T
and T
registers are NV (EEPROM) so they will retain data when the device is
H
L
powered down. T
and T
can be accessed through bytes 2 and 3 of the scratchpad as explained in the
H
L
MEMORY section of this data sheet.
T
AND T
REGISTER FORMAT Figure 3
H
L
bit 7
bit 6
bit 5
bit 4
bit 3
bit 2
bit 1
bit 0
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
S
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
Only bits 11 through 4 of the temperature register are used in the T
and T
comparison since T
and T
H
L
H
L
are 8-bit registers. If the measured temperature is lower than or equal to T
or higher than or equal to T
,
L
H
an alarm condition exists and an alarm flag is set inside the DS1822. This flag is updated after every
temperature measurement; therefore, if the alarm condition goes away, the flag will be turned off after the
next temperature conversion.
The master device can check the alarm flag status of all DS1822s on the bus by issuing an Alarm Search
[ECh] command. Any DS1822s with a set alarm flag will respond to the command, so the master can
determine exactly which DS1822s have experienced an alarm condition. If an alarm condition exists and
the T
or T
settings have changed, another temperature conversion should be done to validate the alarm
H
L
condition.
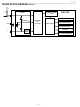
POWERING THE DS1822
The DS1822 can be powered by an external supply on the V
pin, or it can operate in “parasite power”
DD
mode, which allows the DS1822 to function without a local external supply. Parasite power is very useful
for applications that require remote temperature sensing or that are very space constrained. Figure 1
shows the DS1822’s parasite-power control circuitry, which “steals” power from the 1-Wire bus via the
DQ pin when the bus is high. The stolen charge powers the DS1822 while the bus is high, and some of
the charge is stored on the parasite power capacitor (C
) to provide power when the bus is low. When the
PP
DS1822 is used in parasite power mode, the V
pin must be connected to ground.
DD
In parasite power mode, the 1-Wire bus and C
can provide sufficient current to the DS1822 for most
PP
operations as long as the specified timing and voltage requirements are met (refer to the DC
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS and the AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS sections of this
data sheet). However, when the DS1822 is performing temperature conversions or copying data from the
scratchpad memory to EEPROM, the operating current can be as high as 1.5mA. This current can cause
an unacceptable voltage drop across the weak 1-Wire pullup resistor and is more current than can be
supplied by C
. To assure that the DS1822 has sufficient supply current, it is necessary to provide a
PP
strong pullup on the 1-Wire bus whenever temperature conversions are taking place or data is being
copied from the scratchpad to EEPROM. This can be accomplished by using a MOSFET to pull the bus
directly to the rail as shown in Figure 4. The 1-Wire bus must be switched to the strong pullup within
10μs (max) after a Convert T [44h] or Copy Scratchpad [48h] command is issued, and the bus must be
held high by the pullup for the duration of the conversion (t
) or data transfer (t
= 10ms). No other
conv
wr
activity can take place on the 1-Wire bus while the pullup is enabled.
The DS1822 can also be powered by the conventional method of connecting an external power supply to
the V
pin, as shown in Figure 5. The advantage of this method is that the MOSFET pullup is not
DD
required, and the 1-Wire bus is free to carry other traffic during the temperature conversion time.
5 of 21