FAN3214TMX Fairchild Semiconductor, FAN3214TMX Datasheet - Page 11

FAN3214TMX
Manufacturer Part Number
FAN3214TMX
Description
IC GATE DRIVER DUAL 4A 8-SOIC
Manufacturer
Fairchild Semiconductor
Type
Dual-4A, High-Speed, Low-Side Gate Driverr
Datasheet
1.FAN3213TMX.pdf
(18 pages)
Specifications of FAN3214TMX
Product
MOSFET Gate Drivers
Rise Time
12 ns
Fall Time
9 ns
Propagation Delay Time
17 ns
Supply Voltage (max)
20 V
Supply Voltage (min)
- 0.3 V
Supply Current
0.7 mA
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 125 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
Package / Case
SOIC-8
Bridge Type
Full Bridge
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
Number Of Drivers
2
Number Of Outputs
2
Output Current
5 A
Output Voltage
20.3 V
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
FAN3214TMX
Manufacturer:
AD
Quantity:
1 000
Part Number:
FAN3214TMX
Manufacturer:
FAIRCHILD/仙童
Quantity:
20 000
© 2008 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation
FAN3213 / FAN3214 • Rev. 1.0.2
Applications Information
Input Thresholds
The FAN3213 and the FAN3214 drivers consist of two
identical channels that may be used independently at
rated current or connected in parallel to double the
individual current capacity.
The input thresholds meet industry-standard TTL-logic
thresholds independent of the V
a hysteresis voltage of approximately 0.4V. These levels
permit the inputs to be driven from a range of input logic
signal levels for which a voltage over 2V is considered
logic HIGH. The driving signal for the TTL inputs should
have fast rising and falling edges with a slew rate of
6V/µs or faster, so a rise time from 0 to 3.3V should be
550ns or less. With reduced slew rate, circuit noise
could cause the driver input voltage to exceed the
hysteresis voltage and retrigger the driver input, causing
erratic operation.
Static Supply Current
In the I
shown in Figure 8 and Figure 9, each curve is produced
with both inputs floating and both outputs LOW to
indicate the lowest static I
additional current flows through the 100k resistors on
the inputs and outputs shown in the block diagram of
each part (see Figure 4 and Figure 5). In these cases,
the actual static I
the curves plus this additional current.
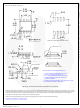
MillerDrive™ Gate Drive Technology
FAN3213 and FAN3214 gate drivers incorporate the
MillerDrive™ architecture shown in Figure 28. For the
output stage, a combination of bipolar and MOS devices
provide large currents over a wide range of supply
voltage and temperature variations. The bipolar devices
carry the bulk of the current as OUT swings between 1/3
to 2/3 V
HIGH or LOW rail.
The purpose of the MillerDrive™ architecture is to speed
up switching by providing high current during the Miller
plateau region when the gate-drain capacitance of the
MOSFET is being charged or discharged as part of the
turn-on / turn-off process.
For applications with zero voltage switching during the
MOSFET turn-on or turn-off interval, the driver supplies
high peak current for fast switching even though the
Miller plateau is not present. This situation often occurs
in synchronous rectifier applications because the body
diode is generally conducting before the MOSFET is
switched ON.
The output pin slew rate is determined by V
and the load on the output. It is not user adjustable, but
a series resistor can be added if a slower rise or fall time
at the MOSFET gate is needed.
DD
DD
and the MOS devices pull the output to the
(static) typical performance characteristics
DD
current is the value obtained from
DD
current. For other states,
DD
voltage, and there is
DD
voltage
11
Under-Voltage Lockout
The FAN321x startup logic is optimized to drive ground-
referenced N-channel MOSFETs with an under-voltage
lockout (UVLO) function to ensure that the IC starts up
in an orderly fashion. When V
3.9V operational level, this circuit holds the output LOW,
regardless of the status of the input pins. After the part
is active, the supply voltage must drop 0.2V before the
part shuts down. This hysteresis helps prevent chatter
when low V
power switching. This configuration is not suitable for
driving high-side P-channel MOSFETs because the low
output voltage of the driver would turn the P-channel
MOSFET on with V
V
To enable this IC to turn a device ON quickly, a local
high-frequency bypass capacitor, C
and ESL should be connected between the VDD and
GND pins with minimal trace length. This capacitor is in
addition to bulk electrolytic capacitance of 10µF to 47µF
commonly found on driver and controller bias circuits.
A typical criterion for choosing the value of C
keep the ripple voltage on the V
is often achieved with a value ≥ 20 times the equivalent
load capacitance C
Ceramic capacitors of 0.1µF to 1µF or larger are
common choices, as are dielectrics, such as X5R and
X7R, with good temperature characteristics and high
pulse current capability.
If circuit noise affects normal operation, the value of
C
C
larger value, based on equivalent load capacitance, and
the other a smaller value, such as 1-10nF mounted
closest to the VDD and GND pins to carry the higher-
frequency components of the current pulses. The
bypass capacitor must provide the pulsed current from
both of the driver channels and, if the drivers are
switching simultaneously, the combined peak current
sourced from the C
a single channel is switching.
BYP
BYP
DD
Figure 28. MillerDrive™ Output Architecture
Bypass Capacitor Guidelines
may be split into two capacitors. One should be a
may be increased, to 50-100 times the C
DD
supply voltages have noise from the
DD
BYP
EQV
below 3.9V.
would be twice as large as when
, defined here as Q
DD
DD
is rising, yet below the
supply to ≤ 5%. This
BYP
, with low ESR
www.fairchildsemi.com
GATE
BYP
EQV
/V
is to
, or
DD
.