LM13700N National Semiconductor, LM13700N Datasheet - Page 7
LM13700N
Manufacturer Part Number
LM13700N
Description
Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp) IC
Manufacturer
National Semiconductor
Specifications of LM13700N
No. Of Amplifiers
2
Slew Rate
50V/µs
No. Of Pins
16
Peak Reflow Compatible (260 C)
No
Input Bias Current
1µA
Supply Voltage
36V
Output Current
20mA
Input Offset Voltage Max
4mV
Gain
2dB
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
LM13700N
Manufacturer:
NS/国半
Quantity:
20 000
Typical Performance Characteristics
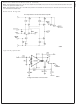
Circuit Description
The differential transistor pair Q
ductance stage in that the ratio of their collector currents is
defined by the differential input voltage according to the
transfer function:
where V
mately 26 mV at 25˚C and I
of transistors Q
Q
Transistors Q
which forces the sum of currents I
where I
pin.
For small differential input voltages the ratio of I
approaches unity and the Taylor series of the In function can
be approximated as:
Collector currents I
and it is necessary to subtract one current from the other.
The remaining transistors and diodes form three current
mirrors that produce an output current equal to I
thus:
The term in brackets is then the transconductance of the
amplifier and is proportional to I
12
and Q
ABC
IN
13
is the differential input voltage, kT/q is approxi-
is the amplifier bias current applied to the gain
, all transistors and diodes are identical in size.
1
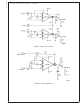
Leakage Current Test Circuit
5
and Q
and Q
4
and I
2
I
4
with Diode D
4
5
respectively. With the exception of
+ I
are not very useful by themselves
5
5
and I
= I
ABC
4
ABC
4
4
and Q
are the collector currents
.
and I
1
form a current mirror
5
5
form a transcon-
to equal I
5
4
minus I
ABC
and I
00798106
:
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
5
4
7
(Continued)
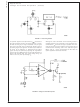
Linearizing Diodes
For differential voltages greater than a few millivolts, Equa-
tion (3) becomes less valid and the transconductance be-
comes increasingly nonlinear. Figure 1 demonstrates how
the internal diodes can linearize the transfer function of the
amplifier. For convenience assume the diodes are biased
with current sources and the input signal is in the form of
current I
ence is I
Since the diodes and the input transistors have identical
geometries and are subject to similar voltages and tempera-
tures, the following is true:
Notice that in deriving Equation (6) no approximations have
been made and there are no temperature-dependent terms.
The limitations are that the signal current not exceed I
and that the diodes be biased with currents. In practice,
replacing the current sources with resistors will generate
insignificant errors.
Applications
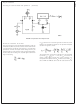
Voltage Controlled Amplifiers
Figure 2 shows how the linearizing diodes can be used in a
voltage-controlled amplifier. To understand the input biasing,
it is best to consider the 13 kΩ resistor as a current source
and use a Thevenin equivalent circuit as shown in Figure 3.
This circuit is similar to Figure 1 and operates the same. The
potentiometer in Figure 2 is adjusted to minimize the effects
of the control signal at the output.
S
OUT
Differential Input Current Test Circuit
. Since the sum of I
, currents I
4
and I
4
5
and I
can be written as follows:
5
is I
ABC
and the differ-
www.national.com
00798107
D
(6)
/2