EVAL-AD5254EBZ Analog Devices Inc, EVAL-AD5254EBZ Datasheet - Page 21

EVAL-AD5254EBZ
Manufacturer Part Number
EVAL-AD5254EBZ
Description
Evaluation Board
Manufacturer
Analog Devices Inc
Datasheet
1.AD5254BRUZ100.pdf
(32 pages)
Specifications of EVAL-AD5254EBZ
Main Purpose
Digital Potentiometer
Utilized Ic / Part
AD5245
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Secondary Attributes
-
Embedded
-
Primary Attributes
-
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
THEORY OF OPERATION
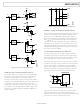
The AD5253/AD5254 are quad-channel digital potentiometers
in 1 kΩ, 10 kΩ, 50 kΩ, or 100 kΩ that allow 64/256 linear resis-
tance step adjustments. The AD5253/AD5254 employ double-
gate CMOS EEPROM technology, which allows resistance
settings and user-defined data to be stored in the EEMEM
registers. The EEMEM is nonvolatile, such that settings remain
when power is removed. The RDAC wiper settings are restored
from the nonvolatile memory settings during device power-up
and can also be restored at any time during operation.
The AD5253/AD5254 resistor wiper positions are determined
by the RDAC register contents. The RDAC register acts like a
scratch-pad register, allowing unlimited changes of resistance
settings. RDAC register contents can be changed using the
device’s serial I
the commands to program the RDAC registers are discussed in
the I
The four RDAC registers have corresponding EEMEM memory
locations that provide nonvolatile storage of resistor wiper
position settings. The AD5253/AD5254 provide commands to
store the RDAC register contents to their respective EEMEM
memory locations. During subsequent power-on sequences, the
RDAC registers are automatically loaded with the stored value.
Whenever the EEMEM write operation is enabled, the device
activates the internal charge pump and raises the EEMEM cell
gate bias voltage to a high level; this essentially erases the
current content in the EEMEM register and allows subsequent
storage of the new content. Saving data to an EEMEM register
consumes about 35 mA of current and lasts approximately
26 ms. Because of charge-pump operation, all RDAC channels
may experience noise coupling during the EEMEM writing
operation.
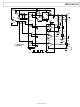
The EEMEM restore time in power-up or during operation is
about 300 μs. Note that the power-up EEMEM refresh time
depends on how fast V
supply voltage decoupling capacitors limit the EEMEM restore
time during power-up. For example, Figure 20 shows the
power-up profile of the V
capacitors and the applied power is a digital signal. The device
initially resets the RDACs to midscale before restoring the
EEMEM contents. The omission of the decoupling capacitors
should only be considered when the fast restoring time is
absolutely needed in the application. In addition, users should
issue a NOP Command 0 immediately after using Command 1
to restore the EEMEM setting to RDAC, thereby minimizing
supply current dissipation. Reading user data directly from
EEMEM does not require a similar NOP command execution.
In addition to the movement of data between RDAC and
EEMEM registers, the AD5253/AD5254 provide other shortcut
commands that facilitate programming, as shown in Table 11.
2
C Interface section.
2
C interface. The format of the data-words and
DD
reaches its final value. As a result, any
DD
where there is no decoupling
Rev. B | Page 21 of 32
Table 11. Quick Commands
Command
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12 to 15
LINEAR INCREMENT/DECREMENT COMMANDS
The increment and decrement commands (10, 11, 5, and 6) are
useful for linear step-adjustment applications. These commands
simplify microcontroller software coding by allowing the
controller to send just an increment or decrement command to
the AD5253/AD5254. The adjustments can be directed to a
single RDAC or to all four RDACs.
±6 dB ADJUSTMENTS
(DOUBLING/HALVING WIPER SETTING)
The AD5253/AD5254 accommodate ±6 dB adjustments of the
RDAC wiper positions by shifting the register contents to left/
right for increment/decrement operations, respectively. Com-
mand 3, Command 4, Command 8, and Command 9 can be
used to increment or decrement the wiper positions in 6 dB
steps synchronously or asynchronously.
Incrementing the wiper position by +6 dB essentially doubles
the RDAC register value, whereas decrementing the wiper
position by –6 dB halves the register content. Internally, the
AD5253/AD5254 use shift registers to shift the bits left and
right to achieve a ±6 dB increment or decrement. The
maximum number of adjustments is nine and eight steps for
incrementing from zero scale and decrementing from full scale,
respectively. These functions are useful for various audio/video
level adjustments, especially for white LED brightness settings
in which human visual responses are more sensitive to large
adjustments than to small adjustments.
Description
NOP.
Restore EEMEM content to RDAC. User should
issue NOP immediately after this command to
conserve power.
Store RDAC register setting to EEMEM.
Decrement RDAC 6 dB (shift data bits right).
Decrement all RDACs 6 dB (shift all data bits right).
Decrement RDAC one step.
Decrement all RDACs one step.
Reset EEMEM contents to all RDACs.
Increment RDAC 6 dB (shift data bits left).
Increment all RDACs 6 dB (shift all data bits left).
Increment RDAC one step.
Increment all RDACs one step.
Reserved.
AD5253/AD5254