ETC5057N/H STMicroelectronics, ETC5057N/H Datasheet - Page 4

ETC5057N/H
Manufacturer Part Number
ETC5057N/H
Description
Telecom ICs Interfc CODEC Filter
Manufacturer
STMicroelectronics
Type
Telecom ICs - Variousr
Datasheet
1.ETC5054D-XHTR.pdf
(18 pages)
Specifications of ETC5057N/H
Operating Supply Voltage
7 V
Supply Current
10 uA
Operating Temperature Range
- 25 C to + 125 C
Mounting Style
Through Hole
Operating Frequency
2.048 MHz
Package / Case
PDIP-16
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
ETC5054 - ETC5057
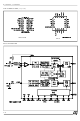
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
POWER-UP
When power is first applied, power-on reset cir-
cuitry initializes the device and places it into
the power-down mode. All non-essential circuits
are deactivated and the D
put in high impedance states. To power-up the
device, a logical low level or clock must be ap-
plied to the MCLK
pulses must be present. Thus, 2 power-down
control modes are available. The first is to pull the
MCLK
both FS
device will power-down approximately 2 ms after
the last FS
the first FS
data output, D
state until the second FS
SYNCHRONOUS OPERATION
For synchronous operation, the same master
clock and bit clock should be used for both the
transmit and receive directions. In this mode, a
clock must be applied to MCLK
MCLK
control. A low level on MCLK
the device and a high level powers down the de-
vice. In either case, MCLK
the master clock for both the transmit and receive
circuits. A bit clock must also be applied to BCLK
and the BCLK
proper internal divider for a master clock of 1.536
MHz, 1.544 MHz or 2.048 MHz. For 1.544 MHz
operation, the device automatically compensates
for the 193rd clock pulse each frame. With a fixed
level on the BCLK
selected as the bit clock for both the transmit and
receive directions. Table 1 indicates the frequen-
cies of operation which can be selected, depend-
ing on the state of BCLK
chronous mode, the bit clock, BCLK
from 64 kHz to 2.048 MHz, but must be synchro-
nous with MCLK
Each FS
the PCM data from the previous encode cycle is
shifted out of the enabled D
tive edge of BCLK
Table 1: Selection of Master Clock Frequencies.
4/18
Clocked
0
1 (or open circuit)
BCLK
R
R
/PDN pin high ; the alternative is to hold
/PDN pin can be used as a power-down
R
X
X
/CLKSEL
and FS
X
X
pulse begins the encoding cycle and
or FS
or FS
X
R
, will remain in the high impedance
/CKSEL can be used to select the
X
.
R
R
R
X
R
R
/PDN pin and FS
. After 8 bit clock periods, the
pulse. Power-up will occur on
inputs continuously low. The
/CLKSEL pin, BCLK
pulse. The TRI-STATE PCM
2.048 MHz
1.536 MHz or
1.544 MHz
2.048 MHz
ETC5057
Master Clock Frequency
X
X
R
pulse.
/CLKSEL. In this syn-
and VF
X
X
will be selected as
output on the posi-
Selected
R
/PDN powers up
R
O outputs are
1.536 MHz or
1.536 MHz or
X
1.544 MHz
2.048 MHz
1.544 MHz
X
ETC5054
and/or FS
X
, may be
and the
X
will be
R
X
TRI-STATE D
pedance state. With and FS
latched via the D
BCLK
be synchronous with MCLK
ASYNCHRONOUS OPERATION
For asynchronous operation, separate transmit
and receive clocks may be applied, MCLK
MCLK
1.536 MHz, 1.544 MHz for the ETC5054, and
need not be synchronous. For best transmission
performance, however, MCLK
chronous with MCLK
by
MCLK
MCLK
description). For 1.544 MHz operation, the device
automatically compensates for the 193rd clock
pulse each frame. FS
and must be synchronous with MCLK
BCLK
be synchronous with BCLK
clock, the logic levels shown in table 1 are not
valid in asynchronous mode. BCLK
may operate from 64 kHz to 2.048 MHz.
SHORT FRAME SYNC OPERATION
The device can utilize either a short frame sync
pulse or a long frame sync pulse. Upon power in-
itialization, the device assumes a short frame
mode. In this mode, both frame sync pulses, FS
and FS
timing relationships specified in figure 2. With FS
high during a falling edge of BCLK
ing edge of BCLK
output buffer, which will output the sign bit. The
following seven rising edges clock out the remain-
ing seven bits, and the next falling edge disables
the D
of BCLK
next falling edge of BCLK
The following seven falling edges latch in the
seven remaining bits. Both devices may utilize the
short frame sync pulse in synchronous or asyn-
chronous operating mode.
LONG FRAME SYNC OPERATION
To use the long frame mode, both the frame sync
pulses, FS
clock periods long, with timing relationships speci-
fied in figure 3. Based on the transmit frame sync,
FS
frame sync pulses are being used. For 64 kHz op-
eration, the frame sync pulse must be kept low for
a minimum of 160 ns (see fig. 1). The D
STATE output buffer is enabled with the rising
edge of FS
ever comes later, and the first bit clocked out is
the sign bit. The following seven BCLK
X
, the device will sense whether short or long
applying
X
X
X
R
R
X
. FS
output. With FS
/PDN pin. This will automatically connect
R
(or BCLK
must be 2.048 MHz for the ETC5057, or
to all internal MCLK
, must be one bit clock period long, with
R
X
R
X
(BCLK
and FS
starts each decoding cycle and must
or the rising edge of BCLK
X
only
output is returned to a high im-
R
R
X
X
if running). FS
input on the negative edge of
R
X
in synchronous mode), the
enables the D
X
, must be three or more bit
, which is easily achieved
static
R
starts each encoding cycle
high during a falling edge
R
X/R
latches in the sign bit.
R
R
R
. BCLK
.
pulse, PCM data is
logic levels to the
R
functions (see pin
X
should be syn-
and FS
X
X
X
R
the next ris-
and BCLK
TRI-STATE
must be a
X
, which-
X
R
X
X
X
rising
must
TRI-
and
and
R
X
X