ISP1506BBS,557 NXP Semiconductors, ISP1506BBS,557 Datasheet

ISP1506BBS,557
Specifications of ISP1506BBS,557
Related parts for ISP1506BBS,557
ISP1506BBS,557 Summary of contents
Page 1
IMPORTANT NOTICE Dear customer from August 2 2008, the wireless operations of NXP have moved to a new company, ST-NXP Wireless result, the following changes are applicable to the attached document. ● Company name - NXP ...
Page 2
ISP1506A; ISP1506B ULPI Hi-Speed USB OTG transceiver Rev. 02 — 28 August 2008 1. General description The ISP1506 is a Universal Serial Bus (USB) On-The-Go (OTG) transceiver that is fully compliant with Supplement to the USB 2.0 Specification Rev. 1.3” ...
Page 3
... NXP Semiconductors N Integrated 5 V charge pump; also supports external charge pump switch N Complete control over bus resistors N Data line and V N Integrated V N Integrated cable (ID) detector I Highly optimized ULPI compliant N 60 MHz, 8-bit interface between the core and the transceiver N Supports 4-bit dual-edge data bus N Supports 60 MHz output clock confi ...
Page 4
... NXP Semiconductors I Set-Top Box (STB) I Video camera 4. Ordering information Table 1. Ordering information Part Type number Marking Crystal or clock frequency [1] ISP1506ABS 06A 19.2 MHz [1] ISP1506BBS 06B 26 MHz [1] The package marking is the first line of text on the IC package and can be used for IC identification. ...
Page 5
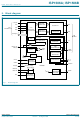
... NXP Semiconductors 5. Block diagram 19 CLOCK 17 STP 16 DIR ULPI INTERFACE 18 NXT 20, 22, 23 DATA[3:0] 14 RESET_N/ PSW_N global clocks 12 XTAL1 13 XTAL2 CC(I/O) 11 REG3V3 15 REG1V8 Fig 1. Block diagram ISP1506A_ISP1506B_2 Product data sheet USB DATA SERIALIZER ULPI INTERFACE CONTROLLER USB DATA DESERIALIZER V valid external BUS REGISTER ...
Page 6
... NXP Semiconductors 6. Pinning information 6.1 Pinning Fig 2. 6.2 Pin description Table 2. Pin description [1][2][3] [4] Symbol Pin Type CC(I/O) RREF CPGND 6 P C_B 7 AI/O C_A 8 AI /FAULT 10 AI/O BUS REG3V3 11 P XTAL1 12 AI XTAL2 13 AO ISP1506A_ISP1506B_2 Product data sheet ...
Page 7
... NXP Semiconductors Table 2. Pin description …continued [1][2][3] [4] Symbol Pin Type RESET_N/ 14 I/O PSW_N REG1V8 15 P DIR 16 O STP 17 I NXT 18 O CLOCK 19 O DATA3 20 I CC(I/O) DATA2 22 I/O DATA1 23 I/O DATA0 24 I/O GND die P pad [1] A detailed description of these pins can be found in [2] Symbol names ending with an underscore N (for example, NAME_N) indicate active LOW signals ...
Page 8
... NXP Semiconductors 7. Functional description 7.1 ULPI interface controller The ISP1506 provides an 8-pin interface that is compliant with Interface (ULPI) Specification Rev. The ULPI interface controller provides the following functions: • ULPI compliant and register set • Allows full control over the USB peripheral, host and OTG functionality • ...
Page 9
... NXP Semiconductors • Squelch circuit to detect high-speed bus activity • High-speed disconnect detector • 45 • 1.5 k pull-up resistor on DP for full-speed peripheral mode • bus terminations on DP and DM for host and OTG modes For details on controlling resistor settings, see 7.4 Voltage regulator The ISP1506 contains a built-in voltage regulator that conditions the V inside the ISP1506 ...
Page 10
... NXP Semiconductors • Charge pump to provide 5 V power on V power from the ISP1506 V 7.6.1 ID detector The ID detector detects which end of the micro-USB cable is plugged in. The detector must first be enabled by setting the ID_PULLUP register bit to logic 1. If the ISP1506 senses a value on ID that is different from the previously reported value, an RXCMD status update will be sent to the USB link interrupt will be asserted. • ...
Page 11
... NXP Semiconductors which also shows a typical OTG V amount of current drive required. If the internal charge pump is not used, the C capacitor is not required. For details on the C_A and C_B pins, see Fig 3. 7.7 Band gap reference voltage The band gap circuit provides a stable internal voltage reference to bias the analog circuitry ...
Page 12
... NXP Semiconductors • STP 7.9.3 RREF Resistor reference analog I/O pin. A resistor, R and GND, as shown in biases internal analog circuitry. Less accurate resistors cannot be used and will render the ISP1506 unusable. 7.9.4 DP and DM DP (data plus) and DM (data minus) are USB differential data pins. These must be connected to the D+ and D pins of the USB receptacle ...
Page 13
... NXP Semiconductors Table 3. C cp(C_A)-(C_B 270 nF 7.9 the main input supply voltage for the ISP1506. Decoupling capacitors are CC recommended. For details, see 7.9.9 V /FAULT BUS This pin provides two options for V this pin must be connected to ground. 7.9.9.1 V BUS This pin acts as an input to V pump, and SRP charge and discharge resistors ...
Page 14
... NXP Semiconductors 7.9.12 RESET_N/PSW_N This pin provides two optional functions. If neither function is used, this pin must be connected to V 7.9.12.1 RESET_N An active LOW asynchronous reset pin that resets all circuits in the ISP1506. The ISP1506 contains an internal power-on reset circuit, and therefore using the RESET_N pin is optional ...
Page 15
... NXP Semiconductors 7.9.15 NXT ULPI next data output pin. The ISP1506 holds NXT at LOW by default. When DIR is LOW and the link is sending data to the ISP1506, NXT will be asserted to notify the link to provide the next data byte. When DIR is at HIGH and the ISP1506 is sending data to the link, NXT will be asserted to notify the link that another valid byte is on the bus ...
Page 16
... NXP Semiconductors 8. Modes of operation 8.1 ULPI modes The ISP1506 ULPI bus can be programmed to operate in three modes. Each mode reconfigures the signals on the data bus as described in the following subsections. Setting more than one mode will lead to undefined behavior. 8.1.1 Synchronous mode This is default mode ...
Page 17
... NXP Semiconductors Table 4. ULPI signal description Signal name Direction on Signal description ISP1506 DIR O Direction: Controls the direction of data bus DATA[3:0]. In synchronous mode, the ISP1506 drives DIR to LOW by default, making the data bus an input so that the ISP1506 can listen for TXCMDs from the link. The ISP1506 drives DIR to HIGH only when it has data for the link ...
Page 18
... NXP Semiconductors 8.1.3 3-pin full-speed or low-speed serial mode If the link requires a 3-pin serial interface to transmit and receive full-speed or low-speed USB data, it can set the ISP1506 to 3-pin serial mode. In 3-pin serial mode, the data bus definition changes to that shown in 3PIN_FSLS_SERIAL bit in the Interface Control register to logic 1. To exit 3-pin serial mode, the link asserts STP ...
Page 19
... NXP Semiconductors Table 7. Operating states and their corresponding resistor settings Signaling mode Register settings XCVR SELECT [1:0] General settings 3-state drivers XXb Power-up or 01b V < V BUS B_SESS_END Host settings Host chirp 00b Host high-speed 00b Host full-speed X1b Host high-speed or 01b ...
Page 20
... NXP Semiconductors Table 7. Operating states and their corresponding resistor settings Signaling mode Register settings XCVR SELECT [1:0] OTG device 01b peripheral high-speed and full-speed suspend OTG device 01b peripheral high-speed and full-speed resume OTG device 00b peripheral Test J or Test K ISP1506A_ISP1506B_2 ...
Page 21
... NXP Semiconductors 9. Protocol description The following subsections describe the protocol for using the ISP1506. Remark: In all figures, the ULPI data is shown in a generic form and not as nibbles on the rising and falling edges of the clock. 9.1 ULPI references The ISP1506 provides an 8-pin ULPI interface to communicate with the link highly recommended that you read Rev. 1.1” ...
Page 22
... NXP Semiconductors completed. After every reset, an RXCMD is sent to the link to update USB status information. After this sequence, the ULPI bus is ready for use and the link can start USB operations. When the internal PLL is stable, the ISP1506 will drive a 60 MHz clock out from the CLOCK pin when DIR deasserts ...
Page 23
... NXP Semiconductors CC(I/O) REG1V8 t PWRUP internal REG1V8 detector internal POR XTAL1 CLOCK DATA[3:0] DIR STP NXT and V are applied to the ISP1506. The ISP1506 regulator starts to turn on. CC CC(I/ ULPI pads detect REG1V8 rising above the REG1V8 regulator threshold and are not in 3-state. These pads may drive either LOW or HIGH recommended that the link ignores the ULPI pins status during The POR threshold is reached and a POR pulse is generated. After the POR pulse, ULPI pins are driven to a defi ...
Page 24
... NXP Semiconductors The interface protect feature prevents unwanted activity of the ISP1506 whenever the ULPI interface is not correctly driven by the link. For example, when the link powers up more slowly than the ISP1506. The interface protect feature can be disabled by setting the INTF_PROT_DIS bit to logic 1. ...
Page 25
... NXP Semiconductors Table 8. DRV_VBUS 9.4.2 Fault detection The ISP1506 supports external V indicator signal. The indicator signal must be connected to the FAULT pin. To enable the ISP1506 to monitor the digital fault input, the link must set the USE_EXT_VBUS_IND bit in the OTG Control register and the IND_PASSTHRU bit in the Interface Control register to logic 1 ...
Page 26
... NXP Semiconductors 9.5.2 RXCMD The ISP1506 communicates status information to the link by asserting DIR and sending an RXCMD byte on the data bus. The RXCMD data byte format is given in The ISP1506 will automatically send an RXCMD whenever there is a change in any of the RXCMD data fields. The link must be able to accept an RXCMD at any time; including single RXCMDs, back-to-back RXCMDs, and RXCMDs at any time during USB receive packets when NXT is LOW ...
Page 27
... NXP Semiconductors Table 11. LINESTATE[1:0] encoding for upstream facing ports: peripheral [1] DP_PULLDOWN = 0. Mode Full-speed XCVRSELECT[1:0] 01, 11 TERMSELECT 1 LINESTATE[1:0] 00 SE0 01 FS-J 10 FS-K 11 SE1 [1] !squelch indicates inactive squelch. !HS_Differential_Receiver_Output indicates inactive HS_Differential_Receiver_Output. Table 12. LINESTATE[1:0] encoding for downstream facing ports: host DP_PULLDOWN and DM_PULLDOWN = 1. Mode ...
Page 28
... NXP Semiconductors V /FAULT BUS IND_COMPL USE_EXT_VBUS_IND, IND_PASSTHRU Fig 9. RXCMD A_VBUS_VLD indicator source 9.5.2.3 Using and selecting the V The V BUS link whenever there is a change in the V must first enable the corresponding interrupts in the USB Interrupt Enable Rising Edge and USB Interrupt Enable Falling Edge registers. ...
Page 29
... NXP Semiconductors OTG devices: provide a minimum there is no need for an overcurrent detection circuit because the internal A_VBUS_VLD comparator is sufficient. If the OTG A-device provides more than 100 overcurrent detector must be used and The OTG A-device also uses SESS_VLD to detect when an OTG B-device is initiating V pulsing SRP ...
Page 30
... NXP Semiconductors 9.6 Register read and write operations Figure 10 addressing and extended addressing register operations. Extended register addressing is optional for links. Note that register operations will be aborted if the ISP1506 unexpectedly asserts DIR during the operation. When a register operation is aborted, the link must retry until successful. For more information on register operations, refer to Pin Interface (ULPI) Specifi ...
Page 31
... NXP Semiconductors than 7 ms after reset time T up its clock within 5.6 ms, leaving 200 s for the link to start transmitting the Chirp K, and 1.2 ms for the Chirp K to complete (worst case with 10 % slow clock). b. Host chirp: If the host does not detect the peripheral chirp, it must continue asserting SE0 until the end of reset ...
Page 32
... NXP Semiconductors USB reset T 0 TXCMD (REGW) SE0 DATA [ 3:0 ] DIR STP NXT 01 (FS) XCVR SELECT TERM SELECT 00 (normal) OP MODE SE0 (00b) J (01b) LINE STATE TXCMD (REGW) SE0 DATA [ 3:0 ] DIR STP NXT 01 (FS) XCVR SELECT TERM SELECT 00 (normal) OP MODE J (01b) ...
Page 33
... NXP Semiconductors 9.8 USB packet transmit and receive An example of a packet transmit and receive is shown in packets, refer to link sends TXCMD CLOCK DATA [ 3:0 ] TXCMD DIR STP NXT Fig 12. Example of using the ISP1506 to transmit and receive USB data 9.8.1 USB packet timing 9 ...
Page 34
... NXP Semiconductors Table 17. Link decision times Packet sequence High-speed link delay Transmit-Transmit (host only) Receive-Transmit (host or peripheral) Receive-Receive 1 (peripheral only) Transmit-Receive 92 (host or peripheral DATA DM CLOCK DATA [3:0] DIR STP NXT TX end delay (two to five clocks) Fig 13. High-speed transmit-to-transmit packet timing ISP1506A_ISP1506B_2 ...
Page 35
... NXP Semiconductors DP or DATA EOP DM CLOCK DATA [3: DIR STP NXT RX end delay (three to eight clocks) Fig 14. High-speed receive-to-transmit packet timing 9.9 Preamble Preamble packets are headers to low-speed packets that must travel over a full-speed bus, between a host and a hub. To enter preamble mode, the link sets XCVRSELECT[1:0] = 11b in the Function Control register ...
Page 36
... NXP Semiconductors CLOCK DATA[3: Fig 15. Preamble sequence 9.10 USB suspend and resume 9.10.1 Full-speed or low-speed host-initiated suspend and resume Figure 16 suspend and sometime later initiates resume signaling to wake up the downstream peripheral. Note that LINESTATE updates. The sequence of events for a host and a peripheral, both with ISP1506 follows. ...
Page 37
... NXP Semiconductors idle DATA [ 3:0 ] DIR STP NXT OPMODE 00b LINE J STATE CLOCK TXCMD (REGW) DATA [ 3:0 ] DIR STP NXT OPMODE SUSPENDM LINE STATE DP DM Timing is not to scale. Fig 16. Full-speed suspend and resume 9.10.2 High-speed suspend and resume Figure 17 suspend and then initiates resume signaling. The high-speed peripheral will wake up and return to high-speed operations ...
Page 38
... NXP Semiconductors The sequence of events related to a host and a peripheral, both with ISP1506 follows. 1. High-speed idle: Initially, the host and the peripheral are idle. The host has its 15 k pull-down resistors enabled (DP_PULLDOWN and DM_PULLDOWN are set to 1b) and Full-speed suspend: When the peripheral sees no bus activity for 3 ms, it enters the suspend state ...
Page 39
... NXP Semiconductors HS idle TXCMD (REGW) DATA [ 3:0 ] DIR STP NXT XCVR 00b SELECT TERM SELECT OP MODE !squelch squelch (01b) (00b) LINE STATE CLOCK TXCMD (REGW) DATA [ 3:0 ] DIR STP NXT XCVR 00b SELECT TERM SELECT OPMODE SUSPENDM !squelch squelch (01b) (00b) ...
Page 40
... NXP Semiconductors 9.10.3 Remote wake-up The ISP1506 supports peripherals that initiate remote wake-up resume. When placed into USB suspend, the peripheral link remembers at what speed it was originally operating. Depending on the original speed, the link follows one of the protocols detailed here. In Figure 18, timing is not to scale, and not all RXCMD LINESTATE updates are shown ...
Page 41
... NXP Semiconductors LINESTATE DATA [ 3:0 ] DIR STP NXT XCVR SELECT TERM SELECT OP MODE TXCMD LINESTATE REGW DATA [ 3:0 ] DIR STP NXT XCVR SELECT TERM SELECT OP MODE Timing is not to scale. Fig 18. Remote wake-up from low-power mode 9.11 No automatic SYNC and EOP generation (optional) This setting allows the link to turn off the automatic SYNC and EOP generation, and must be used for high-speed packets only ...
Page 42
... NXP Semiconductors PHY will not transmit any EOP. The ISP1506 will also detect if the PID byte is A5h, indicating an SOF packet, and automatically send a long EOP when STP is asserted. To transmit chirp and resume signaling, the link must set OPMODE to 10b. CLOCK TXCMD ...
Page 43
... NXP Semiconductors 9.12.1 OTG charge pump A description of the charge pump is given in configured as an A-device, it can provide the V Control of the charge pump is described in 9.12.2 OTG comparators The ISP1506 provides comparators that conform to USB 2.0 Specification Rev. 1.3” and V B_SESS_END ...
Page 44
... NXP Semiconductors SYNC DATA0 (TX_ENABLE) DATA1 (DAT) DATA2 (SE0 Fig 20. Example of transmit followed by receive in 3-pin serial mode 9.14 Aborting transfers The ISP1506 supports aborting transfers on the ULPI bus. For details, refer to “UTMI+ Low Pin Interface (ULPI) Specification Rev. 9.15 Avoiding contention on the ULPI data bus Because the ULPI data bus is bidirectional, avoid situations in which both the link and the PHY simultaneously drive the data bus ...
Page 45
... NXP Semiconductors 10. Register map Table 18. Immediate register set overview Field name Vendor ID Low register Vendor ID High register Product ID Low register Product ID High register Function Control register Interface Control register OTG Control register USB Interrupt Enable Rising Edge register USB Interrupt Enable Falling Edge ...
Page 46
... NXP Semiconductors 10.1 Immediate register set 10.1.1 Vendor ID and Product ID registers 10.1.1.1 Vendor ID Low register Table 20 Table 20. Vendor ID Low register (address R = 00h) bit description Bit Symbol Access VENDOR_ID_ R LOW[7:0] 10.1.1.2 Vendor ID High register The bit description of the register is given in Table 21. ...
Page 47
... NXP Semiconductors Table 25. Function Control register (address R = 04h to 06h 04h 05h 06h) bit description Bit Symbol Description 7 - reserved 6 SUSPENDM Suspend LOW: Active LOW PHY suspend. Places the PHY into low-power mode. The PHY will power down all blocks, except the full-speed receiver, OTG comparators and ULPI interface pins ...
Page 48
... NXP Semiconductors Table 27. Interface Control register (address R = 07h to 09h 07h 08h 09h) bit description Bit Symbol Description 7 INTF_PROT_DIS Interface Protect Disable: Controls circuitry built into the ISP1506 to protect the ULPI interface when the link 3-states STP and DATA[3:0]. When this bit is enabled, the ISP1506 will automatically detect when the link stops driving STP. 0b — ...
Page 49
... NXP Semiconductors Table 29. OTG Control register (address R = 0Ah to 0Ch 0Ah 0Bh 0Ch) bit description Bit Symbol Description 7 USE_EXT_ Use External V VBUS_IND 0b — Use the internal OTG comparator (default). 1b — Use the external V 6 DRV_VBUS_ Drive V EXT external charge pump supply is optional. ...
Page 50
... NXP Semiconductors Table 31. USB Interrupt Enable Rising Edge register (address R = 0Dh to 0Fh 0Dh 0Eh 0Fh) bit description Bit Symbol Description reserved 4 ID_GND_R ID Ground Rise: Enables interrupts and RXCMDs for logic 0 to logic 1 transitions on ID_GND. 3 SESS_END_R Session End Rise: Enables interrupts and RXCMDs for logic 0 to logic 1 transitions on SESS_END ...
Page 51
... NXP Semiconductors Table 34. USB Interrupt Status register (address R = 13h) bit allocation Bit 7 Symbol reserved Reset X Access R Table 35. USB Interrupt Status register (address R = 13h) bit description Bit Symbol Description reserved 4 ID_GND ID Ground: Reflects the current value of the ID detector circuit. 3 SESS_END Session End: Reflects the current value of the session end voltage comparator. ...
Page 52
... NXP Semiconductors 10.1.9 Debug register The bit allocation of the Debug register is given in current value of signals useful for debugging. Table 38. Debug register (address R = 15h) bit allocation Bit 7 Symbol Reset 0 Access R Table 39. Debug register (address R = 15h) bit description Bit Symbol LINESTATE1 0 LINESTATE0 10.1.10 Scratch register Table 40 purposes ...
Page 53
... NXP Semiconductors Table 42. Power Control register (address R = 3Dh to 3Fh 3Dh 3Eh 3Fh) bit description Bit Symbol Description reserved; the link must never write logic 1 to these bits 3 BVALID_FALL BVALID Fall: Enables RXCMDs for HIGH-to-LOW transitions on BVALID. When BVALID changes from HIGH to LOW, the ISP1506 will send an RXCMD to the link with the ALT_INT bit set to logic 1 ...
Page 54
... NXP Semiconductors 11. ElectroStatic Discharge (ESD) 11.1 ESD protection The pins that are connected to the USB connector (DP, DM, ID, V minimum ESD protection. Capacitors 0.1 F and 1 F must be connected in parallel from V Remark: Capacitors 0.1 F and 1 F are also required by Specification Rev. HIGH VOLTAGE DC SOURCE Fig 21 ...
Page 55
... NXP Semiconductors 12. Limiting values Table 43. Limiting values In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 60134). Symbol Parameter V supply voltage CC V input/output supply CC(I/O) voltage V input voltage I V electrostatic discharge ESD voltage I latch-up current lu T storage temperature stg [1] The ISP1506 has been tested according to the additional requirements listed in Section 7 ...
Page 56
... NXP Semiconductors 14. Static characteristics Table 45. Static characteristics: supply pins CC(I/O) Typical values are 3 Symbol Parameter V voltage on pin REG3V3 (REG3V3) V voltage on pin REG1V8 (REG1V8) V power-on reset trip voltage POR(trip) I supply current CC I supply current on CC(I/O) pin V CC(I/O) [1] A continuous stream packets with minimum inter-packet gap and all data bits set to logic 0 for continuous toggling. ...
Page 57
... NXP Semiconductors Table 46. Static characteristics: digital pins (CLOCK, DIR, STP, NXT, DATA[3:0], RESET_N/PSW_N CC(I/O) Typical values are 3 Symbol Parameter V HIGH-level output voltage HIGH-level output current LOW-level output current OL I off-state output current OZ Impedance Z load impedance L Pull-up and pull-down I pull-down current ...
Page 58
... NXP Semiconductors Table 48. Static characteristics: analog I/O pins (DP CC(I/O) Typical values are 3 Symbol Parameter Termination V termination voltage for upstream TERM facing port pull-up Resistance R pull-up resistance on pin DP UP(DP) High-speed USB transceiver Input levels (differential receiver) V high-speed squelch detection ...
Page 59
... NXP Semiconductors Table 49. Static characteristics: charge pump CC(I/O) Typical values are 3 Symbol Parameter Voltage V output voltage on pin V O(VBUS) V leakage voltage on pin V L(VBUS) Current I output current on pin V O(VBUS) Efficiency charge pump efficiency cp Table 50. Static characteristics CC(I/O) Typical values are 3.3 V ...
Page 60
... NXP Semiconductors Table 53. Static characteristics: resistor reference CC(I/O) Typical values are 3 Symbol Parameter V output voltage on pin RREF O(RREF) 120 I CC(cp) (mA) 100 = denotes the charge pump supply current. CC(cp) Fig 22. Charge pump supply current as a function of V output current BUS 5 ...
Page 61
... NXP Semiconductors 15. Dynamic characteristics Table 54. Dynamic characteristics: reset and clock CC(I/O) Typical values are 3 Symbol Parameter Reset t internal power-on reset pulse W(POR) width t REG1V8 HIGH pulse width w(REG1V8_H) t REG1V8 LOW pulse width w(REG1V8_L) t external RESET_N pulse width W(RESET_N) t regulator start-up time ...
Page 62
... NXP Semiconductors Table 55. Dynamic characteristics: digital I/O pins CC(I/O) Symbol Parameter t DATA set-up time with respect to su(DATA) the rising edge of pin CLOCK t DATA hold time with respect to h(DATA) the rising edge of pin CLOCK t DATA output delay with respect d(DATA) ...
Page 63
... NXP Semiconductors Table 56. Dynamic characteristics: analog I/O pins (DP and CC(I/O) Symbol Parameter t driver disable delay from PHZ HIGH level t driver disable delay from PLZ LOW level t driver enable delay to PZH HIGH level t driver enable delay to PZL LOW level Receiver timing ...
Page 64
... NXP Semiconductors CONTROL IN DATA IN CONTROL OUT (DIR, NXT) DATA OUT Fig 30. ULPI timing interface ISP1506A_ISP1506B_2 Product data sheet CLOCK t t su(STP) h(STP) (STP su(DATA) h(DATA) (8-BIT) (8-BIT) Rev. 02 — 28 August 2008 ISP1506A; ISP1506B ULPI HS USB OTG transceiver t , d(DIR) t d(NXT d(DIR d(DATA) d(NXT) © ...
Page 65
... NXP Semiconductors 16. Application information Table 57. Recommended bill of materials [1] Designator Application C highly recommended for bypass all applications C charge pump is used cp(C_A)-(C_B) C highly recommended for filter all applications C mandatory for peripherals VBUS mandatory for host mandatory for OTG D recommended for all ESD ...
Page 66
V BUS USB MICRO-AB GND RECEPTACLE IP4359CX4/LF SHIELD SHIELD 7 SHIELD 8 SHIELD 9 C VBUS (1) Frequency is version dependent: ISP1506A: 19.2 MHz; ISP1506B: 26 MHz. ...
Page 67
IN +3 pullup CHARGE PUMP ON V BUS USB MICRO-AB GND RECEPTACLE SHIELD 6 IP4359CX4/LF SHIELD ESD SHIELD 8 SHIELD 9 (1) Frequency is ...
Page 68
pullup FAULT V BUS SWITCH OUT ON V BUS USB 3 STANDARD-A RECEPTACLE A1 A3 GND 4 IP4359CX4/LF SHIELD SHIELD 6 C VBUS C bypass (1) Frequency is version ...
Page 69
V BUS USB STANDARD-B RECEPTACLE GND SHIELD 5 IP4359CX4/ SHIELD 6 D ESD C bypass (1) Frequency is version dependent: ISP1506A: 19.2 MHz; ISP1506B: 26 MHz. Fig 34. Using the ...
Page 70
... NXP Semiconductors 17. Package outline HVQFN24: plastic thermal enhanced very thin quad flat package; no leads; 24 terminals; body 0.85 mm terminal 1 index area terminal 1 24 index area DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions) (1) A UNIT max. 0.05 0. 0.2 0.00 0.18 Note 1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.075 mm maximum per side are not included. ...
Page 71
... NXP Semiconductors 18. Soldering of SMD packages This text provides a very brief insight into a complex technology. A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in Application Note AN10365 “Surface mount reflow soldering description” . 18.1 Introduction to soldering Soldering is one of the most common methods through which packages are attached to Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs), to form electrical circuits ...
Page 72
... NXP Semiconductors 18.4 Reflow soldering Key characteristics in reflow soldering are: • Lead-free versus SnPb soldering; note that a lead-free reflow process usually leads to higher minimum peak temperatures (see reducing the process window • Solder paste printing issues including smearing, release, and adjusting the process window for a mix of large and small components on one board • ...
Page 73
... NXP Semiconductors Fig 36. Temperature profiles for large and small components For further information on temperature profiles, refer to Application Note AN10365 “Surface mount reflow soldering description” . 19. Abbreviations Table 60. Acronym ASIC ATX CD-RW EOP ESD ESR FS HBM HNP HS ID IEC LS NRZI ...
Page 74
... NXP Semiconductors Table 60. Acronym POR RXCMD SE0 SOF SRP SYNC TTL TXCMD USB USB-IF ULPI UTMI UTMI+ 20. References [1] Universal Serial Bus Specification Rev. 2.0 [2] On-The-Go Supplement to the USB 2.0 Specification Rev. 1.3 [3] UTMI+ Low Pin Interface (ULPI) Specification Rev. 1.1 [4] UTMI+ Specifi ...
Page 75
... NXP Semiconductors 21. Revision history Table 61. Revision history Document ID Release date ISP1506A_ISP1506B_2 20080828 • Modifications: Globally changed mini-USB, mini-A and mini-B connectors to micro-USB, micro-A and micro-B connectors, respectively. • Section 8.2 “USB and OTG state • Figure 6 “Power-up and reset sequence required before the ULPI bus is ready for updated. • ...
Page 76
... Right to make changes — NXP Semiconductors reserves the right to make changes to information published in this document, including without limitation specifications and product descriptions, at any time and without notice ...
Page 77
... NXP Semiconductors 24. Tables Table 1. Ordering information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3 Table 2. Pin description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5 Table 3. Recommended charge pump capacitor value .12 Table 4. ULPI signal description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15 Table 5. Signal mapping during low-power mode . . . . .16 Table 6. Signal mapping for 3-pin serial mode . . . . . . .17 Table 7. Operating states and their corresponding resistor settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18 Table 8. ...
Page 78
... NXP Semiconductors 25. Figures Fig 1. Block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4 Fig 2. Pin configuration HVQFN24; top view . . . . . . . . . .5 Fig 3. External capacitors connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10 Fig 4. Charge pump capacitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11 Fig 5. Internal power-on reset timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 Fig 6. Power-up and reset sequence required before the ULPI bus is ready for use .22 Fig 7. Interface behavior with respect to RESET_N .23 Fig 8 ...
Page 79
... NXP Semiconductors 26. Contents 1 General description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 2 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 3 Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 4 Ordering information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3 5 Block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 6 Pinning information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 6.1 Pinning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 6.2 Pin description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 7 Functional description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 7.1 ULPI interface controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 7.2 USB data serializer and deserializer 7.3 Hi-Speed USB (USB 2.0) ATX . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 7 ...
Page 80
... NXP Semiconductors 10.1.1 Vendor ID and Product ID registers . . . . . . . . 45 10.1.1.1 Vendor ID Low register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45 10.1.1.2 Vendor ID High register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45 10.1.1.3 Product ID Low register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45 10.1.1.4 Product ID High register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45 10.1.2 Function Control register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45 10.1.3 Interface Control register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46 10.1.4 OTG Control register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47 10.1.5 USB Interrupt Enable Rising Edge register . . 48 10 ...