TLE82612EXT Infineon Technologies, TLE82612EXT Datasheet

TLE82612EXT
Specifications of TLE82612EXT
Related parts for TLE82612EXT
TLE82612EXT Summary of contents
Page 1
...
Page 2
Table of Contents 1 HERMES Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 3
Electrical Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 4
Universal System Basis Chip HERMES Rev. 1.0 1 HERMES Overview Scalable System Basis Chip Family • Eight products for complete scalable application coverage • Complete compatibility (hardware and software) across the family • TLE8264-2E (3LIN), TLE8263-2E (2LIN Limp ...
Page 5
HS CAN Transceiver • Compliant to ISO 11898-2 and 11898-5 as well as SAE J2284 • CAN data transmission rate MBaud • Supplied by dedicated input • Low power mode management • Bus wake-up capability via CAN ...
Page 6
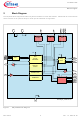
Block Diagram The simplified block diagram illustrates only the basic elements of the SBC devices. Please refer to the information for each device in the product family for more specific hardware configurations SDI ...
Page 7
Pin Configuration 3.1 Pin Assignments RO 1 CSN 2 CLK 3 DSO 36 - Exposed Pad SDI 4 SDO 5 GND cc3shunt V cc3 12 base GND 13 ...
Page 8
Pin Definitions and Functions Pin Symbol Function 1 RO Reset Input/Output; open drain output, integrated pull-up resistor; active low. 2 CSN SPI Chip Select Not Input; CSN is an active low input; serial communication is enabled by pulling the ...
Page 9
Pin Symbol Function 27 n.c. Not connected 28 n.c. Not connected 29 n.c. Not connected 30 n.c. Not connected 31 GND Ground 32 n.c. Not connected 33 LH_SI Limp Home side indicator; Side indicators 1.25Hz 50% duty cycle output; Open ...
Page 10
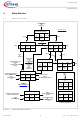
State Machine 4.1 Block Description SPI cmd SBC SW Flash mode Vcc1 WD trig on L.H. act/inact SPI cmd OR WD failed Detection of falling edge at reset pin (any mode) OR undervoltage reset at V CC1µC (any mode) ...
Page 11
State Machine Description The System Basis Chip (SBC) offers ten operating modes: Power On Reset, Init, Normal, Restart, Software Flash, Sleep, Stop, Fail-Safe, Software Development, and Factory Flash Mode. The modes are controlled with one test pin and via ...
Page 12
SBC Normal Mode SBC Normal Mode is used to transmit and receive CAN messages. In this mode, V can be turned-on or off by SPI command. In Normal Mode the watchdog needs to be triggered. It can be cc3 ...
Page 13
SBC Software Flash Mode SBC Software Flash Mode is similar to SBC Normal Mode regarding voltage regulators. In this mode, the Limp Home output can be set to active LOW via SPI and the communication on CAN is activated ...
Page 14
Table 2 SBC Restart Mode Entry Reasons and Actions SBC Mode and Configuration Entering reason Mode Config n.a Init Mode n.a. config 1/3 n.a config 1 config 3 1) Normal config 4 n.a. config 1/3 n.a n.a Software Flash n.a ...
Page 15
SBC Fail-Safe Mode In SBC Fail-Safe Mode, all voltage regulators are OFF and the transceivers are in Wake-Capable Mode. The Limp Home output is active. Conditions to enter the SBC Fail-Safe Mode are: • Watchdog trigger failure in configuration ...
Page 16
General Product Characteristics 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings 1) Absolute Maximum Ratings = -40 °C to +150 °C; all voltages with respect to ground, positive current flowing into pin T j (unless otherwise specified) Pos. Parameter Voltages 5.1.1 Supply Voltage ...
Page 17
Note: Integrated protection functions are designed to prevent IC destruction under fault conditions described in the data sheet. Fault conditions are considered as “outside” normal operating range. Protection functions are not designed for continuous repetitive operation. 5.2 Functional Range Pos. ...
Page 18
Thermal Characteristics Pos. Parameter 5.3.1 Junction Ambient Junction Ambient 5.3.2 Junction to Soldering Point Thermal Prewarning and Shutdown Junction Temperatures; V 5.3.3 , Thermal Pre-warning CC1µC ON Temperature V 5.3.4 , Thermal Prewarning CC1µC Hysteresis V V 5.3.5 Thermal ...
Page 19
Current Consumption all outputs open; Without S positive current defined flowing into pin; unless otherwise specified. Pos. Parameter Normal Mode; 5.4.1 Current Consumption for Internal Logic 5.4.2 Additional current Consumption for CAN ...
Page 20
Current Consumption (cont’ 5 all outputs open; Without S positive current defined flowing into pin; unless otherwise specified. Pos. Parameter Sleep Mode 5.4.4 Current consumption, all Wake Up Sources available. 5.4.5 Quiescent Current ...
Page 21
Internal Voltage Regulator 6.1 Block Description Vs Vref Bandgap Reference Vref Charge Pump Figure 4 Functional Block Diagram The internal voltage regulators are dual low-drop voltage regulators that can supply loads up to input voltage ...
Page 22
Table 3 Internal Voltage Regulators States SBC Mode INIT Mode Normal Mode Sleep Mode Restart Mode Software Flash Mode Stop Mode Fail-Safe Mode 6.4 Application information 6.4.1 Timing Diagram Figure 5 shows the ramp up and down of the V ...
Page 23
Electrical Characteristics 5 CC1µC CC2 = -40 °C to +150 °C; all voltages with respect to ground; positive current defined flowing into pin; unless T j otherwise specified. Pos. ...
Page 24
External Voltage Regulator 7.1 Block Description V is activated via SPI. The external voltage regulator circuitry is designed to drive an external PNP transistor to cc3 increase output current flexibility. Four pins are used: during production. An input voltage ...
Page 25
Application Information 7.4.1 Timing information Figure 7 shows the typical timing, ramp up and ramp down of the External Voltage Regulator, in regards to the pin VextU V_OFF Vcc3 GND Figure ...
Page 26
Table 5 Bills of material for the Device Vendor C Murata SHUNT T ON semi 1 7.4.3 Calculation The maximum current where the limit starts and the bit CC3max R resistor and the Output ...
Page 27
Electrical Characteristics SBC Normal Mode; all outputs open -40 °C to +150 °C; all voltages with respect to ground; positive current defined flowing into pin; unless T j otherwise specified. ...
Page 28
Timing diagram for regulator reaction time “current increase regulation reaction time” and “current decrease regulation reaction time” V CC3 I CCbase Figure 9 Regulator Reaction Time Data Sheet I CC3base,50 rlinc rldec 28 TLE8261-2E External Voltage Regulator t ...
Page 29
High Speed CAN Transceiver 8.1 Block Description V ccHSCAN CANH CANL R SPLIT SPLIT GND Figure 10 Functional Block Diagram 8.2 High-speed CAN Description The Controller Area Network (CAN) transceiver part of the SBC provides high-speed (HS) differential mode ...
Page 30
CAN Normal Mode To transfer the CAN transceiver into the CAN Normal Mode, an SPI word must be sent. This mode is designed for normal data transmission/reception within the HS CAN network. It can be accessed in Normal Mode ...
Page 31
CAN_H WAKE CAN_L PATTERN BUS WAIT BUS OFF Vdiff V cc1µ HSCAN RxD CAN Wake capable mode RO SBC Sleep mode Figure 11 Timing during Transition from Sleep to Normal Mode Wake-Up in SBC Stop Mode In SBC ...
Page 32
CAN OFF Mode CAN OFF Mode, which can be accessed in the SBC Stop, Sleep, Restart and Normal modes, and automatically accessed in SBC Init and Factory Flash modes, is used to completely stop CAN activities. In CAN OFF ...
Page 33
Failure Detection All failures are reported in the SPI diagnostic encoder, the TxD time-out is reported as TxD shorted to GND. In case of local failure and Bus Dominat Clamped failure, the transceiver is automatically switched to the CAN ...
Page 34
Failure Overtemp ON OFF TxD CAN V CC1µC GND V diff Figure 13 Release of the Transmission after Overtemperature 8.4.5 Permanent RxD Recessive Clamping If the RxD signal is permanently recessive (such as shorted to bus, the host microcontroller of ...
Page 35
In the case the application doesn’t request the SPLIT pin feature, the pin has to be left open. CANH TLE 8264 SPLIT 10nF CANL Figure 14 Application example for the SPLIT Pin . Data Sheet 60Ohm CAN split Bus termination ...
Page 36
Electrical Characteristics V V 4.75 V < < ccHSCAN S with respect to ground; positive current flowing into pin; unless otherwise specified. Pos. Parameter CAN Bus Receiver 8.6.1 Differential Receiver ...
Page 37
Electrical Characteristics (cont’ 4.75 V < < ccHSCAN S with respect to ground; positive current flowing into pin; unless otherwise specified. Pos. Parameter CAN Bus Transmitter 8.6.10 CANH/CANL ...
Page 38
Electrical Characteristics (cont’ 4.75 V < < ccHSCAN S with respect to ground; positive current flowing into pin; unless otherwise specified. Pos. Parameter 8.6.28 TxD Input Hysteresis 8.6.29 ...
Page 39
V TxD V cc1µC GND V DIFF V RxD V cc1µC GND Figure 15 Timing Diagrams for Dynamic Characteristics Data Sheet t t d(L),T V diff, rd_N t d(L),R t d(L),TR 0 cc1µC 39 High Speed CAN Transceiver ...
Page 40
WK Pin 9.1 Block Description I WK Figure 16 Functional Block Diagram V The internal voltage regulator ( WK input pin is a bi-level sensitive input. This means that both transitions, HIGH to LOW and LOW to HIGH, result ...
Page 41
V WK Figure 17 Wake-up Timing 9.2.1 Transition from Normal to Sleep Mode. The SBC can not be sent from Normal Mode to Sleep Mode with uncleared interrupt in the WK interrupt bits “ pin” and “WK 1 ...
Page 42
Electrical Characteristics V = -40 °C to +150 °C; all voltages with respect to ground; positive current defined flowing into = 5 pin; unless otherwise specified. Pos. Parameter 9.3.1 WK Input Threshold ...
Page 43
Supervision Functions 10.1 Reset Function 10.1.1 Description The reset output pin RO provides information to the microcontroller, for example, in the event that the output voltage has fallen below the undervoltage threshold reset signal remains LOW initially. When the ...
Page 44
Reset from Outside If the reset pin RO is pulled to low from outside while no reset low is issued by the SBC, the device goes to Restart Mode. In Restart Mode an reset is issued by the SBC, ...
Page 45
Time-out Watchdog The Time-out Watchdog is an easier and less secure type of watchdog. Compared to the Window Watchdog there is no closed window existing. The watchdog trigger can be done any time within the watchdog time. A watchdog ...
Page 46
Window Watchdog Timing (SPI CWmax t CWmin closed window Figure 19 Window Watchdog Definitions Refresh bit RO Watchdog timer reset normal operation Figure 20 Window Watchdog Timing Diagram for ...
Page 47
Inhibition of the watchdog During SBC Stop Mode and SBC SW Flash Mode possible to deactivate the watchdog. To avoid unwished deactivation of the watchdog, a special protocol has to be followed, prior deactivating the watchdog. Please ...
Page 48
Electrical Characteristics V = -40 °C to +150 °C; SBC Normal Mode; all voltages with respect to ground; positive current = 5 defined flowing into pin; unless otherwise specified. Pos. Parameter Reset ...
Page 49
Interrupt Function 11.1 Interrupt Description The interrupt pin has a general purpose function to point out to the microcontroller either a wake up, a failure condition or the switch voltage regulator. Figure 22 gives the hardware ...
Page 50
Table 9 Interrupt sources Interrupt sources V Undervoltage at (except during switch off CC2 V Undervoltage at (except during switch off CC3 V Over current at (except during inhibition) CC3 V Voltage at (during switch on CC2 V Voltage at ...
Page 51
Rising event (Vcc2 above limit ) is shown Vcc2 switched off by SPI Vcc2 INT pin SPI DI programming Read Only Mode Select Bits 111 Conf. Select 000 Conf. Select 001 Conf. Select 002 INT bit UV_V CC2 Figure 23 ...
Page 52
The interrupt UV_Vcc2 that is generated by an under-voltage on sensitive on rising and falling event and the interrupt bit also shows the state of the device and function. Undervoltage Falling event (Vcc2 below limit ) , rising event (Vcc2 ...
Page 53
Interrupt Timing Figure 26 illustrates the interrupt timing. The INT output is set LOW as soon as an interrupt condition occurs. The INT pin is released after a SPI interrupt buffer read out command, that is performed with a ...
Page 54
Electrical Characteristics . V = -40 °C to +150 °C; SBC Normal Mode; all voltages with respect to ground; positive current = 5 defined flowing into pin unless otherwise specified. Pos. Parameter ...
Page 55
Limp Home 12.1 Description The Limp Home outputs are a very useful way to control safety critical functions independent of the microcontroller, such as turning on or off critical load during a microcontroller failure. 12.2 Limp Home output The ...
Page 56
V S LH_ PL / test Figure 29 LH_PL/ Test block diagram 12.2.3 Test Pin The Test pin is used to set the SBC chip into SBC Software Development Mode. When the Test pin is connected to GND, the SBC ...
Page 57
Activation of the Limp Home Output The reason to activate the Limp Home pins and the consequences are listed in Table 10 Limp Home, Function of the SBC Mode SBC Mode Limp Home Outputs INIT Mode OFF Normal Mode ...
Page 58
Vs V SthUVx Vcc1µC V RTx GND RO SBC Sleep SBC Restart t Wake Up RDx Limp home GND V Figure 30 undervoltage time-out timing cc1µC Data Sheet V RTx t Vcc1UVTO SBC Normal SBC Restart TLE8261-2E ...
Page 59
Electrical Characteristics V = -40 °C to +150 °C; SBC Normal Mode; all voltages with respect to ground; positive current = 5 defined flowing into pin unless otherwise specified. Pos. Parameter Limp ...
Page 60
Configuration Select 13.1 Configuration select The Configuration select is used to set the device for two different SBC behaviors; please refer to for detailed information. Depending on the requirements of the application, the goes to Fail-Safe Mode in case ...
Page 61
Serial Peripheral Interface 14.1 SPI Description The 16-bit wide Control Input Word is read via the data input SDI, which is synchronized with the clock input CLK supplied by the microcontroller. The output word appears synchronously at the data ...
Page 62
SPI Input Data MSB Input Data WD refresh Res. Res. Wrong Reset WD set INTERRUPT MASK Res. Res. Cyclic On/off CAN Res. 1 REGISTER CHK WD SUM On/Off Figure ...
Page 63
SPI Output Data MSB Output Data WK state INT Wrong Status or Reset WD set INTERRUPT event Res. Cyclic On/off Res. REGISTER CHK SUM On/Off Res. 14.5 SPI Data Encoding ...
Page 64
SBC Configuration Setting and Read Out 14.5.2.1 Mode selection bits and configuration select Table 12 lists the encoding of the possible SBC mode. Except SBC Restart and Init Mode which are most of time entered automatically, all others SBC ...
Page 65
Interrupt Register Encoder Table 14 lists all interrupts the SBC can generates. The microcontroller should read the correct register to release the INT pin. By default, all interrupt sources are enabled. The microcontroller can decide to inhibit a specific ...
Page 66
Table 14 Interrupt Register encoder (cont’d) CS Bit Name Default Value (INPUT) Configuration select 001 (SBC Failure interrupt) 001 OTP_V 1 cc1µC OT_HSCAN 1 OT_V 1 cc2 UV_V 1 cc3 SPI Fail 1 Reset 1 Wrong WD set 1 V ...
Page 67
CAN failure encoder Table 15 describes the encoding of the possible internal CAN failures. Table 15 CAN Failure Encoder CAN 1 Failure CAN 0 Failure 14.5.2.4 Configuration encoder Table 16 lists ...
Page 68
Table 16 Configuration Encoder Configuration Bit Name Select Configuration select 101 (SBC communication set up register) CAN 1.0 Configuration select 110 (SBC Watchdog register) 110 Ti. Out / Win. Set OFF CHK SUM Configuration select ...
Page 69
Table 18 Watchdog Encoder Bit 10...6 Decimal calculation (ms) 10000 16 n × 464 10001 17 ... ... 11110 30 11111 31 14.5.3 SBC Diagnostic encoder The SBC offers diagnostics information. The encoding of the different possible failures ...
Page 70
Limp Home failure encoder Table 20 describes the encoding of all possible reason to activate automatically the Limp Home output. Bits are set back to “000” when switching Limp Home off via SPI. Table 20 Limp Home Failure Diagnosis ...
Page 71
SPI Output Data 14.6.1 First SPI output data Since the SPI output data is sent when the SBC is receiving data, the output data are dependent of the previous SPI command Read Only command is used. Under ...
Page 72
Read Only command In the Mode Selection Bits a Read Only can be selected. The Read Only access clears the INT bits that are selected in the Configuration Select (some interrupt bits show a state, and can not be ...
Page 73
Electrical Characteristics V = -40 °C to +150 °C; SBC Normal Mode; all voltages with respect to ground; positive current = 5 defined flowing into pin; unless otherwise specified. Pos. Parameter SPI ...
Page 74
Electrical Characteristics (cont’ -40 °C to +150 °C; SBC Normal Mode; all voltages with respect to ground; positive current = 5 defined flowing into pin; unless otherwise specified. Pos. Parameter ...
Page 75
Application Information Note: The following information is given only as a hint for the implementation of the device and should not be regarded as a description or warranty of a certain functionality, condition or quality of the device. VBAT ...
Page 76
Note: This is a very simplified example of an application circuit and bill of material. The function must be verified in the actual application. Table 23 Bills of material Ref. Option Vendor Value Capacitance C1 Y 68µF optional depending on ...
Page 77
Table 23 Bills of material Ref. Option Vendor Value Active components Semi MJD253 Infineon BCP52- Infineon BCR191W T3 N Infineon BCR191W T4 N Infineon BCR191W D1 N Infineon BAS 3010A µC N Infineon XC2xxx IC1 ...
Page 78
ZthJA Curve 60 Zth-JA(Ch4; 600) 50 Zth-JA(Ch4; 300) Zth-JA(Ch4; 100) 40 Zth-JA(Ch4; footprint 0,00001 0,0001 0,001 Figure 38 ZthJA Curve, Function of Cooling Area 600mm² cooling area Figure 39 Board Set-up Board set-up is done ...
Page 79
Hints for SBC Factory Flash Mode The mode is used during production of the module to flash the µC. The idea is that the µC is not supplied from the SBC but from an external 5V power supply. The ...
Page 80
Table 24 PIN in Factory Flash Mode Pin Level Vs typ. 4.5V 5V ± 2% Vcc1µC RO Pull-up resistor INT Pull-up resistor LH High impedance SDO High impedance CLK, SDI Pull-down resistor CSN Pull-up resistor TxDCAN, TxDLIN1, Pull-up resistor TxDLIN2, ...
Page 81
Package Outline 0. 0.65 = 11.05 2) 0.33 ±0. 12.8 Index Marking Exposed Diepad Dimensions Package PG-DSO-36-24, -41, -42 PG-DSO-36-38 PG-DSO-36-38 PG-DSO-36-50 1) Does not include plastic or metal protrusion of 0.15 max. per side ...
Page 82
Revision History Version Date Parameter 1.0 2009-05-25 Data Sheet Changes First Rev. of Data Sheet 82 TLE8261-2E Revision History Rev. 1.0, 2009-05-26 ...
Page 83
... Infineon Technologies Office. Infineon Technologies components may be used in life-support devices or systems only with the express written approval of Infineon Technologies failure of such components can reasonably be expected to cause the failure of that life-support device or system or to affect the safety or effectiveness of that device or system. Life support devices or systems are intended to be implanted in the human body or to support and/or maintain and sustain and/or protect human life ...