S25FL016A0LMFI011 Spansion Inc., S25FL016A0LMFI011 Datasheet - Page 17

S25FL016A0LMFI011
Manufacturer Part Number
S25FL016A0LMFI011
Description
Manufacturer
Spansion Inc.
Datasheet
1.S25FL016A0LMFI011.pdf
(37 pages)
Specifications of S25FL016A0LMFI011
Cell Type
NOR
Density
16Mb
Access Time (max)
10ns
Interface Type
Serial (SPI)
Boot Type
Not Required
Address Bus
1b
Operating Supply Voltage (typ)
3/3.3V
Operating Temp Range
-40C to 85C
Package Type
SOIC W
Program/erase Volt (typ)
2.7 to 3.6V
Sync/async
Synchronous
Operating Temperature Classification
Industrial
Operating Supply Voltage (min)
2.7V
Operating Supply Voltage (max)
3.6V
Word Size
8b
Number Of Words
2M
Supply Current
19mA
Mounting
Surface Mount
Pin Count
8
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
S25FL016A0LMFI011
Manufacturer:
SPANSION
Quantity:
236
9.2
9.3
February 27, 2009 S25FL016A_00_C4
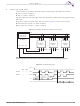
Read Data Bytes at Higher Speed (FAST_READ)
Read Identification (RDID)
The FAST_READ command reads data from the memory array at the frequency (f
input, with a maximum speed of 50 MHz. The host system must first select the device by driving CS# low. The
FAST_READ command is then written to SI, followed by a 3-byte address (A23-A0) and a dummy byte. Each
bit is latched on the rising edge of SCK. The memory array data, at that address, are output serially on SO at
a frequency f
The FAST_READ command sequence is shown in
specified can be at any location. The device automatically increments to the next higher address after each
byte of data is output. The entire memory array can therefore be read with a single FAST_READ command.
When the highest address is reached, the address counter reverts to 00000h, allowing the read sequence to
continue indefinitely.
The FAST_READ command is terminated by driving CS# high at any time during data output. The device
rejects any FAST_READ command issued while it is executing a program, erase, or Write Status Register
operation, and continues the operation uninterrupted.
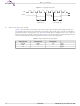
The Read Identification (RDID) command outputs the one-byte manufacturer identification, followed by the
two-byte device identification, to the host system.
JEDEC assigns the manufacturer identification byte; for Spansion devices it is 01h. The device manufacturer
assigns the device identification: the first byte provides the memory type; the second byte indicates the
memory capacity. See
The host system must first select the device by driving CS# low. The RDID command is then written to SI,
and each bit is latched on the rising edge of SCK. The 24-bit device identification data is output from the
memory array on SO at a frequency f
The RDID command sequence is shown in
Driving CS# high after the device identification data has been read at least once terminates the READ_ID
command. Driving CS# high at any time during data output also terminates the RDID operation.
The device rejects any RDID command issued while it is executing a program, erase, or Write Status Register
operation, and continues the operation uninterrupted.
SCK
SO
CS#
SI
Mode 3
Mode 0
Hi-Z
Figure 9.2 Read Data Bytes at Higher Speed (FAST_READ) Command Sequence
SCK
0
, on the falling edge of SCK.
1
2
Command
Table 9.1 on page 18
3
D a t a
4
5
6
7
S h e e t
23 22 21
8
SCK
9
24-Bit Address
S25FL016A
, on the falling edge of SCK.
10
Figure 9.3
or
28 29 30
3
Table 9.4 on page 25
2
1
Figure 9.2
31 32 33
0
and
7
6
Table 9.4 on page
Dummy Byte
34 35 36 37 38
5
and
4
3
Table 9.4 on page
2
for device ID data.
1
39
0
MSB
7
40 41
25.
6
5
42 43 44 45
DATA OUT 1
SCK
4
) presented at the SCK
25. The first byte
3
2
1
46
0
47
MSB
7
DATA OUT 2
17