ISP1161A1BD,118 STEricsson, ISP1161A1BD,118 Datasheet

ISP1161A1BD,118
Specifications of ISP1161A1BD,118
Related parts for ISP1161A1BD,118
ISP1161A1BD,118 Summary of contents
Page 1
... ● Web site ‐ http://www.stnwireless.com is replaced with www.stericsson.com ● Contact information ‐ the list of sales offices previously obtained at http://www.stnwireless.com , is now found at www.stericsson.com under Contacts ...
Page 2
ISP1161A1 USB single-chip host and device controller Rev. 04 — 29 January 2009 1. General description The ISP1161A1 is a single-chip Universal Serial Bus (USB) Host Controller (HC) and Device Controller (DC). The Host Controller portion of the ISP1161A1 complies ...
Page 3
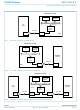
PC (host) USB I/F Fig 1. ISP1161A1 operating as a USB device. EMBEDDED SYSTEM DSC Fig 2. ISP1161A1 operating as a stand-alone USB host. PC (host) USB cable USB I/F Fig 3. ISP1161A1 operating as both USB host and device ...
Page 4
Features Complies with Universal Serial Bus Specification Rev. 2.0 The Host Controller portion of the ISP1161A1 supports data transfer at full-speed (12 Mbit/s) and low-speed (1.5 Mbit/s) The Device Controller portion of the ISP1161A1 supports data transfer at full-speed ...
Page 5
Applications Personal Digital Assistant (PDA) Digital camera Third-generation (3-G) phone Set-Top Box (STB) Information Appliance (IA) Photo printer MP3 jukebox Game console. 4. Ordering information Table 1. Ordering information Type number Package Name Description ISP1161A1BD LQFP64 plastic low profile ...
Page 6
H_WAKEUP 42 H_SUSPEND 33 NDP_SEL 14, 16, 17, 63 D15 ISP1161A1 ...
Page 7
POWER-ON RESET P interface DMA HANDLER Host bus I/F P HANDLER Fig 5. Host controller sub-block diagram. POWER-ON RESET DMA HANDLER Device P HANDLER BUS I/F bus I/F EP HANDLER Fig 6. Device controller sub-block diagram. ISP1161A1_4 Product data sheet ...
Page 8
Pinning information 6.1 Pinning DGND DGND DGND Fig 7. Pin configuration LQFP64. 6.2 Pin description Table 2. [1] Symbol DGND ISP1161A1_4 Product data sheet ...
Page 9
Table 2. [1] Symbol DGND D8 D9 D10 D11 D12 D13 DGND D14 D15 DGND V hold1 n. hold2 DREQ1 DREQ2 DACK1 DACK2 INT1 INT2 ISP1161A1_4 Product data sheet USB single-chip host and device controller Pin ...
Page 10
Table 2. [1] Symbol TEST RESET NDP_SEL EOT DGND D_SUSPEND D_WAKEUP GL D_VBUS H_WAKEUP CLKOUT H_SUSPEND XTAL1 XTAL2 DGND H_PSW1 H_PSW2 D_DM ISP1161A1_4 Product data sheet USB single-chip host and device controller Pin description for LQFP64 …continued Pin Type Description ...
Page 11
Table 2. [1] Symbol D_DP H_DM1 H_DP1 H_DM2 H_DP2 H_OC1 H_OC2 V CC AGND V reg(3. n.c. DGND D0 D1 [1] Symbol names with an overscore (e.g. NAME) represent active LOW signals. ISP1161A1_4 Product data sheet USB single-chip ...
Page 12
Functional description 7.1 PLL clock multiplier A 6 MHz to 48 MHz clock multiplier Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) is integrated on-chip. This allows for the use of a low-cost 6 MHz crystal, which also minimizes EMI. No external components are ...
Page 13
GoodLink Indication of a good USB connection is provided at pin GL through GoodLink technology. During enumeration, the LED indicator will blink on momentarily. When the DC has been successfully enumerated (the device address is set), the LED indicator ...
Page 14
Figure 9 shows the DMA interface between a microprocessor system and the ISP1161A1. The ISP1161A1 provides two DMA channels: • DMA channel 1 (controlled by DREQ1, DACK1 signals) is for the DMA transfer between a microprocessor’s system memory and the ...
Page 15
Figure 10 ISP1161A1 internal control registers. When the microprocessor accesses the HC. When the microprocessor accesses the DC. Fig 10. When the microprocessor accesses the data port. When ...
Page 16
Fig 12. 16-bit register access cycle. Most of the ISP1161A1 internal control registers are 16-bit wide. Some of the internal control registers, however, have 32-bit width. control register is accessed. The complete cycle of accessing a 32-bit register consists of ...
Page 17
CS A1 15:0 ] Fig 15. Accessing DC control registers. 8.4 FIFO buffer RAM access by PIO mode Since the ISP1161A1 internal memory is structured as a FIFO buffer RAM, the FIFO buffer RAM is ...
Page 18
FIFO buffer RAM access by DMA mode The DMA interface between a microprocessor and the ISP1161A1 is shown in When doing a DMA transfer, at the beginning of every burst the ISP1161A1 outputs a DMA request to the microprocessor ...
Page 19
DREQ DACK 15:0 ] data #1 EOT N = 1/2 byte count of transfer data number of cycles/burst. Fig 18. DMA transfer in burst mode. In both figures, the hardware is configured such ...
Page 20
Fig 19. Interrupt pin operating modes. 8.6.2 HC’s interrupt output pin (INT1) To program the four configuration modes of the HC’s interrupt output signal (INT1), set bits InterruptPinTrigger and InterruptOutputPolarity of the HcHardwareConfiguration register (20H to read, A0H to write). ...
Page 21
HcInterruptEnable register MIE RHSC FNO group 2 RHSC FNO HcInterruptStatus register Fig 20. HC interrupt logic. There are two groups of interrupts represented by group 1 and group 2 in pair of ...
Page 22
To re-enable the interrupt generation: 1. Set all bits in the Hc PInterrupt register. 2. Set bit InterruptPinEnable to logic 1. Remark: Bit InterruptPinEnable in the HcHardwareConfiguration register latches the interrupt output. When this bit is set to logic 0, ...
Page 23
In isochronous mode, an interrupt is issued upon each packet transaction. The firmware must take care of timing synchronization with the host. This can be done via the Pseudo Start-Of-Frame (PSOF) interrupt, enabled via bit IEPSOF in the DcInterruptEnable register. ...
Page 24
Event A (see bit INTENA set to logic 0, an interrupt will not be generated at pin INT2. However, it will be registered in the corresponding DcInterrupt register bit. Event B (see bit SOF in the DcInterrupt register is already ...
Page 25
USB host controller (HC) 9.1 HC’s four USB states The ISP1161A1 USB HC has four USB states, USBOperational, USBReset, USBSuspend, and USBResume, which define the HC’s USB signaling and bus states responsibilities. USBOperational write USBSuspend write Fig 23. ISP1161A1 ...
Page 26
Reset HC state = USBOperational Initialize HC Entry Fig 24. ISP1161A1 HC USB transaction loop. Description of 1. Reset: This includes hardware reset by pin RESET and software reset by the HcSoftwareReset command (A9H). The reset function will clear all ...
Page 27
Transfer PTD data into HC’s FIFO buffer RAM: When PTD data is ready in the microprocessor’s system RAM, the HCD must transfer the PTD data from the microprocessor’s system RAM into the ISP1161A1 internal FIFO buffer RAM ...
Page 28
Table 4. Proprietary Transfer Descriptor (PTD): bit allocation Bit 7 6 Byte 0 Byte 1 CompletionCode[3:0] Byte 2 Byte 3 EndpointNumber[3:0] Byte 4 Byte 5 reserved Byte 6 Format Byte 7 ISP1161A1_4 Product data sheet USB single-chip host and device ...
Page 29
Table 5. Proprietary Transfer Descriptor (PTD): bit description Symbol Access Description ActualBytes[9:0] R/W Contains the number of bytes that were transferred for this PTD CompletionCode[3:0] R/W 0000 0001 0010 0011 0100 0101 0110 0111 1000 1001 1010 1011 1100 1101 ...
Page 30
Table 5. Proprietary Transfer Descriptor (PTD): bit description Symbol Access Description DirectionPID[1: — SETUP 01 — OUT 10 — — reserved B5_5 R/W This bit is logic 0 at power-on reset. When this feature is not ...
Page 31
ATL buffer length = 1000H, ITL buffer length = 0H. This will use the internal FIFO buffer RAM for only ATL transfers. Fig 26. HC internal FIFO buffer RAM partitions. The actual requirement for the buffer RAM need not ...
Page 32
Data organization PTD data is used for every data transfer between a microprocessor and the USB bus, and the PTD data resides in the buffer RAM. For an OUT or SETUP transfer, the payload data is placed just after ...
Page 33
Fig 28. PTD data with DWORD alignment in buffer RAM. 9.4.3 Operation and C program example Figure 29 mode. The ISP1161A1 provides one register as the access port for each buffer RAM. For the ITL buffer RAM, the access port ...
Page 34
Host bus I 000H 001H 3FFH ITL0 buffer RAM (8-bit width) Fig 29. PIO access to internal FIFO buffer RAM. Following is an example program that shows how to write data into the ATL ...
Page 35
The example program for writing ATL buffer RAM #include <conio.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <dos.h> // Define register commands #define wHcTransferCounter 0x22 #define wHcuPInterrupt 0x24 #define wHcATLBufferLength 0x2b #define wHcBufferStatus 0x2c // Define I/O Port Address for HC #define HcDataPort ...
Page 36
Set the number of bytes to be transferred HcRegWrite(wHcTransferCounter,0x50); wCount = 0x28; // Get word count outport (HcCmdPort,0x00c1); // Command for ATL buffer write // Write 80 (0x50) bytes of data into ATL buffer RAM for (i=0;i<wCount;i++) { outport(HcDataPort,PTDData[i]); ...
Page 37
Table 6. Run results of the C program example Observed items HC not initialized and not in USBOperational state HcBufferStatus register Bit 2 (ATLBufferFull) 1 Bit 5 (ATLBufferDone) 0 USB Traffic on USB Bus No 9.5 HC operational model Upon ...
Page 38
In the second frame, the HC will process the ISO_A data in the ITL0 buffer. At the same time, the HCD can write ISO_B data into the ITL1 buffer. When the next SOF comes (the beginning of the third frame), ...
Page 39
N) Fig 31. HC time domain behavior: example 2. In example 3 of the next frame has occurred. This will result in undefined behavior for the ISO data on the USB bus in frame (depending on ...
Page 40
Using either internal or external 15 k Fig 33. Use pull-down resistors on downstream ports. 9.8 OC detection and power switching control A downstream port provides 5 V power supply to V hardware functions to monitor the ...
Page 41
Using an internal OC detection circuit The internal OC detection circuit can be used only when power supply. The HCD must set AnalogOCEnable, bit 10 of the HcHardwareConfiguration register, to logic 1. An application using the ...
Page 42
Using an external OC detection circuit When detection circuit cannot be used. An external OC detection circuit must be used instead. Regardless of the V used. To use an external OC detection circuit, AnalogOCEnable, bit 10 ...
Page 43
XOSC_6MHz XOSC (to DC PLL VOLTAGE REGULATOR DC_EnableClock Fig 37. ISP1161A1 suspend and resume clock scheme. In the suspended state, the device will consume considerably less power by turning off the internal 48 MHz clock, PLL and crystal, ...
Page 44
Wake-up by pin CS (software wake-up) During the USBSuspend state, an external microprocessor issues a chip select signal through pin CS. This method of access to the ISP1161A1 internal registers is a software wake-up. 9.9.2.3 Wake-up by USB devices ...
Page 45
HC registers The HC contains a set of on-chip control registers. These registers can be read or written by the Host Controller Driver (HCD). The Control and Status register sets, Frame Counter register sets, and Root Hub register sets ...
Page 46
Table 7. HC Control register summary Command (Hex) Register read write 27 - HcChipID 28 A8 HcScratch - A9 HcSoftwareReset 2A AA HcITLBufferLength 2B AB HcATLBufferLength 2C - HcBufferStatus 2D - HcReadBackITL0Length 2E - HcReadBackITL1Length 40 C0 HcITLBufferPort 41 C1 ...
Page 47
HcControl register (R/W: 01H/81H) The HcControl register defines the operating modes for the HC. RemoteWakeupEnable (RWE) is modified only by the HCD. Code (Hex): 01 — read Code (Hex): 81 — write Table 10. HcControl register: bit allocation Bit ...
Page 48
Table 11. Bit 10.1.3 HcCommandStatus register (R/W: 02H/82H) The HcCommandStatus register is used by the HC to receive commands issued by the HCD, and it also reflects the HC’s current status. To the ...
Page 49
Bit 15 14 Symbol Reset Access Bit 7 6 Symbol Reset 0 0 Access R/W R/W Table 13. Bit 10.1.4 HcInterruptStatus register (R/W: 03H/83H) This register provides the status of ...
Page 50
Bit 15 14 Symbol Reset Access Bit 7 6 Symbol reserved RHSC Reset 0 0 Access R/W R/W Table 15. Bit 10.1.5 HcInterruptEnable register (R/W: 04H/84H) Each enable bit in ...
Page 51
Table 16. HcInterruptEnable register: bit allocation Bit 31 30 Symbol MIE Reset 0 0 Access R/W R/W Bit 23 22 Symbol Reset Access Bit 15 14 Symbol Reset Access Bit 7 6 Symbol reserved RHSC Reset 0 0 Access R/W ...
Page 52
Code (Hex): 05 — read Code (Hex): 85 — write Table 18. HcInterruptDisable register: bit allocation Bit 31 30 Symbol MIE Reset 0 0 Access R/W R/W Bit 23 22 Symbol Reset Access Bit 15 14 Symbol Reset Access Bit ...
Page 53
HC frame counter registers 10.2.1 HcFmInterval register (R/W: 0DH/8DH) The HcFmInterval register contains a 14-bit value which indicates the bit time interval in a frame (that is, between two consecutive SOFs), and a 15-bit value indicating the full-speed maximum ...
Page 54
HcFmRemaining register (R: 0EH) The HcFmRemaining register is a 14-bit down counter showing the bit time remaining in the current frame. Code (Hex): 0E — read Table 22. HcFmRemaining register: bit allocation Bit 31 30 Symbol FRT Reset 0 ...
Page 55
Table 24. HCFmNumber register: bit allocation Bit 31 30 Symbol Reset Access Bit 23 22 Symbol Reset Access Bit 15 14 Symbol Reset Access Bit 7 6 Symbol Reset Access Table 25. Bit 10.2.4 ...
Page 56
Bit 15 14 Symbol Reset 0 0 Access R/W R/W Bit 7 6 Symbol Reset Access Table 27. Bit 10.3 HC Root Hub registers All registers included in this partition are dedicated to the ...
Page 57
HcRhDescriptorA register (R/W: 12H/92H) The HcRhDescriptorA register is the first register of two describing the characteristics of the Root Hub. Reset values are Implementation-Specific (IS). The descriptor length (11), descriptor type and hub controller current (0) fields of the ...
Page 58
Table 29. Bit 10.3.2 HcRhDescriptorB register (R/W: 13H/93H) The HcRhDescriptorB register is the second register of two describing the characteristics of the Root ...
Page 59
Table 30. HcRhDescriptorB register: bit allocation Bit 31 30 Symbol Reset Access Bit 23 22 Symbol Reset N/A N/A Access R R Bit 15 14 Symbol Reset Access Bit 7 6 Symbol Reset N/A N/A Access R R Table 31. ...
Page 60
Table 32. HcRhStatus register: bit allocation Bit 31 30 Symbol CRWE Reset 0 0 Access W R Bit 23 22 Symbol Reset 0 0 Access R R Bit 15 14 Symbol DRWE Reset 0 0 Access R/W R Bit 7 ...
Page 61
Table 33. Bit 10.3.4 HcRhPortStatus[1:2] register (R/W [1]:15H/95H, [2]: 16H/96H) The HcRhPortStatus[1:2] register is used to control and report port events on a per-port basis. NumberDownstreamPorts represents the number of HcRhPortStatus registers that are implemented ...
Page 62
Table 35. Bit ISP1161A1_4 Product data sheet USB single-chip host and device controller HcRhPortStatus[1:2] register: bit description Symbol Description - reserved PRSC PortResetStatusChange: This bit is set at ...
Page 63
Table 35. Bit ISP1161A1_4 Product data sheet USB single-chip host and device controller HcRhPortStatus[1:2] register: bit description Symbol Description PPS (read) PortPowerStatus: This bit reflects the port power status, regardless of the type of ...
Page 64
Table 35. Bit 10.4 HC DMA and interrupt control registers 10.4.1 HcHardwareConfiguration register (R/W: 20H/A0H) 1. Bit 0, InterruptPinEnable, is used as pin INT1’s master interrupt enable. This bit should be used together with register Hc PInterruptEnable ...
Page 65
Table 36. HcHardwareConfiguration register: bit allocation Bit 15 14 Symbol reserved Reset 0 0 Access R/W R/W Bit 7 6 Symbol EOTInput DACKInput Polarity Polarity Reset 0 0 Access R/W R/W Table 37. Bit Symbol ...
Page 66
Code (Hex): A1 — write Table 38. HcDMAConfiguration register: bit allocation Bit 15 14 Symbol Reset Access Bit 7 6 Symbol reserved BurstLen[1:0] Reset 0 0 Access R/W R/W Table 39. Bit ...
Page 67
Table 39. Bit 10.4.3 HcTransferCounter register (R/W: 22H/A2H) This register holds the number of bytes of a PIO or DMA transfer. For a PIO transfer, the number of bytes being read or written to the Isochronous Transfer ...
Page 68
Hc PInterrupt register (R/W: 24H/A4H) All the bits in this register will be active on power-on reset. However, none of the active bits will cause an interrupt on the interrupt pin (INT1) unless they are set by the respective ...
Page 69
Table 43. Bit 1 0 10.4.5 Hc PInterruptEnable register (R/W: 25H/A5H) The bits 6:0 in this register are the same as those in the Hc PInterrupt register. They are used together with bit 0 of the HcHardwareConfiguration register to enable ...
Page 70
Table 45. Bit 10.5 HC miscellaneous registers 10.5.1 HcChipID register (R: 27H) Read this register to get the ID of the ISP1161A1 silicon chip. The higher byte stands for the product name (here 61H ...
Page 71
Code (Hex): 28 — read Code (Hex): A8 — write Table 48. HcScratch register: bit allocation Bit 15 14 Symbol Reset Access Bit 7 6 Symbol Reset Access Table 49. Bit 10.5.3 HcSoftwareReset register (W: A9H) This ...
Page 72
HC buffer RAM control registers 10.6.1 HcITLBufferLength register (R/W: 2AH/AAH) Write to this register to assign the ITL buffer size in bytes: ITL0 and ITL1 are assigned the same value. For example, if HcITLBufferLength register is set to 2 ...
Page 73
Bit 7 6 Symbol Reset Access Table 55. Bit Symbol ATLBufferLength[15:0] 10.6.3 HcBufferStatus register (R: 2CH) Code (Hex): 2C — read Table 56. HcBufferStatus register: bit allocation Bit 15 14 Symbol Reset Access Bit 7 6 Symbol ...
Page 74
HcReadBackITL0Length register (R: 2DH) This register’s value stands for the current number of data bytes inside an ITL0 buffer to be read back by the microprocessor. The HCD must set the HcTransferCounter equivalent to this value before reading back ...
Page 75
HcITLBufferPort register (R/W: 40H/C0H) This is the ITL buffer RAM read/write port. The bits contain the data byte that comes from the ITL buffer RAM’s even address. The bits contain the data byte ...
Page 76
Bit 7 6 Symbol Reset Access Table 65. Bit Symbol DataWord[15:0] The HCD must set the byte count into the HcTransferCounter register and check the HcBufferStatus register before reading from or writing to the buffer. The HCD ...
Page 77
USB device controller (DC) The Device Controller (DC) in the ISP1161A1 is based on the ST-NXP Wireless ISP1181B USB Full-Speed Interface Device IC. The functionality, commands, and register sets are the same as ISP1181B in 16-bit bus mode. If ...
Page 78
The SIE also checks for the device number and endpoint number and verifies whether they are acceptable. • If the endpoint is enabled, the SIE checks the contents of the DcEndpointStatus register. If the endpoint is empty, the data ...
Page 79
A DMA transfer is terminated when any of the following conditions are met: • The DMA count is complete • DMAEN = 0 • The DMA controller asserts EOT. When the DMA transfer is terminated, the buffer is also cleared ...
Page 80
Isochronous bit of an enabled endpoint (FFOISO). Remark: Register changes that affect the allocation of the shared FIFO storage among endpoints must not be made while valid data is present in any FIFO of the enabled endpoints. Such changes ...
Page 81
Endpoint initialization In response to the standard USB request, Set Interface, the firmware must program all 16 ECRs of the ISP1161A1’ sequence (see enabled or not. The hardware will then automatically allocate FIFO storage space. If all ...
Page 82
Suspend and resume 11.4.1 Suspend conditions The ISP1161A1 DC detects a USB suspend status when a constant idle state is present on the USB bus for more than 3 ms. The bus-powered devices that are suspended must not consume ...
Page 83
A USB bus INT_N GOSUSP WAKEUP SUSPEND Fig 38. Suspend and resume timing. In Figure 38: • A: indicates the point at which the USB bus enters the idle state. • B: indicates resume condition, which can ...
Page 84
Resume conditions A wake-up from the suspend state is initiated either by the USB host or by the application: • USB host: drives a K-state on the USB bus (global resume) • Application: remote wake-up through a HIGH level ...
Page 85
DC DMA transfer Direct Memory Access (DMA method to transfer data from one location to another in a computer system, without intervention of the Central Processor Unit (CPU). Many different implementations of DMA exist. The ISP1161A1 DC ...
Page 86
Table 70. Endpoint identifier 12.2 8237 compatible mode The 8237 compatible DMA mode is selected by clearing bit DAKOLY in the DcHardwareConfiguration register (see shown in Table Table 71. Symbol DREQ2 DACK2 EOT RD WR The ...
Page 87
The ISP1161A1’s DC receives a data packet in one of its endpoint FIFOs; the packet must be transferred to memory address 1234H. 2. The ISP1161A1’s DC asserts the DREQ2 signal requesting the 8237 for a DMA transfer. 3. The ...
Page 88
Table 72. Symbol EOT the DACK-only mode, the ISP1161A1’s DC uses the DACK2 signal as a data strobe. Input signals RD and WR are ignored. This mode is used in CPU systems that have a single address ...
Page 89
DcDMACounter register An EOT from the DcDMACounter register is enabled by setting bit CNTREN in the DcDMAConfiguration register. The ISP1161A1 has a 16-bit DcDMACounter register, which specifies the number of bytes to be transferred. When DMA is enabled (DMAEN ...
Page 90
DC commands and registers The functions and registers of the ISP1161A1’s DC are accessed via commands, which consist of a command code followed by optional data bytes (read or write action). An overview of the available commands and registers ...
Page 91
Table 75. DC command and register summary Name Destination Reset Device resets all registers Data flow commands Write Control OUT Buffer illegal: endpoint is read-only (00) Write Control IN Buffer FIFO endpoint 0 IN Write Endpoint n Buffer FIFO endpoint ...
Page 92
Table 75. DC command and register summary Name Destination General commands Read Control OUT Error DcErrorCode register Code endpoint 0 OUT Read Control IN Error Code DcErrorCode register endpoint 0 IN Read Endpoint n Error Code DcErrorCode register (n = ...
Page 93
Transaction — write/read 1 word Table 76. DcEndpointConfiguration register: bit allocation Bit 7 6 Symbol FIFOEN EPDIR Reset 0 0 Access R/W R/W Table 77. Bit 13.1.2 DcAddress register (R/W: B7H/B6H) This command ...
Page 94
The DcMode register controls the DMA bus width, resume and suspend modes, interrupt activity and SoftConnect operation. It can be used to enable debug mode, where all errors and Not Acknowledge (NAK) conditions will generate an interrupt. Code (Hex): B8/B9 ...
Page 95
Table 82. DcHardwareConfiguration register: bit allocation Bit 15 14 Symbol reserved EXTPUL Reset 0 0 Access R/W R/W Bit 7 6 Symbol DAKOLY DRQPOL Reset 0 1 Access R/W R/W Table 83. Bit ...
Page 96
Table 83. Bit 13.1.5 DcInterruptEnable register (R/W: C3H/C2H) This command is used to individually enable or disable interrupts from all endpoints, as well as interrupts caused by events on the USB bus (SOF, SOF lost, EOT, suspend, ...
Page 97
Table 84. DcInterruptEnable register: bit allocation Bit 31 30 Symbol Reset Access Bit 23 22 Symbol IEP14 IEP13 Reset 0 0 Access R/W R/W Bit 15 14 Symbol IEP6 IEP5 Reset 0 0 Access R/W R/W Bit 7 6 Symbol ...
Page 98
Table 86. DcDMAConfiguration register: bit allocation Bit 15 14 Symbol CNTREN SHORTP [1] [1] Reset 0 0 Access R/W R/W Bit 7 6 Symbol EPDIX[3:0] [1] [1] Reset 0 0 Access R/W R/W [1] Unchanged by a bus reset. Table ...
Page 99
Code (Hex): F2/F3 — write/read DcDMACounter register Transaction — write/read 1 word Table 88. DcDMACounter register: bit allocation Bit 15 14 Symbol Reset Access Bit 7 6 Symbol Reset Access Table 89. Bit 13.1.8 Reset Device (F6H) ...
Page 100
Code (Hex — write (control IN, endpoint 1 to 14) Code (Hex): 10 — read (control OUT, endpoint 1 to 14) Transaction — write/read maximum ( words (isochronous endpoint: N bulk/interrupt endpoint: ...
Page 101
Table 92. DcEndpointStatus register: bit allocation Bit 7 6 Symbol EPSTAL EPFULL1 Reset 0 0 Access R R Table 93. Bit 13.2.3 Stall Endpoint/Unstall Endpoint (40H–4FH/80H—8FH) These commands are used to stall ...
Page 102
Validate Endpoint Buffer (R/W: 6FH/61H) This command signals the presence of valid data for transmission to the USB host, by setting the Buffer Full flag of the selected IN endpoint. This indicates that the data in the buffer is ...
Page 103
Table 95. Bit 13.2.7 Acknowledge Setup (F4H) This command acknowledges to the host that a Setup packet was received. The arrival of a Setup packet disables the Validate Buffer and Clear Buffer commands for the control ...
Page 104
Table 97. Bit Table 98. Error code (Binary) 0000 0001 0010 0011 0100 0101 0110 0111 1000 1001 1010 1011 1100 1101 1110 1111 13.3.2 Unlock Device (B0H) This command unlocks the ISP1161A1’s DC from ...
Page 105
Bit 7 6 Symbol Reset Access Table 100. Lock register: bit description Bit 13.3.3 DcScratch register (R/W: B3H/B2H) This command accesses the 16-bit DcScratch register, which can be used by the firmware to save and restore information, ...
Page 106
Table 103. DcFrameNumber register: bit allocation Bit 15 14 Symbol [1] Reset 0 0 Access R R Bit 7 6 Symbol [1] Reset 0 0 Access R R [1] Reset value undefined after a bus reset. Table 104. DcFrameNumber register: ...
Page 107
Table 107. DcChipID register: bit description Bit 13.3.6 Read Interrupt register (R: C0H) This command indicates the sources of interrupts as stored in the 4-byte DcInterrupt register. Each individual endpoint has its own interrupt ...
Page 108
Table 109. DcInterrupt register: bit description Bit ISP1161A1_4 Product data sheet USB single-chip host and device controller Symbol Description SP_EOT A logic 1 indicates that an EOT interrupt has occurred for a short ...
Page 109
Power supply The ISP1161A1 can operate at either 3.3 V. When using the ISP1161A1’s power supply input, only V connected to the 5 V power supply. An application with power ...
Page 110
ISP1161A1 CLKOUT XTAL2 6 MHz XTAL1 Fig 45. Oscillator circuit with external crystal. The 6 MHz oscillator frequency is multiplied to 48 MHz by an internal PLL. This frequency is used to generate a programmable clock output signal at pin ...
Page 111
When the ISP1161A1’s DC enters the ‘suspend’ state (by setting and clearing bit GOSUSP in the DcMode register), outputs D_SUSPEND and CLKOUT change state after approximately 2 ms delay. When NOLAZY = 0 the clock signal on output CLKOUT does ...
Page 112
Power-on reset (POR) When V CC typically (600 ns to 1000 ns when V with respect give a better view of the functionality, with dips at t2–t3 and t4–t5. If the dip at t4–t5 ...
Page 113
Limiting values Table 110. Absolute maximum ratings In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 60134). Symbol Parameter V supply voltage on pin V CC(5V) V supply voltage on pin V CC(3.3V) V input voltage I I latch-up ...
Page 114
Static characteristics Table 112. Static characteristics; supply pins Symbol Parameter internal regulator output reg(3.3) I operating supply current ...
Page 115
Table 113. Static characteristics: digital pins Symbol Parameter Leakage current I input leakage current LI C pin capacitance IN Open-drain outputs I OFF-state output current ...
Page 116
Dynamic characteristics Table 115. Dynamic characteristics Symbol Parameter Reset t pulse width on input RESET W(RESET) Crystal oscillator f crystal frequency XTAL R series ...
Page 117
Programmed I/O timing • If you are accessing only the HC, then the HC Programmed I/O timing applies. • If you are accessing only the DC, then the DC Programmed I/O timing applies. • If you are accessing both ...
Page 118
15 data D [ 15:0 ] valid Fig 51. HC Programmed interface timing 20.1.2 DC Programmed I/O timing Table 118. Dynamic characteristics: DC Programmed interface timing Symbol Parameter Read timing (see ...
Page 119
A0 (2) CS/DACK2 RD t RLDV D[15:0] (1) For t both CS and RD must be de-asserted. SHRL (2) Programmable polarity: shown as active LOW. Fig 52. DC Programmed interface read timing (I/O and 8237 compatible DMA). A0 (2) CS/DACK2 ...
Page 120
Table 119. Dynamic characteristics: HC single-cycle DMA timing Symbol Parameter t read process data hold time RHDZ t write process data set-up time WSU t write process data hold time WHD t DACK1 HIGH to DREQ1 HIGH AHRH t DACK1 ...
Page 121
Table 120. Dynamic characteristics: HC burst mode DMA timing Symbol Parameter T DREQ1 cycle DC t DREQ1 pulse spacing (read) DS(read) t DREQ1 pulse spacing (write) DS(write) t RD/WR LOW to EOT LOW RLIS [ 8)t ...
Page 122
External EOT timing for HC burst mode DMA Fig 57. External EOT timing for HC burst mode DMA. 20.2.5 DC single-cycle DMA timing (8237 mode) Table 121. Dynamic characteristics: DC single-cycle DMA timing (8237 mode) Symbol Parameter t DREQ2 ...
Page 123
DREQ2 (1) DACK2 DATA (1) Programmable polarity: shown as active LOW. Fig 59. DC single-cycle DMA read timing in DACK-only mode. 20.2.7 DC single-cycle DMA write timing in DACK-only mode Table 123. Dynamic characteristics: DC single-cycle DMA write timing in ...
Page 124
EOT timing in DC single-cycle DMA Table 124. Dynamic characteristics: EOT timing in DC single-cycle DMA Symbol Parameter t input RD/WR HIGH after DREQ RSIH on t DACK off after input RD/WR IHAP HIGH t EOT pulse width EOT ...
Page 125
DREQ2 (1) DACK2 (1) Programmable polarity: shown as active LOW. Fig 62. DC burst mode DMA timing. 20.2.10 EOT timing in DC burst mode DMA Table 126. Dynamic characteristics: EOT timing in DC burst mode DMA Symbol ...
Page 126
Application information 21.1 Typical interface circuit (1) For MOSFET 150 m . DSon (2) 470 assuming that Fig 64. Typical interface circuit to Hitachi SH-3 (SH7709) RISC processor. ISP1161A1_4 Product data sheet ...
Page 127
Interfacing a ISP1161A1 with a SH7709 RISC processor This section shows a typical interface circuit between the ISP1161A1 and a RISC processor. The Hitachi SH-3 series RISC processor SH7709 is used as the example. The main ISP1161A1 signals to ...
Page 128
The device stack provides API directly to the application task for device function; the host stack provides API for Class driver and device driver, both of which provide API for application tasks for host function. MECHANISM ...
Page 129
Test information The dynamic characteristics of the analog I/O ports (D+ and listed in were determined using the circuit shown in Load capacitance: (1) C Speed: (1) full-speed mode only: internal 1.5 k Fig 66. Load ...
Page 130
Package outline LQFP64: plastic low profile quad flat package; 64 leads; body 1 pin 1 index DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions) A ...
Page 131
LQFP64: plastic low profile quad flat package; 64 leads; body 1 pin 1 index DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions) A UNIT A ...
Page 132
Soldering of SMD packages This text provides a very brief insight into a complex technology. A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in Application Note AN10365 “Surface mount reflow soldering description”. 24.1 Introduction to soldering Soldering ...
Page 133
Reflow soldering Key characteristics in reflow soldering are: • Lead-free versus SnPb soldering; note that a lead-free reflow process usually leads to higher minimum peak temperatures (see reducing the process window • Solder paste printing issues including smearing, release, ...
Page 134
MSL: Moisture Sensitivity Level Fig 69. Temperature profiles for large and small components For further information on temperature profiles, refer to Application Note AN10365 “Surface mount reflow soldering description”. 25. Revision history Table 129. Revision history Document ID Release ...
Page 135
Tables Table 1. Ordering information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4 Table 2. Pin description for LQFP64 . . . . . . . ...
Page 136
Table 84. DcInterruptEnable register: bit allocation . . . . .96 ...
Page 137
Figures Fig 1. ISP1161A1 operating as a USB device Fig 2. ISP1161A1 operating as a stand-alone USB host. 2 Fig 3. ISP1161A1 operating as both USB host and device simultaneously. . ...
Page 138
Contents 1 General description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 2 Features . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 139
DC data transfer operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76 11.1.1 IN data transfer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 140
Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137 USB single-chip host and device controller 140 Please ...
Page 141
Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST-NXP products. ST-NXP Wireless NV and its subsidiaries (“ST-NXP”) reserve the right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at ...