PCK946BD,151 NXP Semiconductors, PCK946BD,151 Datasheet - Page 6

PCK946BD,151
Manufacturer Part Number
PCK946BD,151
Description
IC DRVR CLK CMOS 1:10 32LQFP
Manufacturer
NXP Semiconductors
Type
Fanout Buffer (Distribution), Divider, Multiplexerr
Datasheet
1.PCK946BD157.pdf
(13 pages)
Specifications of PCK946BD,151
Number Of Circuits
1
Ratio - Input:output
2:10
Differential - Input:output
No/No
Input
LVCMOS, LVTTL
Output
CMOS
Frequency - Max
150MHz
Voltage - Supply
3 V ~ 3.6 V
Operating Temperature
0°C ~ 70°C
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
32-LQFP
Frequency-max
150MHz
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Other names
935281249151
PCK946BD-S
PCK946BD-S
PCK946BD-S
PCK946BD-S
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
PCK946BD,151
Manufacturer:
NXP Semiconductors
Quantity:
10 000
Philips Semiconductors
10. Application information
9397 750 12296
Product data sheet
10.1 Driving transmission lines
V
The PCK946 clock driver was designed to drive high speed signals in a terminated
transmission line environment. To provide the optimum flexibility to the user the output
drivers were designed to exhibit the lowest impedance possible. With an output
impedance of approximately 10
transmission lines.
In most high performance clock networks point-to-point distribution of signals is the
method of choice. In a point-to-point scheme either series terminated or parallel
terminated transmission lines can be used. The parallel technique terminates the signal at
the end of the line with a 50
level of DC current and thus only a single terminated line can be driven by each output of
the PCK946 clock driver. For the series terminated case however there is no DC current
draw, thus the outputs can drive multiple series terminated lines.
output driving a single series terminated line versus two series terminated lines in parallel.
When taken to its extreme the fan-out of the PCK946 clock driver is effectively doubled
due to its capability to drive multiple lines.
The waveform plots of
versus two lines. In both cases the drive capability of the PCK946 output buffers is more
than sufficient to drive 50
measurements in the simulations a delta of only 43 ps exists between the two differently
loaded outputs. This suggests that the dual line driving need not be used exclusively to
maintain the tight output-to-output skew of the PCK946. The output waveform in
shows a step in the waveform, this step is caused by the impedance mismatch seen
looking into the driver. The parallel combination of the 43
impedance does not match the parallel combination of the line impedances. The voltage
wave launched down the two lines will equal:
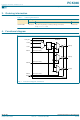
Fig 3. Single versus dual transmission lines
L
=
V
S
------------------------------
R
s
+
Z
R
o
o
+
Z
o
Rev. 01 — 13 December 2005
IN
IN
Figure 4
=
3.0
transmission lines on the incident edge. Note from the delay
PCK946
PCK946
OUTPUT
BUFFER
OUTPUT
BUFFER
--------- -
53.5
resistance to 0.5V
25
show simulation results of an output driving a single line
the drivers can drive either parallel or series terminated
7
7
R o
R o
=
1.40 V
R s = 43
R s = 43
R s = 43
CC
Low voltage 1 : 10 CMOS clock driver
Z o = 50
Z o = 50
Z o = 50
. This technique draws a fairly high
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2005. All rights reserved.
series resistor plus the output
002aaa678
OutA
OutB0
OutB1
Figure
3, illustrates an
PCK946
Figure 4
6 of 13