BZX55C3V0RLG ON Semiconductor, BZX55C3V0RLG Datasheet - Page 5

BZX55C3V0RLG
Manufacturer Part Number
BZX55C3V0RLG
Description
Manufacturer
ON Semiconductor
Type
Voltage Regulatorr
Datasheet
1.BZX55C3V0RLG.pdf
(10 pages)
Specifications of BZX55C3V0RLG
Number Of Elements
Single
Package Type
DO-35
Zener Voltage (typ)
3V
Voltage Tolerance
7%
Knee Impedance
85Ohm
Operating Temperature Classification
Military
Rev Curr
4uA
Mounting
Through Hole
Pin Count
2
Operating Temp Range
-65C to 200C
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Compliant
diode is temperature dependent, it is necessary to determine
junction temperature under any set of operating conditions
in order to calculate its value. The following procedure is
recommended:
θ
is the power dissipation. The value for θ
depends on the device mounting method. θ
to 40°C/W for the various clips and tie points in common use
and for printed circuit board wiring.
thermocouple placed on the lead as close as possible to the
tie point. The thermal mass connected to the tie point is
normally large enough so that it will not significantly
respond to heat surges generated in the diode as a result of
pulsed operation once steady-state conditions are achieved.
Using the measured value of T
may be determined by:
ΔT
temperature and may be found from Figure 2 for dc power:
of P
Changes in voltage, V
θ
from Figures 4 and 5.
vary with time and may also be affected significantly by the
zener resistance. For best regulation, keep current
excursions as low as possible.
than would be expected by considering only junction
temperature, as current crowding effects cause temperatures
to be extremely high in small spots, resulting in device
degradation should the limits of Figure 7 be exceeded.
LA
VZ
Since the actual voltage available from a given zener
Lead Temperature, T
The temperature of the lead can also be measured using a
For worst-case design, using expected limits of I
Under high power-pulse operation, the zener voltage will
Surge limitations are given in Figure 7. They are lower
JL
, the zener voltage temperature coefficient, is found
is the lead-to-ambient thermal resistance (°C/W) and P
APPLICATION NOTE — ZENER VOLTAGE
D
is the increase in junction temperature above the lead
and the extremes of T
T
T
Z
L
ΔT
L
, can then be found from:
J
ΔV = θ
, should be determined from:
= θ
= T
JL
LA
= θ
L
P
+ ΔT
VZ
D
L
JL
J
, the junction temperature
(ΔT
T
+ T
P
J
JL
D
.
.
A
J
.
) may be estimated.
.
LA
LA
is generally 30
will vary and
Z
, limits
http://onsemi.com
D
5
0.007
0.005
0.002
0.001
1000
7000
5000
2000
1000
0.07
0.05
0.02
0.01
500
400
300
200
100
700
500
200
100
0.7
0.5
0.2
0.1
70
50
20
10
0
7
5
2
1
0
3
4
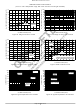
Figure 2. Typical Thermal Resistance
Figure 3. Typical Leakage Current
5
0.2
V
Z
L, LEAD LENGTH TO HEAT SINK (INCH)
2.4−60 V
, NOMINAL ZENER VOLTAGE (VOLTS)
6
7
0.4
8
62−200 V
TYPICAL LEAKAGE CURRENT
AT 80% OF NOMINAL
BREAKDOWN VOLTAGE
9
10
0.6
11
L
12
0.8
+125°C
+25°C
13
L
14
15
1