LC51024MV-52F484C Lattice, LC51024MV-52F484C Datasheet

LC51024MV-52F484C
Available stocks
Related parts for LC51024MV-52F484C
LC51024MV-52F484C Summary of contents
Page 1
... I/Os Packages © 2006 Lattice Semiconductor Corp. All Lattice trademarks, registered trademarks, patents, and disclaimers are as listed at www.latticesemi.com/legal. All other brand or product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders. The specifications and information herein are subject to change without notice. ...
Page 2
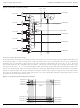
... The ispXPLD 5000MX family represents a new class of device, referred to as the eXpanded Programmable Logic Devices (XPLDs). These devices extend the capability of Lattice’s popular SuperWIDE ispMACH 5000 architecture by providing flexible memory capability. The family supports single- or dual-port SRAM, FIFO, and ternary CAM operation. Extra logic has also been included to allow effi ...
Page 3
... Lattice Semiconductor 5000MX. Incoming signals may connect to the global routing pool or the registers in the MFBs. An Output Sharing Array (OSA) increases the number of I/O available to each MFB, allowing a complete function high-performance access to the I/O. There are four clock pins that drive four global clock nets within the device. Two sysCLOCK PLLs are provided to allow the synthesis of new clocks and control of clock skews ...
Page 4
... Lattice Semiconductor Cascading For Wide Operation In several modes it is possible to cascade adjacent MFBs to support wider operation. Table 2 details the different cascading options. There are chains of MFBs in each device which determine those MFBs that are adjacent for the purposes of cascading. Table 3 indicates these chains. The ispXPLD 5000MX design tools automatically cascade blocks if required by a particular design ...
Page 5
... Lattice Semiconductor Figure 3. MFB in SuperWIDE Logic Mode† 68 Inputs Routing 68 Inputs Adjacent Figure 4. Macrocell Slice in Logic Mode AND-Array From GRP 68 AND Array Dual-OR Array from from MFB Shared PT Clk Shared PT Clk En Shared PT Reset Carry Out From Carry-in n-7 PTSA Bypass PTSA ...
Page 6
... Lattice Semiconductor AND-Array The programmable AND-Array consists of 68 inputs and 164 output product terms. The 68 inputs from the GRP are used to form 136 lines in the AND-Array (true and complement of the inputs). Each line in the array can be con- nected to any of the 164 output product terms via a wired AND. Each of the 160 logic product terms feed the Dual- OR Array with the remaining four control product terms feeding the Shared PT Clock, Shared PT Clock Enable, Shared PT Reset and Shared PT OE. Starting with PT0 sets of fi ...
Page 7
... Lattice Semiconductor Figure 6. Dual-OR PT Sharing Array From PT0 From PT1 From PT2 From PT3 From PT4 Product Term Sharing Array The Product Term Sharing Array (PTSA) consists of 32 inputs from the Dual-OR Array (Expandable PTSA OR) and 32 outputs directly to the macrocells. Each output is the OR term of any combination of the seven Expandable PTSA OR terms connected to that output ...
Page 8
... Lattice Semiconductor Macrocell The 32 registered macrocells in the MFB are driven by the 32 outputs from the PTSA or the PTSA bypass. Each macrocell contains a programmable XOR gate, a programmable register/latch flip-flop and the necessary clocks and control logic to allow combinatorial or registered operation. All macrocells have an output that feeds the GRP. ...
Page 9
... Additional depth is supported by multiplexing the RAM output. For FIFO and CAM modes additional width is supported through the cascading of MFBs. The Lattice design tools automatically combine blocks to support the memory size specified in the user’s design. Bus Size Matching All of the memory modes apart from CAM mode support different widths on each of the ports ...
Page 10
... Lattice Semiconductor True Dual-Port SRAM Mode In Dual-Port SRAM Mode the multi-function array is configured as a dual port SRAM. In this mode two independent read/write ports access the same 8,192-bits of memory. Data widths and 16 are supported by the MFB. Figure 9 shows the block diagram of the dual port SRAM. ...
Page 11
... Lattice Semiconductor Pseudo Dual-Port SRAM Mode In Pseudo Dual-Port SRAM Mode the multi-function array is configured as a SRAM with an independent read and write ports that access the same 16,384-bits of memory. Data widths and 32 are supported by the MFB. Figure 10 shows the block diagram of the Pseudo Dual-Port SRAM. ...
Page 12
... Lattice Semiconductor Single-Port SRAM Mode In Single-Port SRAM Mode the multi-function array is configured as a single-port SRAM. In this mode one ports accesses 16,384-bits of memory. Data widths and 32 are supported by the MFB. Figure 11 shows the block diagram of the single-port SRAM. Write data, address, chip select and read/write signals are always synchronous (registered.) The output data sig- nals can be synchronous or asynchronous ...
Page 13
... Lattice Semiconductor FIFO Mode In FIFO Mode the multi-function array is configured as a FIFO (First In First Out) buffer with built in control. The read and write clocks can be different or the same dependent on the application. Four flags show the status of the FIFO; Full, Empty, Almost Full, and Almost Empty. The thresholds for Full, Almost full and Almost empty are pro- grammable by the user ...
Page 14
... Lattice Semiconductor CAM Mode In CAM Mode the multi-function array is configured as a Ternary Content Addressable Memory (CAM). CAM behaves like a reverse memory where the input is data and the output is an address. It can be used to perform a variety of high-performance look-up functions. As such, CAM has two modes of operation. In write or update mode the CAM behaves as a RAM and data is written to the supplied address ...
Page 15
... Lattice Semiconductor Clock Distribution The ispXPLD 5000MX family has four dedicated clock input pins: GCLK0-GCLK3. GLCK0 and GCLK3 can be routed through a PLL circuit or routed directly to the internal clock nets. The internal clock nets (CLK0-CLK3) are directly related to the dedicated clock pins (see Secondary Clock Divider exception when using the sysCLOCK cir- cuit) ...
Page 16
... PLL’s VCO circuit. The PLL also has a delay feature that allows the out- put clock to be advanced or delayed to improve set-up and clock-to-out times for better performance. For more information on the PLL, please refer to Lattice technical note number TN1003, Lattice sysCLOCK PLL Usage Guidelines. ...
Page 17
... Lattice Semiconductor Output Sharing Array (OSA) A number of I/O pads are available in each sysIO bank to route the selected number of macrocells from the MFB outputs directly to the I/O pads in logic mode. In the ispXPLD 5000MX, the large number of inputs and PTs to the MFB as well as the presence of the PTSA can cover most routing flexibility of signals to I/O cells. The Output Shar- ing Array gives additional routing capability and I/O access to an MFB when a wide output function takes up the whole MFB and cannot be easily divided across multiple MFBs ...
Page 18
... Table 12 lists the sysIO standards with the typical values for V V and V For more information on the sysIO capability, please refer to Lattice technical note number CCO, REF TT. TN1000, sysIO Usage Guidelines for Lattice Devices, available at www.latticesemi.com. ...
Page 19
... Receiver Driver LVPECL Receiver 1. For more information, refer to Lattice technical note TN1000, sysIO Usage Guidelines for Lattice Devices, available at www.latticesemi.com. Control, Clock, sysCONFIG and JTAG Signals Global clock pins support the same sysIO standards as general purpose I/O. When required the V derived from the adjacent bank. When differential standards are supported two adjacent clock pins are paired to form the input ...
Page 20
... The ispXPLD 5000MX devices can be programmed across the commercial temperature and voltage range. The PC-based Lattice software facilitates in-system programming of ispXPLD 5000MX devices. The software takes the JEDEC file output produced by the design implementation software, along with information about the scan chain, and creates a set of vectors used to drive the scan chain. The software can use these vectors to drive a scan chain via the parallel port of a PC. Alternatively, the software can output fi ...
Page 21
... The ispXPLD 5000MX devices use zero power non-volatile cells along with full CMOS design to provide low static power consumption. The 1.8V core reduces dynamic power consumption compared with devices with higher core voltages. For information on estimating power consumption, please refer to Lattice technical note number TN1031, Power Estimation in ispXPLD 5000MX Devices. ...
Page 22
... Stress above those listed under the “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. Functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational sections of this specification is not implied (while programming, following the programming specifications). 2. Compliance with the Lattice Thermal Management document is required. 3. All voltages referenced to GND. 4. Overshoot and Undershoot of - ...
Page 23
... Lattice Semiconductor DC Electrical Characteristics Symbol Parameter Input or I/O Leakage IL Input High Leakage Current I/O Active Pullup Current PU I I/O Active Pulldown Current PD I Bus Hold Low Sustaining Current V BHLS I Bus Hold High Sustaining Current V BHHS I Bus Hold Low Overdrive Current BHLO ...
Page 24
... Lattice Semiconductor Supply Current Symbol Parameter ispXPLD 5256 1,2 I Operating Power Supply Current CC Standby Power Supply Current I CCO (per I/O Bank) PLL Power Supply Current I CCP (per PLL Bank) Standby IEEE 1149.1 TAP Power I CCJ Supply Current ispXPLD 5512 1,2 I Operating Power Supply Current ...
Page 25
... Lattice Semiconductor Supply Current (Continued) Symbol Parameter ispXPLD 51024 1,2 I Operating Power Supply Current CC Standby Power Supply Current I CCO (per I/O Bank) PLL Power Supply Current I CCP (per PLL Bank) Standby IEEE 1149.1 TAP Power I CCJ Supply Current 1. Device configured with 16-bit counters. ...
Page 26
... Lattice Semiconductor sysIO Recommended Operating Conditions Standard Min. LVCMOS 3.3 3.0 LVCMOS 2.5 2.3 1 LVCMOS 1.8 1.65 LVTTL 3.0 PCI 3.3 3.0 AGP-1X 3.15 SSTL 2 2.3 SSTL 3 3.0 CTT 3.3 3.0 CTT 2.5 2.3 HSTL Class I 1.4 HSTL Class III 1.4 HSTL Class IV 1 ...
Page 27
... Lattice Semiconductor sysIO Single Ended DC Electrical Characteristics V IL Input/Output Standard Min (V) Max (V) LVCMOS 3.3 -0.3 LVTTL -0.3 LVCMOS 2.5 -0 LVCMOS 1.8 -0.3 0.68 3 LVCMOS 1.8 -0.3 0.68 4 PCI 3.3 -0.3 1.08 4 AGP-1X -0.3 1.08 SSTL3 class I -0.3 V REF SSTL3 class II -0.3 ...
Page 28
... Lattice Semiconductor sysIO Differential DC Electrical Characteristics Parameter Description LVDS V Input Voltage INP V Differential Input Threshold THD I Input Current IN V Output High Voltage for Output Low Voltage for Output Voltage Differential OD ΔV Change in V Between High and Low Output Voltage Offset OS ΔV ...
Page 29
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5000MX Family External Switching Characteristics Parameter Description Data Propagation Delay 5-PT Bypass t Data propagation delay PD_PTSA MFB Register Setup Time t S Before Clock, 5-PT Bypass MFB Register Setup Time t S_PTSA Before Clock MFB Register Setup Time t Before Clock, Input Register ...
Page 30
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5000MX Family External Switching Characteristics (Continued) Parameter Description Clock Frequency to RAM in: Single Port Mode 5 f (RAM) MAX Dual Port Mode Pseudo Dual Port Mode 5 f (FIFO) Clock Frequency to FIFO MAX t Power-on Time PWR_ON 1. Timing numbers are based on default LVCMOS 1.8 I/O buffers. Use timing adjusters provided to calculate timing for other standards. ...
Page 31
... The Lattice design tools report the timing delays based on the same timing model. Note that internal timing parameters are for reference only, and are not tested. The external timing parameters are tested and guaranteed for every device ...
Page 32
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5000MX Family Internal Switching Characteristics Parameter Description In/Out Delays t Input Buffer Delay IN Global Clock Input t GCLK_IN Buffer Delay Global RESET Pin t RST Delay Global OE Pin t GOE Delay Delay through t BUF Output Buffer t Output Enable Time EN Output Disable t DIS ...
Page 33
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5000MX Family Internal Switching Characteristics (Continued) Parameter Description Registered Delays D-Register Setup t S Time, Global Clock D-Register Setup t S_PT Time, PT Clock D-Register Hold t H Time Register Clock to t COi OSA Time Clock Enable Setup t CESi Time Clock Enable Hold ...
Page 34
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5000MX Family Internal Switching Characteristics (Continued) Parameter Description Additional Delay for t PT Cascading CASC between MFBs Carry Chain Delay, t CICOMFB MFB to MFB Carry Chain Delay, t Macro-Cell to CICOMC Macro-Cell Routing Delay for t Extended Function FLAG Flags Additional Flag Delay when ...
Page 35
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5000MX Family Internal Switching Characteristics (Continued) Parameter Description Write-Enable setup t FIFOWES before Write Clock Write-Enable hold t FIFOWEH after Write Clock Read-Enable setup t FIFORES before Read Clock Read-Enable hold t FIFOREH after Read Clock Reset to Output t FIFORSTO Delay Reset Recovery ...
Page 36
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5000MX Family Internal Switching Characteristics (Continued) Parameter Description Write Mask t Register Setup CAMWMSKS Time before Clock Write Mask t Register Setup CAMWMSKH Time after Clock Reset to CAM t CAMRSTO Output Delay Reset Recovery t CAMRSTR Time t Reset Pulse Width CAMRSTPW CAM – Compare Mode ...
Page 37
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5000MX Family Internal Switching Characteristics (Continued) Parameter Description Address Hold time t SPADDH after Clock Time R/W Setup before t SPRWS Clock Time R/W Hold time after t SPRWH Clock Time Data Setup before t SPDATAS Clock Time Data Hold time after ...
Page 38
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5000MX Family Internal Switching Characteristics (Continued) Parameter Description R/W Hold time after t PDPRWH Clock Time Data Setup before t PDPDATAS Clock Time Data Hold time after t PDPDATAH Clock Time Read Clock to t PDPRCLKO Output Delay Opposite Clock t PDPCLKSKEW Cycle Delay ...
Page 39
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5000MX Family Internal Switching Characteristics (Continued) Parameter Description Clock Enable B t Setup before Clock DPCEBS B Time Clock Enable Hold t B after Clock B DPCEBH Time Address B Setup t DPADDBS before Clock B Time Address B Hold t time after Clock B DPADDBH Time R/W B Setup before ...
Page 40
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5000MX Family Timing Adders Parameter Description t Input Adjusters IOI LVTTL_in Using 3.3V TTL Using 1.8V LVCMOS_18_in CMOS Using 2.5V LVCMOS_25_in CMOS Using 3.3V LVCMOS_33_in CMOS AGP_1X_in Using AGP 1x CTT25_in Using CTT 2.5V CTT33_in Using CTT 3.3V GTL+_in Using GTL+ Using HSTL 2 ...
Page 41
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5000MX Family Timing Adders (Continued) Parameter Description Using 1.8V LVCMOS_18_8mA_out CMOS Standard, 8mA Drive Using 1.8V LVCMOS_18_12mA_out CMOS Standard, 12mA Drive Using 2.5V LVCMOS_25_4mA_out CMOS Standard, 4mA Drive Using 2.5V LVCMOS_25_5.33mA_out CMOS Standard, 5.33 mA Drive Using 2.5V LVCMOS_25_8mA_out ...
Page 42
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5000MX Family Timing Adders (Continued) Parameter Description Using HSTL 2.5V, HSTL_I_out Class I Using HSTL 2.5V, HSTL_III_out Class III Using HSTL 2.5V, HSTL_IV_out Class IV Using Low Voltage Differen- LVDS_out tial Signaling (LVDS) Using Low LVPECL_out Voltage PECL Using PCI ...
Page 43
... Lattice Semiconductor sysCLOCK PLL Timing Symbol Parameter t Input clock, high time PWH t Input clock, low time PWL Input Clock, rise and fall time Input clock stability, cycle to cycle (peak) INSTB f M Divider input, frequency range MDIVIN f M Divider output, frequency range ...
Page 44
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXP sysCONFIG Port Timing Specifications Symbol sysCONFIG Write Cycle Timing t Input setup time CCLK rise SUCS t Hold time CCLK rise HCS t Input setup time of write data to CCLK rise SUWD t Hold time of write data to CCLK rise HWD t Low time to reset device SRAM ...
Page 45
... Lattice Semiconductor Boundary Scan Timing Specifications Parameter t TCK [BSCAN] clock pulse width BTCP t TCK [BSCAN] clock pulse width high BTCPH t TCK [BSCAN] clock pulse width low BTCPL t TCK [BSCAN] setup time BTS t TCK [BSCAN] hold time BTH t TCK [BSCAN] rise/fall time ...
Page 46
... Lattice Semiconductor Power Consumption ispXPLD 5000MC Typical I 800 700 600 500 400 300 200 100 0 0 100 Operating Frequency (MHz) Note: The device is configured with maximum number of 16-bit counters, no PLL, typical current at 1.8V, 25°C. Power Estimation Coefficients Device K0 ispXPLD 5256 2 ...
Page 47
... Lattice Semiconductor • K11 = Current per column driver (µA/MHz) Power Estimation Equations ICC = ICC_DC + IMFB_CPLD + IMFB_ SRAM/PDPRAM/FIFO + IMFB_DPRAM + IMFB_CAM + IPLL_D ICC_DC Use the appropriate value for 5000MC (1.8V power supply) or 5000MV/B (2.5V/3.3V power supply) from the data sheet. IMFB_CPLD = ((K0 * CPLD MFB inputs + K1 * CPLD Logical Product Terms + K2 * CPLD GRP from MFB + K3 * CPLD GRP from IFB) * AF+ K4) * FREQ / 1000µ ...
Page 48
... Lattice Semiconductor Switching Test Conditions Figure 21 shows the output test load that is used for AC testing. The specific values for resistance, capacitance, voltage, and other test conditions are shown in Table 14. Figure 21. Output Test Load, LVTTL and LVCMOS Standards Device Output *C Table 14. Test Fixture Required Components Test Condition Default LVCMOS 1.8 I/O (L -> ...
Page 49
... Lattice Semiconductor Signal Descriptions Signal Names TMS TCK TDI TDO TOE GOE0, GOE1 RESET yzz GND CCO0, CCO1, CCO2, CCO3 REF0, REF1, REF2, REF3 GCLK0, GCLK1, GCLK2, GCLK3 CLK_OUT0, CLK_OUT1 PLL_RST0, PLL_RST1 PLL_FBK0, PLL_FBK1 GNDP V CCP V CCJ x DATA CSB CFG0 PROGRAMB ...
Page 50
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5000MX Power Supply and NC Connections 4 Signals 208 PQFP 256 fpBGA VCC 10, 49, 76, 114, D4, D13, F6, F11, L6, 153, 180 L11, N4, N13 VCCO0 5, 17, 189, 204 A1, F7, G6 VCCO1 42, 57, 72 K6, L7, T1 VCCO2 85, 100, 107, K11, L10, T16 121 VCCO3 146, 161, 176 ...
Page 51
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5256MX Logic Signal Connections Primary Macrocell/ sysIO Bank LVDS Pair Function 0 61N 0 61P 0 62N 0 62P 0 63N 0 63P - - 0 64N 0 64P H18/CLK_OUT0 0 65N 0 65P - - 0 66N - - 0 66P - - GND (Bank 0) 0 67N 0 67P H6/PLL_RST0 0 68N 0 68P H4/PLL_FBK0 0 69N 0 69P - GCLK0P - - - GCLK0N - - - ...
Page 52
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5256MX Logic Signal Connections (Continued) Primary Macrocell/ sysIO Bank LVDS Pair Function 1 4N A16/CSB 1 5P A18/READ 1 5N A20/CCLK - - - - PROGRAMB - - GND (Bank 10P 1 10N 1 11P 1 11N 1 - B16/VREF1 1 12P 1 12N - - GND (Bank 1) 1 13P - - 1 13N 1 14P 1 14N - - 1 15P 1 15N 2 16P ...
Page 53
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5256MX Logic Signal Connections (Continued) Primary Macrocell/ sysIO Bank LVDS Pair Function 2 20P 2 20N C16/VREF2 2 21P 2 21N 2 22P 2 22N 2 23P 2 23N 2 24P 2 24N - - - - GND (Bank 2) 2 25P 2 25N 2 26P 2 26N 2 27P 2 27N - - 2 28P 2 28N 2 29P 2 29N - - 2 30P - - 2 30N ...
Page 54
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5256MX Logic Signal Connections (Continued) Primary Macrocell/ sysIO Bank LVDS Pair Function 3 34N 3 34P 3 35N 3 35P E24/PLL_FBK1 3 36N E22/PLL_RST1 3 36P - - GND (Bank 3) 3 37N - - 3 37P - - 3 38N 3 38P 3 39N 3 39P E10/CLK_OUT1 - - 3 40N 3 40P 3 41N 3 41P 3 42N 3 42P - - GND (Bank 3) ...
Page 55
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5256MX Logic Signal Connections (Continued) Primary Macrocell/ sysIO Bank LVDS Pair Function 3 51N 3 51P 0 52N 0 52P - - 0 53N 0 53P 0 54N - - 0 54P - - GND (Bank 0) 0 55N 0 55P 0 56N G16/VREF0 0 56P 0 57N 0 57P 0 58N 0 58P 0 59N 0 59P 0 60N 0 60P - - - - GND (Bank 0) Global Clock LVDS pair options: GCLK0 and GCLK1, as well as GCLK2 and GCLK3, can be paired together to receive differential clocks ...
Page 56
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5512MX Logic Signal Connections sysIO LVDS Primary Macrocell/ Bank Pair Function 0 109N O30 0 109P O28 0 110N O26 0 110P O24 0 111N O22 — — V CCO0 0 111P O20 — — GND (Bank 0) 0 112N O18 0 112P O16 0 113N O14 0 113P ...
Page 57
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5512MX Logic Signal Connections (Continued) sysIO LVDS Primary Macrocell/ Bank Pair Function — GCLK0N GCLK1 — — GND — — TDI — — TMS — — TCK — — TDO 1 0P A0/DATA0 1 0N A2/DATA1 1 1P A4/DATA2 1 1N A6/DATA3 ...
Page 58
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5512MX Logic Signal Connections (Continued) sysIO LVDS Primary Macrocell/ Bank Pair Function 1 13P B24 — — V CCO1 1 13N B26 1 14P B28 1 14N B30 1 15P C0 1 15N C2 1 16P C4 1 16N C8 1 17P C10 1 17N C12 1 18P C16 1 18N C18 — ...
Page 59
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5512MX Logic Signal Connections (Continued) sysIO LVDS Primary Macrocell/ Bank Pair Function — — V CCO2 2 29N E10 — — GND (Bank 2) 2 30P E12 2 30N E16 2 31P E18 2 31N E20/V REF2 2 32P E22 2 32N E24 2 33P E26 2 33N ...
Page 60
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5512MX Logic Signal Connections (Continued) sysIO LVDS Primary Macrocell/ Bank Pair Function 2 47N G26 — — GND (Bank 2) 2 48P G28 2 48N G30 2 49P H0 2 49N H2 2 50P H4 — — 50N H6 2 51P H8 2 51N H10 2 52P H12 ...
Page 61
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5512MX Logic Signal Connections (Continued) sysIO LVDS Primary Macrocell/ Bank Pair Function 3 61N I14 3 61P I12 3 62N I10 3 62P I8/CLK_OUT1 3 63N I6 — — 63P I4 3 64N I2 3 64P I0 — — GND (Bank 3) 3 65N J30 — — V CCO3 ...
Page 62
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5512MX Logic Signal Connections (Continued) sysIO LVDS Primary Macrocell/ Bank Pair Function 3 79N K8 3 79P K6 3 80N K5 3 80P K4 3 81N K2 3 81P K0 — — GND (Bank 3) 3 82N L30 — — V CCO3 3 82P L28 3 83N L26 3 83P ...
Page 63
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5512MX Logic Signal Connections (Continued) sysIO LVDS Primary Macrocell/ Bank Pair Function 0 96N M12 0 96P M10 0 97N M8 0 97P M6 0 98N M5 0 98P M4 0 99N M2 — — V CCO0 0 99P M0 — — GND (Bank 0) 0 100N N30 0 100P N28 ...
Page 64
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5768MX Logic Signal Connections Primary Macrocell/ sysIO Bank LVDS Pair Function 0 127N S22 0 127P S20 0 128N S18 0 128P S16 0 129N S14 - - VCCO0 0 129P S12 - - GND (Bank 0) 0 130N S10 0 130P S8 0 131N S6 0 131P S4 0 132N VCC 0 132P ...
Page 65
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5768MX Logic Signal Connections (Continued) Primary Macrocell/ sysIO Bank LVDS Pair Function 0 143N U22 - - VCCO0 0 143P U20 - - GND (Bank 0) 0 144N U18 0 144P U16 0 145N U14 0 145P U12 0 146N U10 0 146P U8 0 147N U6 0 147P U4 0 148N VCCO0 ...
Page 66
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5768MX Logic Signal Connections (Continued) Primary Macrocell/ sysIO Bank LVDS Pair Function - - TCK - - TDO 1 0P A30/DATA0 1 0N A28/DATA1 1 1P A26/DATA2 1 1N A24/DATA3 1 2P A22/DATA4 1 2N A20/DATA5 - - GND (Bank A18/DATA6 - - VCCO1 1 3N A16/DATA7 - - GND 1 4P A14/INITB 1 4N A12/CSB 1 5P ...
Page 67
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5768MX Logic Signal Connections (Continued) Primary Macrocell/ sysIO Bank LVDS Pair Function 1 - C28 - - GND (Bank 1) 1 15P C26 - - VCCO1 1 15N C24 - - GND 1 16P C22 - - VCC 1 16N C20 1 17P C18 1 17N C16 1 18P C14 1 18N C12 1 19P C10 1 19N ...
Page 68
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5768MX Logic Signal Connections (Continued) Primary Macrocell/ sysIO Bank LVDS Pair Function 2 29N GND 2 30P E4 2 30N E6 2 31P VCCO2 2 31N E10 - - GND (Bank 2) 2 32P E12 2 32N E14 2 33P E16 2 33N E18/VREF2 2 34P E20 2 34N E22 2 35P ...
Page 69
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5768MX Logic Signal Connections (Continued) Primary Macrocell/ sysIO Bank LVDS Pair Function 2 46N G6 2 47P VCCO2 2 47N G10 - - GND (Bank 2) 2 48P G12 2 48N G14 2 49P G16 2 49N G18 2 50P G20 2 50N G22 2 51P G24 - - VCCO2 2 51N G26 ...
Page 70
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5768MX Logic Signal Connections (Continued) Primary Macrocell/ sysIO Bank LVDS Pair Function - GCLK3N GCLK2 - - VCCP - GCLK3P GCLK3 3 61N J0 3 61P J2 3 62N J4 3 62P J6 3 63N J8 3 63P J10 - - GND (Bank 3) 3 64N J12 - - VCCO3 3 64P J14 - - GND ...
Page 71
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5768MX Logic Signal Connections (Continued) Primary Macrocell/ sysIO Bank LVDS Pair Function 3 76P L30/PLL_FBK1 3 77N M0/PLL_RST1 3 77P - - GND (Bank 3) 3 78N - - VCCO3 3 78P - - GND 3 79N 3 79P M10 3 80N M12 3 80P M14/CLK_OUT1 3 81N M16 - - VCC 3 81P M18 3 82N M20 ...
Page 72
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5768MX Logic Signal Connections (Continued) Primary Macrocell/ sysIO Bank LVDS Pair Function 3 93N 3 93P - - GND (Bank 3) 3 94N - - VCCO3 3 94P - - GND 3 95N - - VCC 3 95P O10 3 96N O12 3 96P O14 3 97N O16 3 97P O18 3 98N O20 3 98P O22 3 99N ...
Page 73
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5768MX Logic Signal Connections (Continued) Primary Macrocell/ sysIO Bank LVDS Pair Function - - VCC 0 109P Q28 - - GND 0 110N Q26 0 110P Q24 0 111N Q22 - - VCCO0 0 111P Q20 - - GND (Bank 0) 0 112N Q18 0 112P Q16 0 113N Q14/VREF0 0 113P Q12 0 114N Q10 ...
Page 74
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5768MX Logic Signal Connections (Continued) Primary Macrocell/ sysIO Bank LVDS Pair Function 0 126N S26 0 126P S24 Global Clock LVDS pair options: GCLK0 and GCLK1, as well as GCLK2 and GCLK3, can be paired together to receive differential clocks; where GCLK0 and GCLK3 are the positive LVDS inputs. ...
Page 75
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 51024MX Logic Signal Connections sysIO Primary Bank LVDS Pair Macrocell/Function 0 159N AA22 0 159P AA20 0 160N AA18 0 160P AA16 0 161N AA14 - - VCCO0 0 161P AA12 - - GND (Bank 0) 0 162N AA10 0 162P AA8 0 163N AA6 0 163P AA4 0 164N AA2 - - VCC 0 164P ...
Page 76
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 51024MX Logic Signal Connections (Continued) sysIO Primary Bank LVDS Pair Macrocell/Function 0 175N AC22 - - VCCO0 0 175P AC20 - - GND (Bank 0) 0 176N AC18 0 176P AC16 0 177N AC14 0 177P AC12 0 178N AC10 0 178P AC8 0 179N AC6 0 179P AC4 0 180N AC2 - - VCCO0 ...
Page 77
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 51024MX Logic Signal Connections (Continued) sysIO Primary Bank LVDS Pair Macrocell/Function - - - - TDO GND (Bank VCCO1 GND VCC GND (Bank VCCO1 10P 1 10N 1 11P 1 11N 1 12P 1 12N - - GND (Bank 1) 1 13P - - VCCO1 1 13N - - GND 1 14P - - VCC 1 14N 1 15P Alternate Outputs ...
Page 78
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 51024MX Logic Signal Connections (Continued) sysIO Primary Bank LVDS Pair Macrocell/Function 1 15N 1 16P E30/DATA0 1 16N E28/DATA1 1 17P E26/DATA2 1 17N E24/DATA3 1 18P E22/DATA4 1 18N E20/DATA5 - - GND (Bank 1) 1 19P E18/DATA6 - - VCCO1 1 19N E16/DATA7 - - GND 1 20P E14/INITB 1 20N E12/CSB 1 21P ...
Page 79
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 51024MX Logic Signal Connections (Continued) sysIO Primary Bank LVDS Pair Macrocell/Function - - GND (Bank 1) 1 31P G26 - - VCCO1 1 31N G24 - - GND 1 32P G22 - - VCC 1 32N G20 1 33P G18 1 33N G16 1 34P G14 1 34N G12 1 35P G10 1 35N G8 1 36P ...
Page 80
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 51024MX Logic Signal Connections (Continued) sysIO Primary Bank LVDS Pair Macrocell/Function - - GND 2 46P 2 46N 2 47P - - VCCO2 2 47N I10 - - GND (Bank 2) 2 48P I12 2 48N I14 2 49P I16 2 49N I18/VREF2 2 50P I20 2 50N I22 2 51P I24 2 51N I26 2 52P ...
Page 81
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 51024MX Logic Signal Connections (Continued) sysIO Primary Bank LVDS Pair Macrocell/Function 2 63P - - VCCO2 2 63N K10 - - GND (Bank 2) 2 64P K12 2 64N K14 2 65P K16 2 65N K18 2 66P K20 2 66N K22 2 67P K24 - - VCCO2 2 67N K26 - - GND (Bank 2) 2 68P ...
Page 82
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 51024MX Logic Signal Connections (Continued) sysIO Primary Bank LVDS Pair Macrocell/Function - - VCCO2 2 79N N10 - - GND (Bank 2) 2 80P N12 2 80N N14 2 81P N16 2 81N N18 2 82P N20 2 82N N22 2 83P N24 2 83N N26 2 84P N28 - - VCCO2 2 84N N30 ...
Page 83
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 51024MX Logic Signal Connections (Continued) sysIO Primary Bank LVDS Pair Macrocell/Function - GCLK3P GCLK3 3 93N 3 93P 3 94N 3 94P 3 95N 3 95P R10 - - GND (Bank 3) 3 96N R12 - - VCCO3 3 96P R14 - - GND 3 97N R16 3 97P R18 3 98N R20 3 98P R22 3 99N ...
Page 84
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 51024MX Logic Signal Connections (Continued) sysIO Primary Bank LVDS Pair Macrocell/Function - - GND (Bank 3) 3 110N - - VCCO3 3 110P - - GND 3 111N 3 111P U10 3 112N U12 3 112P U14/CLK_OUT1 3 113N U16 - - VCC 3 113P U18 3 114N U20 3 114P U22 - - GND (Bank 3) 3 115N ...
Page 85
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 51024MX Logic Signal Connections (Continued) sysIO Primary Bank LVDS Pair Macrocell/Function 3 126N VCCO3 3 126P GND 3 127N VCC 3 127P W10 3 128N W12 3 128P W14 3 129N W16 3 129P W18 3 130N W20 3 130P W22 3 131N W24 3 131P W26 - - GND (Bank 3) 3 132N ...
Page 86
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 51024MX Logic Signal Connections (Continued) sysIO Primary Bank LVDS Pair Macrocell/Function 0 142N Y26 0 142P Y24 0 143N Y22 - - VCCO0 0 143P Y20 - - GND (Bank 0) 0 144N Y18 0 144P Y16 0 145N Y14/VREF0 0 145P Y12 0 146N Y10 0 146P 0 147N 0 147P 0 148N 0 148P ...
Page 87
... Lattice Semiconductor Part Number Description Device Family LC Device Number 5256 = 256 Macrocells 5512 = 512 Macrocells 5768 = 768 Macrocells 51024 = 1,024 Macrocells Memory M Supply Voltage 1.8V Speed 4 = 4.0ns 45 = 4.5ns 5 = 5.0ns 52 = 5.2ns 75 = 7.5ns Ordering Information Note: For voltage families offered in industrial temperature grades and for all but the slowest commercial speed grade, the speed grades on these devices are dual marked ...
Page 88
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5000MC (1.8V) Commercial Devices (Continued) Device Part Number LC51024MC-52F484C LC51024MC-75F484C LC51024MC LC51024MC-52F672C LC51024MC-75F672C Device Part Number LC5256MC-5F256I LC5256MC LC5256MC-75F256I LC5512MC-75Q208I LC5512MC LC5512MC-75F256I LC5512MC-75F484I LC5768MC-75F256I LC5768MC LC5768MC-75F484I LC51024MC-75F484I LC51024MC LC51024MC-75F672I Device Part Number LC5256MB-4F256C LC5256MB LC5256MB-5F256C LC5256MB-75F256C LC5512MB-45Q208C LC5512MB-75Q208C ...
Page 89
... LC51024MB-75F672I Device Part Number LC5256MV-4F256C LC5256MV LC5256MV-5F256C LC5256MV-75F256C LC5512MV-45Q208C LC5512MV-75Q208C LC5512MV-45F256C LC5512MV LC5512MV-75F256C LC5512MV-45F484C LC5512MV-75F484C LC5768MV-5F256C LC5768MV-75F256C LC5768MV LC5768MV-5F484C LC5768MV-75F484C LC51024MV-52F484C LC51024MV-75F484C LC51024MV LC51024MV-52F672C LC51024MV-75F672C Device Part Number LC5256MV-5F256I LC5256MV LC5256MV-75F256I LC5512MV-75Q208I LC5512MV LC5512MV-75F256I LC5512MV-75F484I LC5768MV-75F256I LC5768MV LC5768MV-75F484I LC51024MV-75F484I LC51024MV LC51024MV-75F672I ...
Page 90
... Lattice Semiconductor Lead-Free Packaging ispXPLD 5000MC (1.8V) Lead-Free Commercial Devices Device Part Number LC5256MC-4FN256C LC5256MC LC5256MC-5FN256C LC5256MC-75FN256C LC5512MC-45QN208C LC5512MC-75QN208C LC5512MC-45FN256C LC5512MC LC5512MC-75FN256C LC5512MC-45FN484C LC5512MC-75FN484C LC5768MC-5FN256C LC5768MC-75FN256C LC5768MC LC5768MC-5FN484C LC5768MC-75FN484C LC51024MC-52FN484C LC51024MC-75FN484C LC51024MC LC51024MC-52FN672C LC51024MC-75FN672C ispXPLD 5000MC (1.8V) Lead-Free Industrial Devices Device ...
Page 91
... Lattice Semiconductor ispXPLD 5000MB (2.5V) Lead-Free Commercial Devices Device Part Number LC5256MB-4FN256C LC5256MB LC5256MB-5FN256C LC5256MB-75FN256C LC5512MB-45QN208C LC5512MB-75QN208C LC5512MB-45FN256C LC5512MB LC5512MB-75FN256C LC5512MB-45FN484C LC5512MB-75FN484C LC5768MB-5FN256C LC5768MB-75FN256C LC5768MB LC5768MB-5FN484C LC5768MB-75FN484C LC51024MB-52FN484C LC51024MB-75FN484C LC51024MB LC51024MB-52FN672C LC51024MB-75FN672C ispXPLD 5000MB (2.5V) Lead-Free Industrial Devices Device Part Number ...
Page 92
... LC5512MV-75QN208I LC5512MV LC5512MV-75FN256I LC5512MV-75FN484I LC5768MV-75FN256I LC5768MV LC5768MV-75FN484I LC51024MV-75FN484I LC51024MV LC51024MV-75FN672I For Further Information In addition to this data sheet, the following technical notes may be helpful when designing with the ispXPLD 5000MX family: • sysIO Usage Guidelines for Lattice Devices (TN1000) • Lattice sysCLOCK PLL Design and Usage Guidelines (TN1003) • ...