MPC8241LZQ200D Freescale Semiconductor, MPC8241LZQ200D Datasheet - Page 49

MPC8241LZQ200D
Manufacturer Part Number
MPC8241LZQ200D
Description
IC MPU 32BIT 200MHZ PPC 357-PBGA
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.MPC8241LZQ200D.pdf
(58 pages)
Specifications of MPC8241LZQ200D
Processor Type
MPC82xx PowerQUICC II 32-bit
Speed
200MHz
Voltage
1.8V
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
357-PBGA
Family Name
MPC82XX
Device Core
PowerQUICC II
Device Core Size
32b
Frequency (max)
200MHz
Instruction Set Architecture
RISC
Supply Voltage 1 (typ)
1.8V
Operating Supply Voltage (max)
1.9V
Operating Supply Voltage (min)
1.7V
Operating Temp Range
0C to 105C
Operating Temperature Classification
Commercial
Mounting
Surface Mount
Pin Count
357
Package Type
BGA
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Features
-
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Not Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
MPC8241LZQ200D
Manufacturer:
FREESCALE
Quantity:
513
Company:
Part Number:
MPC8241LZQ200D
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
MPC8241LZQ200D
Manufacturer:
FREESCALE
Quantity:
20 000
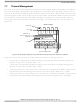
7.7.1
For the PBGA, die-up, packaging technology, shown in
resistance paths are as follows:
Figure 30
printed-circuit board.
For this die-up, wire-bond PBGA package, heat generated on the active side of the chip is conducted
mainly through the mold cap, the heat sink attach material (or thermal interface material), and finally
through the heat sink where forced-air convection removes it.
7.7.2
A thermal interface material should be used between the top of the mold cap and the bottom of the heat
sink minimizes thermal contact resistance. For applications that attach the heat sink by a spring clip
mechanism,
(silicone, graphite/oil, floroether oil), a bare joint, and a joint with thermal grease as a function of contact
pressure. As shown, the performance of these thermal interface materials improves with increasing contact
pressure. Thermal grease significantly reduces the interface thermal resistance. That is, the bare joint offers
a thermal resistance approximately seven times greater than the thermal grease joint.
A spring clip attaches heat sinks to holes in the printed-circuit board (see
synthetic grease offers the best thermal performance, considering the low interface pressure. The selection
of any thermal interface material depends on factors such as thermal performance requirements,
manufacturability, service temperature, dielectric properties, and cost.
Freescale Semiconductor
•
•
The die junction-to-case thermal resistance
The die junction-to-ball thermal resistance
depicts the primary heat transfer path for a package with an attached heat sink mounted to a
Internal Package Conduction Resistance
Adhesives and Thermal Interface Materials
Figure 31
Figure 30. PBGA Package with Heat Sink Mounted to a Printed-Circuit Board
(Note the internal versus external package resistance)
External Resistance
External Resistance
Internal Resistance
shows the thermal performance of three thin-sheet thermal-interface materials
MPC8241 Integrated Processor Hardware Specifications, Rev. 10
Printed-Circuit Board
Heat Sink
Radiation
Radiation
Figure
Convection
Convection
28, the intrinsic conduction thermal
Thermal Interface Material
Die/Package
Die Junction
Package/Leads
Figure
28). Therefore, the
System Design Information
49