CS80C286-12 Intersil, CS80C286-12 Datasheet

CS80C286-12
Specifications of CS80C286-12
Available stocks
Related parts for CS80C286-12
CS80C286-12 Summary of contents
Page 1
... The 80C286 also supports virtual memory systems by providing a segment-not-present excep- tion and restartable instructions. 12.5MHz 16MHz - CG80C286-12 CG80C286-16 IG80C286-12 - 5962- - 9067802MXC - CS80C286-12 CS80C286-16 IS80C286-12 IS80C286-16 1 80C286 20MHz 25MHz PKG. NO. CG80C286-20 - G68 G68.B ...
Page 2
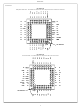
Pinouts Component Pad View - As viewed from underside of the component when mounted on the board CLK CC RESET A11 A10 A13 A12 P.C. Board View - ...
Page 3
Pinouts (Continued) P.C. Board View - As viewed from the component side of the P.C. board. PIN 1 INDICATOR BHE NC NC PEACK A23 A22 V A21 A20 A19 A18 A17 A16 A15 A14 Functional Diagram ADDRESS UNIT (AU) OFFSET ...
Page 4
Pin Descriptions The following pin function descriptions are for the 80C286 microprocessor. PIN SYMBOL NUMBER TYPE CLK 31 I SYSTEM CLOCK: provides the fundamental timing for the 80C286 system divided by two inside the 80C286 to generate the ...
Page 5
Pin Descriptions The following pin function descriptions are for the 80C286 microprocessor. (Continued) PIN SYMBOL NUMBER TYPE M/ MEMORY I/O SELECT: distinguishes memory access from I/O access. If HIGH during T ory cycle or a halt/shutdown cycle is ...
Page 6
... All unused inputs should be pulled to their inactive state with pull up/down resistors. Functional Description Introduction The Intersil 80C286 microprocessor is a static CMOS ver- sion of the NMOS 80286 microprocessor. The 80C286 is an advanced, high-performance microprocessor with specially optimized capabilities for multiple user and multi-tasking sys- tems ...
Page 7
The 80C286 can be single-stepped using only the CPU clock. This state can be maintained as long as necessary. Single step clock information allows simple interface circuitry to provide critical information for system debug. Static design also allows very low ...
Page 8
STATUS FLAGS: CARRY PARITY AUXILIARY CARRY ZERO SIGN OVERFLOW FLAGS: NT IOPL 15 MSW: RESERVED FIGURE 2. STATUS AND CONTROL REGISTER BIT FUNCTIONS BIT POSITION NAME 0 CF Carry Flag - Set on high-order bit carry ...
Page 9
Instruction Set The instruction set is divided into seven categories: data transfer, arithmetic, string manipulation, shift/rotate/logical, high level, processor control and control transfer instruc- tions. These categories are summarized in Table 2. An 80C286 instruction can reference zero, one, or ...
Page 10
TABLE 2D. SHIFT/ROTATE LOGICAL INSTRUCTIONS LOGICALS NOT “Not” byte or word AND “And” byte or word OR “Inclusive or” byte or word XOR “Exclusive or” byte or word TEST “Test” byte or word SHIFTS SHL/SAL Shift logical/arithmetic left byte or ...
Page 11
Memory Organization Memory is organized as sets of variable-length segments. Each segment is a linear contiguous sequence 64K (2 bit bytes. Memory is addressed using a two-component address (a pointer) that consists of a 16-bit segment selector ...
Page 12
Combinations of these three address elements define the six memory addressing modes, described below. DIRECT MODE: The operand's offset is contained in the instruction 16-bit displacement element. REGISTER INDIRECT MODE: The operand's offset is in one ...
Page 13
FUNCTION Divide Error Exception Single Step Interrupt NMI Interrupt Breakpoint Interrupt INTO Detected Overflow Exception BOUND Range Exceeded Exception Invalid Opcode Exception Processor Extension Not Available Exception Reserved - Do Not Use Processor Extension Error Interrupt Reserved User Defined I/O ...
Page 14
Single Step Interrupt The 80C286 has an internal interrupt that allows programs to execute one instruction at a time called the single step interrupt and is controlled by the single step flag bit (TF) in the flag word. ...
Page 15
TABLE 8. RECOMMENDED MSW ENCODINGS FOR PROCESSOR EXTENSION CONTROL Initial encoding after RESET. 80C286 operation is identical to 80C86/88 processor extension is available. Software will emulate its function ...
Page 16
Reserved Memory Locations The 80C286 reserves two fixed areas of memory in real address mode (see Figure 7); system initialization area and interrupt table area. Locations from addresses FFFF0(H) through FFFFF(H) are reserved for system initialization. Initial execution begins at ...
Page 17
Protected Virtual Address Mode The 80C286 executes a fully upward-compatible superset of the 80C86 instruction set in protected virtual address mode (protected mode). Protected mode also provides memory management and protection mechanisms and associated instructions. The 80C286 enters protected virtual ...
Page 18
TABLE 10. CODE AND DATA SEGMENT DESCRIPTOR FORMATS - ACCESS RIGHTS BYTE DEFINITION BIT POSITION NAME 7 Present ( Descriptor Privilege Level (DPL) 4 Segment Descriptor ( Executable (E) 2 Expansion Direction (ED) ...
Page 19
Data segments ( may be either read-only or read- write as controlled by the W bit of the access rights byte. Read-only ( data segments may not be written into. Data segments may ...
Page 20
Segment Descriptor Cache Registers A segment descriptor cache register is assigned to each of the four segment registers (CS, SS, DS, ES). Segment descriptors are automatically loaded (cached) into a seg- ment descriptor cache register (Figure 12) whenever the associated ...
Page 21
CPU 15 0 GDT LIMIT 23 GDT BASE 24-BIT PHYS LDT DESCR SELECTOR 15 0 LDT LIMIT 23 LDT BASE 24-BIT PHYS AD PROGRAM INVISIBLE (AUTOMATICALLY LOADED FROM LDT DESCR WITHIN GDT) FIGURE 14. LOCAL AND GLOBAL ...
Page 22
Task Privilege A task always executes at one of the four privilege levels. The task privilege level at any specific instant is called the Current Privilege Level (CPL) and is defined by the lower two bits of the CS register. ...
Page 23
Control Transfer Four types of control transfer can occur when a selector is loaded into control transfer operation (see Table 13). Each transfer type can only occur if the operation which loaded the selector references the correct ...
Page 24
TABLE 15. OPERAND REFERENCE CHECKS ERROR DESCRIPTION Write into code segment Read from execute-only code segment Write to read-only data segment Segment limit exceeded (See Note) NOTE: Carry out in offset calculations is ignored. TABLE 16. PRIVILEGED INSTRUCTION CHECKS ERROR ...
Page 25
IRET instruction the IRET instruc- tion performs the regular current task by popping values off the stack; when IRET performs a task switch opera- tion back to the previous task. ...
Page 26
CPU TASK REGISTER TR SYSTEM SEGMENT 15 0 DESCRIPTOR PROGRAM INVISIBLE 15 0 LIMIT BASE 23 0 TASK STATE SEGMENT FIGURE 18. TASK STATE SEGMENT AND TSS REGISTERS System Interface The 80C286 system interface appears in two forms: a local ...
Page 27
... Byte-wide I/O devices attached to the upper data byte (D with odd I/O addresses. Devices on the lower data byte are accessed with even I/O addresses. An interrupt controller such as Intersil's 82C59A must be connected to the lower data byte (D 7-0 Bus Operation ...
Page 28
RESET HLDA HLDA HOLD IDLE HLDA • NEW CYCLE NEW CYCLE HLDA • NEW CYCLE ALWAYS STATUS T S READY • NEW CYCLE FIGURE 21. 80C286 BUS STATES Bus States The idle (T ) state indicates ...
Page 29
φ1 CLK PROC CLK VALID ADDR ( • S1 READY PIPELINING: VALID ADDRESS ( AVAILABLE IN LAST PHASE OF BUS CYCLE (N). 80C286 READ ...
Page 30
T S φ1 φ2 CLK PROC CLK VALID ADDR (N- • S0 ALE READY RD EX1 CMDLY RD EX2 CMDLY FIGURE 23. CMDLY CONTROLS THE LEADING EDGE OF COMMAND SIGNAL Bus Cycle Termination At ...
Page 31
Data Bus Control Figures 25, 26, and 27 show how the DT/R, DEN, data bus, and address signals operate for different combinations of read, write, and idle bus operations. DT/R goes active (LOW) for a read operation. DT/R remains HIGH ...
Page 32
MEMORY CYCLE φ1 φ2 φ1 CLK PROC CLK VALID ADDR • S1 SRDY READY (SEE NOTE 8) ARDY NOTES: 8. SRDYEN is active low SRDYEN is high, ...
Page 33
READ CYCLE φ2 φ1 φ2 CLK VALID ADDR • MRDC MWTC DEN DT/R FIGURE 25. BACK TO BACK READ-WRITE CYCLE 80C286 WRITE CYCLE T ...
Page 34
φ2 φ1 CLK • MRDC MWTC DEN DT φ2 φ1 CLK VALID ADDR N • S1 ...
Page 35
... The processor extension interface uses I/O port addresses 00F8(H), and 00FC(H) which are part of the I/O port address range reserved by Intersil. An ESC instruction with Machine Status Word bits and will perform I/O bus S operations to one or more of these I/O port addresses inde- pendent of the value of lOPL and CPL ...
Page 36
BUS HOLD ACKNOWLEDGE BUS CYCLE TYPE φ1 φ2 φ1 CLK (SEE NOTE 14) HOLD HLDA (SEE NOTE 11) S1 • M/IO, COD/INTA BHE, LOCK SRDY + ...
Page 37
Local Bus Usage Priorities The 80C286 local bus is shared among several internal units and external HOLD requests. In case of simultaneous requests, their relative priorities are: (Highest) Any transfers which assert LOCK either explic- itly (via the LOCK instruction ...
Page 38
T C BUS CYCLE TYPE φ1 φ2 φ1 CLK S1 • S0 M/IO, COD/INTA LOCK (SEE NOTE 21 BHE PREVIOUS WRITE CYCLE 15 0 READY INTA MCE ALE DT/R DEN NOTES: 18. ...
Page 39
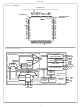
FIGURE 30. BASIC 80C286 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION 39 ...
Page 40
FIGURE 31. MULTIBUS SYSTEM BUS INTERFACE 40 ...
Page 41
Absolute Maximum Ratings Supply Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 42
AC Electrical Specifications are Referenced to 0.8V and 2.0V Points of the Signals as Illustrated in Data Sheet Waveforms, Unless Otherwise Specified SYMBOL PARAMETER TIMING REQUIREMENTS 1 System Clock (CLK) Period 2 System Clock (CLK) LOW ...
Page 43
AC Electrical Specifications Timings are Referenced to the 1.5V Point of the Signals as Illustrated in Data Sheet Waveforms, Unless Otherwise Specified SYMBOL PARAMETER TIMING REQUIREMENTS 1 System Clock (CLK) Period 2 System Clock (CLK) LOW Time ...
Page 44
AC Specifications (Continued) 4.0V CLK INPUT 0.45V 4.0V CLK INPUT 0.45V 2.4V OTHER DEVICE INPUT 0.4V DEVICE OUTPUT NOTE: For AC testing, input rise and fall times are driven at 1ns per volt. 80C286 C80C86-12, -16 I80C286-10, -12, -16 AC ...
Page 45
AC Specifications (Continued) 4.0V CLK INPUT 0.45V 4.0V CLK INPUT 0.45V 2.4V OTHER DEVICE INPUT 0.4V DEVICE OUTPUT NOTE: Typical Output Rise/Fall Time is 6ns. For AC testing, input rise and fall times are driven at 1ns per volt. 80C286 ...
Page 46
AC Electrical Specifications 82C284 and 82C288 Timing Specifications are given for reference only and no guarantee is implied. 82C284 Timing SYMBOL PARAMETER TIMING REQUIREMENTS 11 SRDY/SRDYEN Setup Time 12 SRDY/SRDYEN Hold Time 13 ARDY/ARDYEN Setup Time 14 ARDY/ARDYEN Hold Time ...
Page 47
Waveforms ILLUSTRATED WITH ZERO BUS CYCLE TYPE φ CLK 12A S1 • M/IO, COD, INTA BHE, LOCK READY SRDY ...
Page 48
Waveforms (Continued) BUS CYCLE TYPE V CH φ1 CLK PCLK (SEE NOTE 47) 4 INTR, NMI HOLD, PEREQ (SEE NOTE 45 ERROR, BUSY (SEE NOTE 46) FIGURE 35. 80C286 ASYNCHRONOUS INPUT SIGNAL TIMING NOTES: 45. ...
Page 49
Waveforms (Continued) BUS T CYCLE TYPE H φ CLK HLDA S1 • S0 12B CLK BHE, LOCK (SEE NOTE 52 M/IO, COD/INTA PCLK NOTES: ...
Page 50
Waveforms (Continued) BUS CYCLE TYPE φ2 φ1 CH CLK V I/O READ IF PROC. EXT. TO MEMORY CL MEMORY READ IF MEMORY TO PROC. EXT. S1 • S0 A23 - A0 M/IO, COD INTA 12A ...
Page 51
Waveforms (Continued) BYTE 1 BYTE OPCODE d w MOD REG R/M BYTE 1 BYTE ...
Page 52
Real Address Mode Only 1. This is a protected mode instruction. Attempted execu- tion in real address mode will result in an undefined opcode exception (6 segment overrun exception (13) will occur if a word operand references at ...
Page 53
Instruction Set Summary (Continued) FUNCTION FORMAT Accumulator to Memory 1010001w addr-low Register/Memory to Seg- 10001110 mod 0 reg ment Register Segment Register to Regis- 10001100 mod 0 reg ter/Memory PUSH = Push Memory 11111111 mod Register 01010 reg Segment ...
Page 54
Instruction Set Summary (Continued) FUNCTION FORMAT LEA = Load EA to Register 10001101 mod LDS = Load Pointer to DS 11000101 mod LES = Load Pointer to ES 11000100 mod LAHF Load AH with Flags 10011111 SAHF = Store ...
Page 55
Instruction Set Summary (Continued) FUNCTION FORMAT Immediate from Regis- 100000sw mod ter/Memory Immediate from Accumula- 0010110w data tor SBB = Subtract with Borrow Reg/Memory and Register 000110dw mod to Either Immediate from Regis- 100000sw mod ter/Memory Immediate from Accumula- ...
Page 56
Instruction Set Summary (Continued) FUNCTION FORMAT Register - Byte Register - Word Memory - Byte Memory - Word IMUL = Integer Multiply 1111011w mod (Signed) Register - Byte Register - Word Memory - Byte Memory - Word IMUL = ...
Page 57
Instruction Set Summary (Continued) FUNCTION FORMAT AAD = ASCII Adjust for 11010101 00001010 Divide CBW = Convert Byte to 10011000 Word CWD = Convert Word to 10011001 Double Word LOGIC Shift/Rotate Instructions Register/Memory by 1 1101000w mod Register/Memory by ...
Page 58
Instruction Set Summary (Continued) FUNCTION FORMAT Immediate Data and Regis- 1111011w mod ter/Memory Immediate Data and Accu- 1010100w data mulator Reg/Memory and Register 000010dw mod to Either Immediate to Regis- 1000000w mod ter/Memory Immediate to Accumulator ...
Page 59
... Accordingly, the reader is cautioned to verify that data sheets are current before placing orders. Information furnished by Intersil is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Intersil or its subsidiaries for its use; nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties which may result from its use ...
Page 60
Instruction Set Summary (Continued) FUNCTION FORMAT Via Call Gate to Different Privilege Level, X Param- eters Via TSS Via Task Gate Indirect Intersegment 11111111 mod Protected Mode Only (Indirect Intersegment) Via Call Gate to Same Privilege Level Via Call ...