MAX13041ASD+ Maxim Integrated Products, MAX13041ASD+ Datasheet - Page 16

MAX13041ASD+
Manufacturer Part Number
MAX13041ASD+
Description
IC CAN TXRX +/-80V HS 14-SOIC
Manufacturer
Maxim Integrated Products
Type
Transceiverr
Datasheet
1.MAX13041ASD.pdf
(20 pages)
Specifications of MAX13041ASD+
Number Of Drivers/receivers
1/1
Protocol
CAN
Voltage - Supply
4.75 V ~ 5.25 V
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
14-SOIC (3.9mm Width), 14-SOL
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
±80V Fault-Protected High-Speed CAN Transceiver
with Low-Power Management and Wake-On CAN
The local failure flag is set when the junction temperature
(T
old, T
sive current dissipation from damaging the device. The
transmitter remains disabled until T
degrees, and the local failure flag is cleared.
The local failure flag is cleared and the transmitter is re-
enabled whenever RXD is dominant while TXD is reces-
sive. This situation occurs normally when the MAX13041
is receiving CAN bus data in the absence of a bus failure.
In PWON/listen-only mode, ERR changes to a logic-high
to reflect the change in the local failure flag. If there is no
activity on the CAN bus, the local failure flag can also be
cleared by switching to normal mode from another oper-
ating mode. A typical method involves switching to
PWON/listen-only mode and reading the local failure flag
on ERR. Subsequently, switch back to normal mode to
clear the flag. This sequence is then repeated to verify
that the failure has been resolved.
As with all Maxim devices, ESD-protection structures
are incorporated on all pins to protect against electro-
static discharges encountered during handling and
assembly. The CANH and CANL lines are further pro-
tected by advanced ESD structures to guard these pins
from damage caused by ESD of up to ±12kV as mea-
sured by the Human Body Model (HBM). Protection
structures prevent damage caused by ESD events in all
operating modes, and when the device is unpowered.
Several ESD testing standards exist for gauging the
robustness of ESD structures. The ESD protection of
the MAX13041 is characterized for the human body
model (HBM). Figure 6 shows the model used to simu-
late an ESD event resulting from contact with the
human body. The model consists of a 100pF storage
capacitor that is charged to a high voltage, and subse-
quently discharged through a 1.5kΩ resistor. Figure 7
shows the current waveform when the storage capaci-
tor is discharged into a low impedance.
ESD performance depends on a variety of conditions.
Please contact Maxim for a reliability report document-
ing test setup, methodology, and results.
16
J
) exceeds the shutdown junction temperature thresh-
______________________________________________________________________________________
J(SD)
. The transmitter is disabled to prevent exces-
Recovering from Local Faults
Thermal Shutdown Fault
ESD Test Conditions
J
ESD Protection
drops T
ESD Models
J(SD)HYST
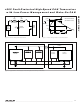
The MAX13041 is primarily intended for automotive
ECU applications where battery power is permanently
supplied to the node (see Figure 8.) This type of appli-
cation is referred to as a clamp-30 node. ECU modules,
which are supplied by the battery only when the ignition
switch is closed, are referred to as clamp-15 modules.
Because clamp-30 modules are permanently supplied
by battery voltage, low power consumption is an essen-
tial design requirement. The MAX13041 provides
advanced power management to the entire node by
controlling one or more external voltage regulators.
While CAN transceivers, such as the MAX13041,
operate from a supply voltage of +5V, many micro-
processors are supplied by voltages of +3.3V and
lower. By controlling the supply voltage regulator for the
microprocessor, the MAX13041 can force a low-power
sleep mode for the entire node.
In multidrop CAN applications, it is important to main-
tain a direct point-to-point wiring scheme. A single pair
of wires should connect each transceiver on the CAN
bus, and the bus wires should be properly split-termi-
nated with two 60Ω resistors at each end as described
in Figure 3 . For best EMC performance, do not use a
star topology. Any deviation from the point-to-point
wiring scheme results in a stub. High-speed edges of
the CAN signal reflect from the unterminated stub ends,
interfering with communication on the bus. To minimize
the effect of these reflections, care should be taken to
minimize the length of stubs.
Bypass V
ceramic capacitors. Place all capacitors as close as
possible to the device.
CC
, V
Clamp-30, Type-A CAN Modules
Applications Information
BAT
, and V
Power-Supply Decoupling
I/O
EMC Considerations
to ground with 0.1µF