PIC18F45K22-I/P Microchip Technology Inc., PIC18F45K22-I/P Datasheet - Page 95

PIC18F45K22-I/P
Manufacturer Part Number
PIC18F45K22-I/P
Description
40 PDIP .600in TUBE, 32KB, Flash, 1536bytes-RAM, 8-bit Family, nanoWatt XLP
Manufacturer
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet
1.PIC18F45K22-IP.pdf
(496 pages)
Specifications of PIC18F45K22-I/P
A/d Inputs
28-Channel, 10-Bit
Comparators
2
Cpu Speed
16 MIPS
Eeprom Memory
256 Bytes
Input Output
35
Interface
I2C/SPI/UART/USART
Memory Type
Flash
Number Of Bits
8
Package Type
40-pin PDIP
Programmable Memory
32K Bytes
Ram Size
1.5K Bytes
Speed
64 MHz
Temperature Range
–40 to 125 °C
Timers
3-8-bit, 4-16-bit
Voltage, Range
1.8-5.5 V
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
RoHS Compliant part
Electrostatic Device
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
PIC18F45K22-I/P
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP
Quantity:
3 400
Part Number:
PIC18F45K22-I/P
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP/微芯
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
PIC18F45K22-I/PT
Manufacturer:
SST
Quantity:
3 400
Company:
Part Number:
PIC18F45K22-I/PT
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
PIC18F45K22-I/PT
Manufacturer:
MIC
Quantity:
20 000
- Current page: 95 of 496
- Download datasheet (5Mb)
6.0
The Flash program memory is readable, writable and
erasable during normal operation over the entire V
range.
A read from program memory is executed one byte at
a time. A write to program memory is executed on
blocks of 64 bytes at a time. Program memory is
erased in blocks of 64 bytes at a time. The difference
between the write and erase block sizes requires from
1 to 8 block writes to restore the contents of a single
block erase. A bulk erase operation can not be issued
from user code.
Writing or erasing program memory will cease
instruction fetches until the operation is complete. The
program memory cannot be accessed during the write
or erase, therefore, code cannot execute. An internal
programming timer terminates program memory writes
and erases.
A value written to program memory does not need to be
a valid instruction. Executing a program memory
location that forms an invalid instruction results in a
NOP.
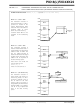
FIGURE 6-1:
2010 Microchip Technology Inc.
Note 1: Table Pointer register points to a byte in program memory.
TBLPTRU
FLASH PROGRAM MEMORY
Table Pointer
TBLPTRH
TABLE READ OPERATION
(1)
TBLPTRL
Program Memory
(TBLPTR)
Preliminary
DD
Instruction: TBLRD*
Program Memory
6.1
In order to read and write program memory, there are
two operations that allow the processor to move bytes
between the program memory space and the data RAM:
• Table Read (TBLRD)
• Table Write (TBLWT)
The program memory space is 16 bits wide, while the
data RAM space is 8 bits wide. Table reads and table
writes move data between these two memory spaces
through an 8-bit register (TABLAT).
The table read operation retrieves one byte of data
directly from program memory and places it into the
TABLAT register.
table read.
The table write operation stores one byte of data from the
TABLAT register into a write block holding register. The
procedure to write the contents of the holding registers
into program memory is detailed in
to Flash Program
operation of a table write with program memory and data
RAM.
Table operations work with byte entities. Tables
containing data, rather than program instructions, are
not required to be word aligned. Therefore, a table can
start and end at any byte address. If a table write is being
used to write executable code into program memory,
program instructions will need to be word aligned.
PIC18(L)F2X/4XK22
Table Reads and Table Writes
Figure 6-1
Memory”.
shows the operation of a
Table Latch (8-bit)
Figure 6-2
Section 6.5 “Writing
TABLAT
DS41412D-page 95
shows the
Related parts for PIC18F45K22-I/P
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
20-Pin USB Flash Microcontrollers
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP [Microchip Technology]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
PIC18F With 128-segment LCD Driver And 12-bit ADC, 8KB Flash, 768B RAM, CCP, MSS
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
PIC18F With 128-segment LCD Driver And 12-bit ADC, 16KB Flash, 768B RAM, CCP, MS
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
PIC18F With 192-segment LCD Driver And 12-bit ADC, 8KB Flash, 768B RAM, CCP, MSS
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
PIC18F With 192-segment LCD Driver And 12-bit ADC, 16KB Flash, 768B RAM, CCP, MS
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Microcontrollers (MCU) 48KB 3328 RAM 52 I/O
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Microcontrollers (MCU) 64KB 3328 RAM 52 I/O
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
32kB Flash, 2kB RAM, 1kB EE, NanoWatt XLP, LCD 64 QFN 9x9x0.9mm T/R
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
32kB Flash, 2kB RAM, 1kB EE, NanoWatt XLP, LCD 64 TQFP 10x10x1mm T/R
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
128kB Flash, 4kB RAM, 1kB EE, 16MIPS, NanoWatt XLP, LCD, 5V 80 TQFP 12x12x1mm T/
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
32kB Flash, 2kB RAM, 1kB EE, NanoWatt XLP, LCD 64 QFN 9x9x0.9mm TUBE
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
32kB Flash, 2kB RAM, 1kB EE, NanoWatt XLP, LCD 64 TQFP 10x10x1mm TRAY
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology

Part Number:
Description:
128kB Flash, 4kB RAM, 1kB EE, 16MIPS, NanoWatt XLP, LCD, 5V 80 TQFP 12x12x1mm TR
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology