MAX13041ASD/V+ Maxim Integrated Products, MAX13041ASD/V+ Datasheet - Page 11

MAX13041ASD/V+
Manufacturer Part Number
MAX13041ASD/V+
Description
IC CAN TXRX +/-80V HS 14SOIC
Manufacturer
Maxim Integrated Products
Type
Transceiverr
Datasheet
1.MAX13041ASD.pdf
(20 pages)
Specifications of MAX13041ASD/V+
Number Of Drivers/receivers
1/1
Protocol
CAN
Voltage - Supply
4.75 V ~ 5.25 V
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
14-SOIC (3.9mm Width), 14-SOL
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
The MAX13041 ±80V fault-protected, high-speed CAN
transceiver is intended for high-speed industrial and
automotive network applications where high reliability
and advanced power management are required. The
device links a CAN protocol controller to the physical
bus wires of the controller area network (CAN) and
allows communication at speeds up to 1Mbps. Built-in
level shifting allows for direct connection to protocol con-
trollers operating from lower voltages. The extended
fault-protected voltage range of ±80V on CAN bus lines
allows for use in +12V or +42V automotive, and higher
voltage +24V and +36V heavy-duty truck applications.
Advanced power management features make the
MAX13041 ideal for automotive electronic control unit
(ECU) modules that are permanently supplied by bat-
tery, regardless of the ignition switch position (clamp-
30, type-A modules). The device controls one or more
external voltage regulators to provide a low-power
sleep mode for an entire clamp-30 node. Wake-on CAN
capability allows the MAX13041 to restore power to the
node upon detection of CAN bus activity. The
MAX13041 is functionally compatible with the Philips
TJA1041A and is a pin-to-pin replacement with
improved performance.
The ISO11898 specification describes the physical
layer of a controller area network (CAN). A CAN imple-
mentation is comprised of multiple transceiver modules
linked by a pair of bus wires. Communication between
modules occurs through transmission and reception of
differential logic states on the bus lines. Two compli-
mentary logic states are defined by ISO11898. A domi-
nant state results when the differential voltage on the
CAN bus lines is greater than 0.9V. A recessive bus
state results when the differential voltage is less than
0.5V (Figure 1). The CAN bus exhibits a wired-AND
characteristic, meaning the bus is only recessive when
all connected transmitters are recessive. Any transmit-
ter asserting a dominant logic state forces the entire
CAN bus dominant.
The MAX13041 accepts logic-level data from the CAN
protocol controller on TXD. Drive TXD low to assert a
dominant state on the CAN bus. Drive TXD high to
release the CAN bus to a recessive state. TXD is inter-
nally pulled up to V
sented to the protocol controller as a logic level on
RXD. The MAX13041 receiver remains active during
transmission to allow for the bit-wise arbitration scheme
specified by the CAN protocol.
±80V Fault-Protected High-Speed CAN Transceiver
with Low-Power Management and Wake-On CAN
______________________________________________________________________________________
I/O
. The state of the CAN bus is pre-
Detailed Description
CAN Interface
The MAX13041 provides level shifting on TXD, RXD,
EN, STB, WAKE and ERR for compatibility with lower-
voltage protocol controllers. Set the interface logic lev-
els for TXD, RXD, EN, STB, WAKE, and ERR by
connecting V
controller, or another voltage from +2.8V to +5.25V.
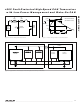
The CAN bus specification requires a total bus load resis-
tance of 60Ω. Each end of the bus should be terminated
with 120Ω, the characteristic impedance of the bus line.
Electromagnetic emission (EME) is reduced by a split-ter-
mination method, whereby each end of the bus line is ter-
minated by 120Ω split into two 60Ω resistors in series
(see Figure 3). A bypass capacitor shunts noise to
ground from the node connecting the 60Ω resistors.
When the CAN bus is recessive, the common-mode
voltage is pulled low by the leakage current from inac-
tive modules. When the CAN bus subsequently goes
dominant, the proper common-mode voltage is
restored by the transmitting device. A common-mode
voltage step results, generating excessive EME. To mit-
igate this problem, the common-mode voltage of the
bus is forced to V
node (see Figure 3). During normal and PWON/listen-
only modes, a stabilized DC voltage of V
on SPLIT. Connect SPLIT to the node connecting the
two 60Ω termination resistors to stabilize the common-
mode voltage of the bus and prevent EME from com-
mon-mode voltage steps.
The MAX13041 provides advanced power management
for a clamp-30 node by controlling one or more external
voltage regulators. Five operating modes provide differ-
ent functionality to minimize power consumption.
Figure 3. Biased Split Termination
Power-Management Operating Modes
Split-Termination and Common-Mode
CANH
SPLIT
CANL
I/O
to the supply voltage of a CAN protocol
CC
/2 by biasing the split-termination
Voltage Stabilization
R
60Ω
R
60Ω
T
T
Level Shifting
CC
C
/2 is present
SPLIT
11