MC68HC11E1CFN3R2 Freescale Semiconductor, MC68HC11E1CFN3R2 Datasheet - Page 204

MC68HC11E1CFN3R2
Manufacturer Part Number
MC68HC11E1CFN3R2
Description
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.MC68HC11E1CFN3R2.pdf
(242 pages)
Specifications of MC68HC11E1CFN3R2
Cpu Family
HC11
Device Core Size
8b
Frequency (max)
3MHz
Interface Type
SCI/SPI
Program Memory Type
ROMLess
Program Memory Size
Not Required
Total Internal Ram Size
512Byte
# I/os (max)
38
Number Of Timers - General Purpose
8
Operating Supply Voltage (typ)
3.3/5V
Operating Supply Voltage (max)
5.5V
Operating Supply Voltage (min)
3V
On-chip Adc
8-chx8-bit
Instruction Set Architecture
CISC
Operating Temp Range
-40C to 85C
Operating Temperature Classification
Industrial
Mounting
Surface Mount
Pin Count
52
Package Type
PLCC
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Not Compliant
- Current page: 204 of 242
- Download datasheet (2Mb)
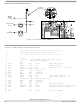
Allowing for Bootstrap Mode
In systems where the PD0/RxD pin is normally used as a general-purpose output, a serial signal from the
host can be connected to the pin without resulting in output driver conflicts. It may be important to consider
what the existing logic will do with the SCI serial data instead of the signals that would have been
produced by the PD0 pin. In systems where the PD0 pin is used normally as a general-purpose input, the
driver circuit that drives the PD0 pin must be designed so that the serial data can override this driver, or
the driver must be disconnected during the bootstrap download. A simple series resistor between the
driver and the PD0 pin solves this problem as shown in
can then be connected to the PD0/RxD pin, and the series resistor will prevent direct conflict between the
host driver and the normal PD0 driver.
TxD Pin
The bootloader program uses the PD1/TxD pin to send verification data back to the host computer. To
minimize the possibility of conflicts with circuitry connected to this pin, port D is configured for wire-OR
mode by the bootloader program during initialization. Since the wire-OR configuration prevents the pin
from driving active high levels, a pullup resistor to V
In systems where the PD1/TxD pin is normally used as a general-purpose output, there are no output
driver conflicts. It may be important to consider what the existing logic will do with the SCI serial data
instead of the signals that would have been produced by the PD1 pin.
In systems where the PD1 pin is normally used as a general-purpose input, the driver circuit that drives
the PD1 pin must be designed so that the PD1/TxD pin driver in the MCU can override this driver. A simple
series resistor between the driver and the PD1 pin can solve this problem. The TxD pin can then be
configured as an output, and the series resistor will prevent direct conflict between the internal TxD driver
and the external driver connected to PD1 through the series resistor.
Other
The bootloader firmware sets the DWOM control bit, which configures all port D pins for wire-OR
operation. During the bootloading process, all port D pins except the PD1/TxD pin are configured as
high-impedance inputs. Any port D pin that normally is used as an output should have a pullup resistor so
it does not float during the bootloading process.
204
CONTROL
EXISTING
SYSTEM
SIGNAL
FROM
Figure 5. Preventing Driver Conflict
HOST
M68HC11 Bootstrap Mode, Rev. 1.1
EXISTING
SHIFTER
DRIVER
RS232
LEVEL
CONNECTED ONLY DURING
BOOTLOADING
RESISTOR
DD
SERIES
is needed if the TxD signal is used.
Figure
5. The serial data from the host computer
RxD/PD0
(BEING USED
AS INPUT)
MC68HC11
Freescale Semiconductor
Related parts for MC68HC11E1CFN3R2
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet: