MT48LC4M32B2B5-7:GTR Micron Technology Inc, MT48LC4M32B2B5-7:GTR Datasheet

MT48LC4M32B2B5-7:GTR
Specifications of MT48LC4M32B2B5-7:GTR
Related parts for MT48LC4M32B2B5-7:GTR
MT48LC4M32B2B5-7:GTR Summary of contents
Page 1
... Column addressing Marking 4M32B2 Table 3: 128Mb (x32) SDRAM Part Numbers TG P Part Number F5 MT48LC4M32B2TG B5 MT48LC4M32B2P MT48LC4M32B2F5 -6 MT48LC4M32B2B5 -7 :G Notes: 1. FBGA Device decoder. None Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice. 1 128Mb: x32 SDRAM Features Access Time Setup ...
Page 2
... WRITE with Auto Precharge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35 Electrical Specifications .42 Temperature and Thermal Impedance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42 Notes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48 Timing Diagrams .50 Package Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66 PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32TOC.fm - Rev. L 1/09 EN Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice. 2 ©2001 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved. 128Mb: x32 SDRAM Table of Contents ...
Page 3
... List of Figures Figure 1: Functional Block Diagram 4 Meg x 32 SDRAM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6 Figure 2: Pin Assignment (Top View) 86-Pin TSOP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7 Figure 3: 90-Ball VFBGA Pin Assignment (Top View Figure 4: Mode Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13 Figure 5: CAS Latency . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15 Figure 6: Activating a Specific Row in a Specific Bank . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 Figure 7: Example: Meeting tRCD (MIN) When 2 < tRCD (MIN)/tCK< .21 Figure 8: READ Command ...
Page 4
... List of Tables Table 1: Key Timing Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1 Table 2: Configurations Table 3: 128Mb (x32) SDRAM Part Numbers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1 Table 4: Pin Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9 Table 5: Ball Descriptions .10 Table 6: Burst Definition .14 Table 7: CAS Latency . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16 Table 8: Truth Table–Commands and DQM Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17 Table 9: Truth Table – CKE .37 Table 10: Truth Table – Current State Bank n, Command To Bank .38 Table 11: Truth Table – ...
Page 5
... A0–A11 select the row). The address bits registered coincident with the READ or WRITE command are used to select the starting column location for the burst access. The SDRAM provides for programmable read or write burst lengths (BL locations, or the full page, with a burst terminate option. An auto precharge function may be enabled to provide a self-timed row precharge that is initiated at the end of the burst sequence ...
Page 6
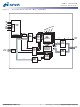
... Figure 1: Functional Block Diagram 4 Meg x 32 SDRAM CKE CLK CONTROL CS# LOGIC WE# CAS# RAS# REFRESH COUNTER MODE REGISTER 12 12 A0–A11, ADDRESS 14 BA0, BA1 REGISTER 8 PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev. L 1/09 EN BANK0 12 BANK0 ROW- 12 ROW- ADDRESS ADDRESS MUX MEMORY 4096 LATCH & (4,096 x 256 x 32) ...
Page 7
... Pin/Ball Assignments and Descriptions Figure 2: Pin Assignment (Top View) 86-Pin TSOP PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev. L 1/09 EN Pin/Ball Assignments and Descriptions DQ0 DQ1 4 DQ2 DQ3 7 DQ4 DQ5 10 DQ6 DQ7 DQM0 16 17 WE# CAS# 18 RAS CS# A11 21 BA0 22 BA1 23 A10 DQM2 DQ16 DQ17 33 DQ18 ...
Page 8
... Figure 3: 90-Ball VFBGA Pin Assignment (Top View PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev. L 1/09 EN Pin/Ball Assignments and Descriptions DQ26 DQ24 V SS DQ28 DQ27 DQ25 DQ29 DQ30 DQ31 DQM3 CLK CKE A9 DQM1 DQ8 DQ10 DQ9 DQ12 DQ14 SS DQ11 DQ13 DQ15 V SS Ball and Array Micron Technology, Inc ...
Page 9
... PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev. L 1/09 EN Type Input Clock: CLK is driven by the system clock. All SDRAM input signals are sampled on the positive edge of CLK. CLK also increments the internal burst counter and controls the output registers. Input Clock enable: CKE activates (HIGH) and deactivates (LOW) the CLK signal. ...
Page 10
... PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev. L 1/09 EN Type Input Clock: CLK is driven by the system clock. All SDRAM input signals are sampled on the positive edge of CLK. CLK also increments the internal burst counter and controls the output registers. Input Clock enable: CKE activates (HIGH) and deactivates (LOW) the CLK signal. ...
Page 11
... Functional Description In general, this 128Mb SDRAM (1 Meg banks quad-bank DRAM that oper- ates at 3.3V and includes a synchronous interface (all signals are registered on the posi- tive edge of the clock signal, CLK). Each of the 33,554,432-bit banks is organized as 4,096 rows by 256 columns by 32-bits. Read and write accesses to the SDRAM are burst oriented; accesses start at a selected location and continue for a programmed number of locations in a programmed sequence ...
Page 12
... Register Definition Mode Register The mode register is used to define the specific mode of operation of the SDRAM. This definition includes the selection of a burst length (BL), a burst type, a CAS latency (CL), an operating mode and a write burst mode, as shown in Figure 4 on page 13. The mode register is programmed via the LOAD MODE REGISTER command and will retain the stored information until it is programmed again or the device loses power ...
Page 13
... Mode Register Definition M11, M10, BA0, BA1 = “0” to ensure compatibility with future devices. Write Burst Mode M9 0 Programmed Burst Length 1 Single Location Access M8 M7 M6– Defined – – – PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev. L 1/09 EN A11 A10 Reserved WB Op Mode CAS Latency ...
Page 14
... For a full-page burst, the full row is selected and A0–A7 select the starting column. 5. Whenever a boundary of the block is reached within a given sequence above, the following access wraps within the block. 6. For A0–A7 select the unique column to be accessed, and mode register bit M3 is ignored. PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev. L 1/09 EN Starting Column Address ...
Page 15
... T2, as shown in Figure 5. Table 7 on page 16 indicates the operating frequencies at which each CL setting can be used. Figure 5: CAS Latency CLK COMMAND DQ CLK COMMAND DQ CLK COMMAND DQ Reserved states should not be used as unknown operation or incompatibility with future versions may result. PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev READ NOP OUT ...
Page 16
... Write Burst Mode When programmed via M0–M2 applies to both read and write bursts; when the programmed BL applies to read bursts, but write accesses are single-location (nonburst) accesses. Table 7: CAS Latency PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev. L 1/09 EN Allowable Operating Frequency (MHz) Speed ≤ ≤ Micron Technology, Inc ...
Page 17
... SDRAM, regardless of whether the CLK signal is enabled. The SDRAM is effectively dese- lected. Operations already in progress are not affected. NO OPERATION (NOP) The NO OPERATION (NOP) command is used to perform a NOP to an SDRAM which is selected (CS# is LOW). This prevents unwanted commands from being registered during idle or wait states. Operations already in progress are not affected. ...
Page 18
... This is accomplished by using A10 to enable auto precharge in conjunction with a specific READ or WRITE PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev RP) after the precharge command is issued. Input A10 determines Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice. ...
Page 19
... SELF REFRESH The SELF REFRESH command can be used to retain data in the SDRAM, even if the rest of the system is powered down. When in the self refresh mode, the SDRAM retains data without external clocking. The SELF REFRESH command is initiated like an AUTO REFRESH command except CKE is disabled (LOW). Once the SELF REFRESH command is registered, all the inputs to the SDRAM become “ ...
Page 20
... Self refresh is not supported on automotive temperature (AT) devices. BANK/ROW ACTIVATION Before any READ or WRITE commands can be issued to a bank within the SDRAM, a row in that bank must be “opened.” This is accomplished via the ACTIVE command, which selects both the bank and the row to be activated. See Figure 6. ...
Page 21
... Figure 9 on page 22 shows general timing for each possible CL setting. Figure 8: READ Command CLK CKE RAS# CAS# WE# A0–A7 A8, A9, A11 A10 BA0,1 PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev RCD (MIN) When 2 < RCD (MIN ACTIVE NOP t RCD (MIN) t RCD (MIN) +0 ...
Page 22
... This is shown in Figure 10 on page 23 for CAS latencies of one, two and three; data element either the last of a burst of four or the last desired of a longer burst. This 128Mb SDRAM uses a pipelined architecture and there- fore does not require the 2n rule associated with a prefetch architecture. ...
Page 23
... Figure 10: Consecutive READ Bursts CLK COMMAND ADDRESS CLK COMMAND ADDRESS CLK COMMAND ADDRESS Notes: 1. Each READ command may be to either bank. DQM is LOW. PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev READ NOP NOP NOP BANK, COL OUT OUT OUT READ NOP NOP ...
Page 24
... READ burst, provided that I/O contention can be avoided given system design, there may be a possibility that the device driving the input data will go Low-Z before the SDRAM DQs go High-Z. In this case, at least a single-cycle delay should occur between the last read data and the WRITE command. ...
Page 25
... Figure 13: READ-to-WRITE with Extra Clock Cycle CLK DQM COMMAND ADDRESS Notes used for illustration. The READ command may be to any bank, and the WRITE com- mand may be to any bank. PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev READ NOP NOP NOP BANK, ...
Page 26
... In the case of a fixed-length burst being executed to completion, a PRECHARGE command issued at the optimum time (as described above) provides the same operation that would result from the same fixed-length burst with auto precharge. The disadvan- PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev met. Note that part of the row precharge time is T0 ...
Page 27
... This is shown in Figure 15 for each possible CL; data element the last desired data element of a longer burst. Figure 15: Terminating a READ Burst CLK COMMAND ADDRESS CLK COMMAND ADDRESS CLK COMMAND ADDRESS Notes: 1. DQM is LOW. PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev READ NOP NOP NOP TERMINATE BANK, COL OUT ...
Page 28
... WRITE command, and the data provided coincident with the new command applies to the new command. An example is shown in Figure 18 on page 29. Data either the last of a burst of two or the last desired of a longer burst. This 128Mb SDRAM uses a pipelined architecture and therefore does not require the 2n rule associated with a prefetch architecture ...
Page 29
... COMMAND ADDRESS Notes: 1. DQM is LOW. Each WRITE command may be to any bank. Figure 19: Random WRITE Cycles CLK COMMAND ADDRESS Notes: 1. Each WRITE command may be to any bank. DQM is LOW. PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev WRITE NOP NOP NOP BANK, COL n D ...
Page 30
... The disadvan- tage of the PRECHARGE command is that it requires that the command and address buses be available at the appropriate time to issue the command; the advantage of the PRECHARGE command is that it can be used to truncate fixed-length or full-page bursts. PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev ...
Page 31
... DQM is LOW at that time) will be the input data applied one clock previous to the BURST TERMINATE command. This is shown in Figure 22, where data n is the last desired data element of a longer burst. Figure 22: Terminating a WRITE Burst CLK COMMAND ADDRESS Notes: 1. DQMs are LOW. PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev > WR NOP ...
Page 32
... The power-down state is exited by registering a NOP or COMMAND INHIBIT and CKE HIGH at the desired clock edge (meeting PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev. L 1/09 EN HIGH CS# All Banks Bank Selected ...
Page 33
... Clock suspend mode is exited by registering CKE HIGH; the internal clock and related operation will resume on the subsequent positive clock edge. Figure 25: CLOCK SUSPEND During WRITE Burst CLK CKE INTERNAL CLOCK COMMAND ADDRESS D Notes: 1. For this example greater, and DM is LOW. PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev CKS ( ( ) ) ...
Page 34
... Concurrent Auto Precharge An access command to (READ or WRITE) another bank while an access command with auto precharge enabled is executing is not allowed by SDRAMs, unless the SDRAM supports concurrent auto precharge. Micron SDRAMs support concurrent auto precharge. Four cases where concurrent auto precharge occurs are defined below. ...
Page 35
... Interrupted by a WRITE (with or without auto precharge): A WRITE to bank m will interrupt a WRITE on bank n when registered. The precharge to bank n will begin after valid data WRITE to bank n will be data registered one clock prior to a WRITE to bank m (see Figure 30 on page 36). PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev CLK ...
Page 36
... Figure 29: WRITE With Auto Precharge Interrupted by a READ Internal States Notes: 1. DQM is LOW. Figure 30: WRITE With Auto Precharge Interrupted by a WRITE Internal States Notes: 1. DQM is LOW. PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev CLK WRITE - AP READ - AP COMMAND NOP NOP BANK n BANK m BANK n ...
Page 37
... H Notes: 1. CKE clock edge. 2. Current state is the state of the SDRAM immediately prior to clock edge n. 3. COMMAND MAND 4. All states and sequences not shown are illegal or reserved. 5. Exiting power-down at clock edge n will put the device in the all banks idle state in time for clock edge (provided that 6 ...
Page 38
... MAND INHIBIT or NOP commands, or allowable commands to the other bank should be issued on any clock edge occurring during these states. Allowable commands to the other bank are determined by its current state and Table 10, and according to Table 11 on page 40. PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev. L 1/09 EN WE# COMMAND (ACTION ...
Page 39
... Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice. 39 128Mb: x32 SDRAM Register Definition t RFC is met, the SDRAM will be in the all t MRD is met, the SDRAM will met, all banks will be in the idle state. ©2001 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
Page 40
... AUTO REFRESH, SELF REFRESH and LOAD MODE REGISTER commands may only be issued when all banks are idle BURST TERMINATE command cannot be issued to another bank; it applies to the bank represented by the current state only. PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev. L 1/09 EN CAS# WE# COMMAND (ACTION ...
Page 41
... WRITE to bank m will interrupt the WRITE on bank n when registered. The PRECHARGE to bank n will begin after istered. The last valid WRITE to bank n will be data registered one clock to the WRITE to bank m (see Figure 30 on page 36). PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev met, where WR begins when the WRITE to bank m is reg- Micron Technology, Inc ...
Page 42
... Storage temperature (plastic) Power dissipation Temperature and Thermal Impedance It is imperative that the SDRAM device’s temperature specifications, shown in Table 13 on page 43, be maintained in order to ensure the junction temperature is in the proper operating range to meet data sheet specifications. An important step in maintaining the proper junction temperature is using the device’ ...
Page 43
... For designs expected to last beyond the die revision listed, contact Micron Applications Engineering to confirm thermal impedance values. 2. Thermal resistance data is sampled from multiple lots and the values should be viewed as typical. 3. These are estimates; actual results may vary. PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev. L 1/09 EN Symbol ...
Page 44
... Figure 31: Example Temperature Test Point Location, 54-Pin TSOP: Top View Test point Figure 32: Example Temperature Test Point Location, 90-Ball VFBGA: Top View Test point PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev. L 1/09 EN 22.22mm 11.11mm 8.00mm 4.00mm 13.00mm 6.50mm Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice. ...
Page 45
... Auto refresh current CKE, CS# = HIGH Self refresh current: CKE ≤ 0.2V Table 17: Capacitance Note 2 applies to the entire table; notes appear on page 48 Parameter Input Capacitance: CLK Input Capacitance: All other input-only pins Input/Output Capacitance: DQs PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev. L 1/09 EN Symbol Vil ...
Page 46
... ACTIVE to READ or WRITE delay Refresh period (4,096 rows) Refresh period - Automotive (4,096 rows) PRECHARGE command period ACTIVE bank a to ACTIVE bank b command Transition time Write recovery time Exit self refresh to ACTIVE command PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev Symbol Min Max t AC (3) 5 ...
Page 47
... Data-in to ACTIVE command Data-in to PRECHARGE command Last data-in to burst STOP command Last data-in to new READ/WRITE command Last data-in to PRECHARGE command LOAD MODE REGISTER command to ACTIVE or REFRESH command Data-out to High-Z from PRECHARGE command PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev. L 1/09 EN Electrical Specifications SYMBOL -6 t CCD 1 t ...
Page 48
... V IH cannot be greater than one third of the cycle rate. V for a pulse width ≤ 3ns, and the pulse width cannot be greater than one third of the cycle rate. PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev dependent on output loading and cycle rates. Specified values are obtained ≤ ...
Page 49
... CK = 7ns for -7, 6ns for -6. 28. Check factory for availability of specially screened devices having t CK for 100 MHz and slower ( PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev and PRECHARGE commands). CKE may be used to reduce the 10ns and higher) in manual precharge. Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice. ...
Page 50
... ALL BA0, BA1 BANKS ( ( ) ) High 100µs (MIN) Power-up: V and Precharge DD CK stable all banks Notes: 1. The mode register may be loaded prior to the AUTO REFRESH cycles if desired. 2. Outputs are guaranteed High-Z after command is issued. PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev ...
Page 51
... AH BA0, BA1 BANK(S) High-Z DQ Two clock cycles Precharge all All banks idle, enter active banks power-down mode Notes: 1. Violating refresh requirements during power-down may result in a loss of data. PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev CKS NOP NOP ( ( ( ( ( ( Input buffers gated off while in ...
Page 52
... NOP t CMS t CMH DQM0 A0-A9, A11 COLUMN A10 BA0, BA1 BANK DQ Notes: 1. For this example and auto precharge is disabled. 2. A8, A9, and A11 = “Don’t Care.” PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev NOP NOP OUT OUT 128Mb: x32 SDRAM Timing Diagrams T6 ...
Page 53
... DQM 0-3 A0–A9, A11 ALL BANKS A10 SINGLE BANK BA0, BA1 BANK(S) High-Z DQ Precharge all active banks t Notes: 1. RFC must not be interrupted by any executable command; COMMAND INHIBIT or NOP commands must be applied on each positive clock edge during PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev ...
Page 54
... XSR requires minimum of two clocks regardless of frequency or timing general rule, any time self refresh is exited, the DRAM may not reenter the self refresh mode until all rows have been refreshed by the AUTO REFRESH command at the distributed refresh rate, 3a. The DRAM has been in self refresh mode for a minimum of 64µs prior to exiting. ...
Page 55
... BA0, BA1 BANK DQ Notes: 1. For this example and the READ burst is followed by a “manual” PRECHARGE. 2. x16: A9 and A11 = “Don’t Care” x32: A8, A9,and A11 = “Don’t Care” See Table 18 on page 46. PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev NOP READ ...
Page 56
... A0–A9, A11 ROW ENABLE AUTO PRECHARGE ROW A10 BA0, BA1 BANK DQ t RCD t RAS t RC Notes: 1. For this example and A8, A9, and A11 = “Don’t Care.” PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev READ NOP NOP t CMS t CMH COLUMN m 2 BANK OUT ...
Page 57
... A10 BA0, BA1 BANK RCD - BANK 0 t RAS - BANK BANK 0 t RRD Notes: 1. For this example and A8, A9, and A11 = “Don’t Care.” PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev READ NOP ACTIVE t CMS t CMH COLUMN m 2 ROW ROW BANK 0 BANK 4 ...
Page 58
... ROW ROW A10 BA0, BA1 BANK BANK DQ t RCD Notes: 1. For this example A8, A9, and A11 = “Don’t Care.” 3. Page left open; no PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev NOP NOP NOP t CMH Dout m D m+1 OUT t LZ 256 locations within same row ...
Page 59
... A0-A9, A11 ROW ENABLE AUTO PRECHARGE ROW A10 DISABLE AUTO PRECHARGE BA0, BA1 BANK DQ t RCD Notes: 1. For this example A8, A9, and A11 = “Don’t Care.” PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev READ NOP NOP t CMS t CMH COLUMN m 2 BANK OUT ...
Page 60
... BA0, BA1 BANK DQ t RCD t RAS t RC Notes: 1. For this example and the WRITE burst is followed by a “manual” PRECHARGE required between <D 3. A8, A9, and A11 = “Don’t Care.” PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev NOP WRITE NOP t CMS t CMH COLUMN m 3 ...
Page 61
... For this example and the WRITE burst is followed by a “manual” PRECHARGE. 2. Faster frequencies require two clocks (when 3. A8, A9, and A11 = “Don’t Care.” CLK available if running 100 MHz or slower. Check factory for availability. PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev WRITE ...
Page 62
... COLUMN m 3 ROW ENABLE AUTO PRECHARGE ROW A10 BA0, BA1 BANK RCD t RAS t RC Notes: 1. For this example Faster frequencies require two clocks (when 3. A8, A9, and A11 = “Don’t Care.” PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev NOP NOP NOP t CMH BANK ...
Page 63
... BANK RCD - BANK 0 t RAS - BANK BANK 0 t RRD Notes: 1. For this example Faster frequencies require two clocks (when 3. A8, A9, and A11 = “Don’t Care.” PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev WRITE NOP ACTIVE NOP t CMH ROW ROW BANK 0 BANK 1 ...
Page 64
... AH A0-A9, A11 ROW ROW A10 BA0, BA1 BANK DQ t RCD Notes: 1. A8, A9, and A11 = “Don’t Care.” must be satisfied prior to PRECHARGE command. 3. Page left open; no PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev WRITE NOP NOP t CMH t CMS COLUMN m 1 BANK ...
Page 65
... A0-A9, A11 ROW ROW A10 BA0, BA1 BANK DQ t RCD Notes: 1. For this example A8, A9, and A11 = “Don’t Care.” PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev NOP WRITE NOP t CMS t CMH COLUMN m 2 ENABLE AUTO PRECHARGE DISABLE AUTO PRECHARGE BANK ...
Page 66
... All dimensions are in millimeters. 2. Package width and length do not include mold protrusion; allowable mold protrusion is 0.25mm per side. 3. “2X” means the notch is present in two locations (both ends of the device). PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev. L 1/09 EN 0.61 2X 0.10 +0.07 -0.03 2X 2.80 11.76 ± ...
Page 67
... This data sheet contains minimum and maximum limits specified over the complete power supply and temperature range for production devices. Although considered final, these specifications are subject to change, as further product development and data characterization sometimes occur. PDF: 09005aef80872800/Source: 09005aef80863355 128MbSDRAMx32_2.fm - Rev. L 1/09 EN 6.40 0.80 TYP BALL A1 ID ...