SAF-C167CR-LM Infineon Technologies AG, SAF-C167CR-LM Datasheet

SAF-C167CR-LM
Available stocks
Related parts for SAF-C167CR-LM
SAF-C167CR-LM Summary of contents
Page 1
Microcomputer Components 16-Bit CMOS Single-Chip Microcontroller C167CR Data Sheet 06.95 Advance Information ...
Page 2
... A critical component is a component used in a life-support device or system whose failure can reasonably be expected to cause the failure of that life-support de- vice or system affect its safety or ef- fectiveness of that device or system. 2 Life support devices or systems are in- tended ( implanted in the human body, or (b) to support and/or maintain and sustain human life ...
Page 3
C167CR Revision History: Previous Releases: Page Subjects (changes compared to C167) 32 Register PICON added HYS, ILS IHS RST RWH P6L CC ID ...
Page 4
... Emulators, Evaluation Boards, HLL-Debuggers, Simulators, Logic Analyzer Disassemblers, Programming Boards On-Chip Bootstrap Loader 144-Pin MQFP Package (EIAJ) This document describes the SAB-C167CR-LM, the SAF-C167CR-LM and the SAK-C167CR-LM. For simplicity all versions are referred to by the term C167CR throughout this document. Semiconductor Group 16 bit Division ( bit) ...
Page 5
C167CR Revision History: Previous Releases: Page Subjects (changes compared to C167) 32 Register PICON added HYS, ILS IHS RST RWH RWL changed. P6L ...
Page 6
... It combines high CPU performance ( million instructions per second) with high peripheral functionality and enhanced IO-capabilities. It also provides on-chip high-speed RAM and clock generation via PLL. Figure 1 Logic Symbol Ordering Information Type Ordering Code SAB-C167CR-LM Q67121-C942 SAF-C167CR-LM Q67121-C946 SAK-C167CR-LM Q67121-C967 Semiconductor Group C167CR Package Function P-MQFP-144-1 16-bit microcontroller with ...
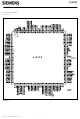
Page 7
Pin Configuration (top view) Figure 2 Semiconductor Group C167CR 4 C167CR A22/CAN_TxD /CAN_RxD ...
Page 8
Pin Definitions and Functions Symbol Pin Input (I) Number Output (O) P6 I/O P6 ... ... P8 I/O P8 I/O ... ...
Page 9
Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d) Symbol Pin Input (I) Number Output (O) P5 P5. P2 ...
Page 10
Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d) Symbol Pin Input (I) Number Output (O) P3 70, I/O P3.13 80, I/O P3. ...
Page 11
Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d) Symbol Pin Input (I) Number Output (O) WR WRL READY 97 I ALE PORT0: I/O P0L.0 - 100 - P0L.7, 107 P0H.0 - 108, P0H.7 111-117 Semiconductor Group ...
Page 12
Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d) Symbol Pin Input (I) Number Output (O) PORT1: I/O P1L.0 - 118 - P1L.7, 125 P1H.0 - 128 - P1H.7 135 132 I 133 I 134 I 135 I XTAL1 138 I XTAL2 137 O ...
Page 13
Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d) Symbol Pin Input (I) Number Output (O) V 17, 46, – CC 56, 72, 82, 93, 109, 126, 136, 144 V 18, 45, – SS 55, 71, 83, 94, 110, 127, 139, 143 Semiconductor Group ...
Page 14
Functional Description The architecture of the C167CR combines advantages of both RISC and CISC processors and of advanced peripheral subsystems in a very well-balanced way. The following block diagram gives an overview of the different on-chip components and of the ...
Page 15
Memory Organization The memory space of the C167CR is configured in a Von Neumann architecture which means that code memory, data memory, registers and I/O ports are organized within the same linear address space which includes 16 MBytes. The entire ...
Page 16
Central Processing Unit (CPU) The main core of the CPU consists of a 4-stage instruction pipeline, a 16-bit arithmetic and logic unit (ALU) and dedicated SFRs. Additional hardware has been spent for a separate multiply and divide unit, a bit-mask ...
Page 17
The CPU disposes of an actual register context consisting wordwide GPRs which are physically allocated within the on-chip RAM area. A Context Pointer (CP) register determines the base address of the active register bank to be ...
Page 18
Interrupt System With an interrupt response time within a range from just 250 ns to 600 ns (in case of internal program execution), the C167CR is capable of reacting very fast to the occurrence of non- deterministic events. The architecture ...
Page 19
Source of Interrupt or PEC Service Request CAPCOM Register 0 CAPCOM Register 1 CAPCOM Register 2 CAPCOM Register 3 CAPCOM Register 4 CAPCOM Register 5 CAPCOM Register 6 CAPCOM Register 7 CAPCOM Register 8 CAPCOM Register 9 CAPCOM Register 10 ...
Page 20
Source of Interrupt or PEC Service Request CAPCOM Timer 1 CAPCOM Timer 7 CAPCOM Timer 8 GPT1 Timer 2 GPT1 Timer 3 GPT1 Timer 4 GPT2 Timer 5 GPT2 Timer 6 GPT2 CAPREL Register A/D Conversion Complete ADCIR A/D Overrun ...
Page 21
The C167CR also provides an excellent mechanism to identify and to process exceptions or error conditions that arise during run-time, so-called ‘Hardware Traps’. Hardware traps cause immediate non-maskable system reaction which is similar to a standard interrupt service (branching to ...
Page 22
Capture/Compare (CAPCOM) Units The CAPCOM units support generation and control of timing sequences channels with a maximum resolution of 400 ns (at 20-MHz system clock). The CAPCOM units are typically used to handle high speed I/O ...
Page 23
CAPCOM2 Figure 5 CAPCOM Unit Block Diagram Semiconductor Group *) 20 C167CR ...
Page 24
PWM Module The Pulse Width Modulation Module can generate up to four PWM output signals using edge- aligned or center-aligned PWM. In addition the PWM module can generate PWM burst signals and single shot outputs. The frequency range of the ...
Page 25
The state of this latch may be used to clock timer T5 may be output on a port pin (T6OUT). The overflows/underflows of timer T6 can additionally be used to clock the CAPCOM timers T0 or T1, and ...
Page 26
... Block Diagram of GPT2 Watchdog Timer The Watchdog Timer represents one of the fail-safe mechanisms which have been implemented to prevent the controller from malfunctioning for longer periods of time. The Watchdog Timer is always enabled after a reset of the chip, and can only be disabled in the time interval until the EINIT (end of initialization) instruction has been executed. Thus, the chip’ ...
Page 27
A/D Converter For analog signal measurement, a 10-bit A/D converter with 16 multiplexed input channels and a sample and hold circuit has been integrated on-chip. It uses the method of successive approximation. The sample time (for loading the capacitors) and ...
Page 28
Serial Channels Serial communication with other microcontrollers, processors, terminals or external peripheral components is provided by two serial interfaces with different functionality, an Asynchronous/ Synchronous Serial Channel (ASC0) and a High-Speed Synchronous Serial Channel (SSC). ASC0 is upward compatible with ...
Page 29
Parallel Ports The C167CR provides up to 111 I/O lines which are organized into eight input/output ports and one input port. All port lines are bit-addressable, and all input/output lines are individually (bit-wise) programmable as inputs or outputs via direction ...
Page 30
Instruction Set Summary The table below lists the instructions of the C167CR in a condensed way. The various addressing modes that can be used with a specific instruction, the operation of the instructions, parameters for conditional execution of instructions, and ...
Page 31
Instruction Set Summary (cont’d) Mnemonic MOV(B) MOVBS MOVBZ JMPA, JMPI, JMPR JMPS J(N)B JBC JNBS CALLA, CALLI, CALLR CALLS PCALL TRAP PUSH, POP SCXT RET RETS RETP RETI SRST IDLE PWRDN SRVWDT DISWDT EINIT ATOMIC EXTR EXTP(R) EXTS(R) NOP Semiconductor ...
Page 32
Special Function Registers Overview The following table lists all SFRs which are implemented in the C167CR in alphabetical order. Bit-addressable SFRs are marked with the letter “b” in column “Name”. SFRs within the Extended SFR-Space (ESFRs) are marked with the ...
Page 33
Special Function Registers Overview (cont’d) Name Physical 8-Bit Address Address CC3 FE86 43 H CC3IC b FF7E BF H CC4 FE88 44 H CC4IC b FF80 C0 H CC5 FE8A 45 H CC5IC b FF82 C1 H CC6 FE8C 46 ...
Page 34
Special Function Registers Overview (cont’d) Name Physical 8-Bit Address Address CC17IC b F162 CC18 FE64 32 H CC18IC b F164 CC19 FE66 33 H CC19IC b F166 CC20 FE68 34 H ...
Page 35
Special Function Registers Overview (cont’d) Name Physical 8-Bit Address Address CCM0 b FF52 A9 H CCM1 b FF54 AA H CCM2 b FF56 AB H CCM3 b FF58 AC H CCM4 b FF22 91 H CCM5 b FF24 92 H ...
Page 36
Special Function Registers Overview (cont’d) Name Physical 8-Bit Address Address ODP2 b F1C2 ODP3 b F1C6 ODP6 b F1CE ODP7 b F1D2 ODP8 b F1D6 ...
Page 37
Special Function Registers Overview (cont’d) Name Physical 8-Bit Address Address PP3 F03E PSW b FF10 88 H PT0 F030 PT1 F032 PT2 F034 PT3 F036 ...
Page 38
Special Function Registers Overview (cont’d) Name Physical 8-Bit Address Address SSCEIC b FF76 BB H SSCRB F0B2 SSCRIC b FF74 BA H SSCTB F0B0 SSCTIC b FF72 B9 H STKOV FE14 0A H STKUN ...
Page 39
Special Function Registers Overview (cont’d) Name Physical 8-Bit Address Address T6IC b FF68 F050 T78CON b FF20 90 H T7IC b F17A T7REL F054 F052 E 29 ...
Page 40
... Absolute Maximum Ratings Ambient temperature under bias ( SAB-C167CR-LM............................................................................................................ SAF-C167CR-LM SAK-C167CR-LM Storage temperature ( T )........................................................................................– 150 Voltage on pins with respect to ground ( CC Voltage on any pin with respect to ground ( Input current on any pin during overload condition Absolute sum of all input currents during overload condition.............................................. |100 mA| Power dissipation..................................................................................................................... 1.5 W Note: Stresses above those listed under “ ...
Page 41
... +70 ˚C for SAB-C167CR- ˚C for SAF-C167CR- 125 ˚C for SAK-C167CR-LM A Parameter Input low voltage (TTL) Input low voltage (Special Threshold) Input high voltage, all except RSTIN and XTAL1 (TTL) Input high voltage RSTIN ...
Page 42
Parameter 4) Port 6 active current PORT0 configuration current XTAL1 input current 5) Pin capacitance (digital inputs/outputs) Power supply current Idle mode supply current Power-down mode supply current Notes 1) This specification is not valid for outputs which are switched ...
Page 43
Figure 8 Supply/Idle Current as a Function of Operating Frequency Semiconductor Group 40 C167CR ...
Page 44
... A/D Converter Characteristics ˚C for SAB-C167CR- – ˚C for SAF-C167CR- – 125 ˚C for SAK-C167CR- 0.1 V; AREF CC Parameter Analog input voltage range Sample time Conversion time Total unadjusted error Internal resistance of reference ...
Page 45
Notes 1) V may exceed AIN AGND AREF cases will be X000 or X3FF H 2) During the sample time the input capacitance internal resistance of the analog source must allow the capacitance to reach its final ...
Page 46
Testing Waveforms AC inputs during testing are driven at 2.4 V for a logic ‘1’ and 0.4 V for a logic ‘0’. Timing measurements are made at Figure 9 Input Output Waveforms For timing purposes a port pin is no ...
Page 47
AC Characteristics Definition of Internal Timing The internal operation of the C167CR is controlled by the internal CPU clock CPU clock can trigger internal (e.g. pipeline) or external (e.g. bus cycles) operations. The specification of the external timing (AC Characteristics) ...
Page 48
Phase Locked Loop When pin P0.15 (P0H.7) is high (‘1’) during reset the on-chip phase locked loop is enabled and provides the CPU clock. The PLL multiplies the input frequency by 4 (i.e. f fourth transition of the PLL circuit ...
Page 49
... AC Characteristics External Clock Drive XTAL1 ˚C for SAB-C167CR- ˚C for SAF-C167CR- 125 ˚C for SAK-C167CR-LM A Parameter Oscillator period High time Low time Rise time Fall time 1) T For temperatures above 2) The clock input signal must reach the defined levels ...
Page 50
... Multiplexed Bus ˚C for SAB-C167CR- ˚C for SAF-C167CR- 125 ˚C for SAK-C167CR- (for PORT0, PORT1, Port 4, ALE, RD, WR, BHE, CLKOUT) = 100 (for Port 6, CS) = 100 ALE cycle time = 6 TCL + 2 ...
Page 51
Parameter Symbol RD to valid data in t (with RW-delay valid data in (no RW-delay) t ALE low to valid data in Address to valid data Data hold after RD rising edge t Data ...
Page 52
Parameter Symbol RdCS to Valid Data In t (no RW delay) t RdCS, WrCS Low Time (with RW delay) t RdCS, WrCS Low Time (no RW delay) Data valid to WrCS t t Data hold after RdCS Data float after ...
Page 53
ALE CSx A23-A16 (A15-A8) BHE t 6 Read Cycle BUS RD RdCSx Write Cycle BUS WR, WRL, WRH WrCSx Figure 14-1 External Memory Cycle: Multiplexed Bus, With Read/Write Delay, Normal ALE Semiconductor Group ...
Page 54
ALE t 38 CSx A23-A16 (A15-A8) BHE t 6 Read Cycle BUS RD RdCSx Write Cycle BUS WR, WRL, WRH WrCSx Figure 14-2 External Memory Cycle: Multiplexed Bus, With Read/Write Delay, Extended ALE Semiconductor Group ...
Page 55
ALE CSx A23-A16 (A15-A8) BHE t 6 Read Cycle BUS RD RdCSx Write Cycle BUS WR, WRL, WRH WrCSx Figure 14-3 External Memory Cycle: Multiplexed Bus, No Read/Write Delay, Normal ALE Semiconductor Group ...
Page 56
ALE t 38 CSx A23-A16 (A15-A8) BHE t 6 Read Cycle BUS RD RdCSx Write Cycle BUS WR, WRL, WRH WrCSx Figure 14-4 External Memory Cycle: Multiplexed Bus, No Read/Write Delay, Extended ALE Semiconductor Group ...
Page 57
... Demultiplexed Bus ˚C for SAB-C167CR- ˚C for SAF-C167CR- 125 ˚C for SAK-C167CR- (for PORT0, PORT1, Port 4, ALE, RD, WR, BHE, CLKOUT) = 100 (for Port 6, CS) = 100 ALE cycle time = 4 TCL + 2 ...
Page 58
Parameter Symbol ALE rising edge after RD Address hold after RD ALE falling edge low to Valid Data hold after RD, WR ALE falling edge to t RdCS, ...
Page 59
ALE CSx A23-A16 A15-A0 BHE t 6 Read Cycle BUS (D15-D8) D7-D0 RD RdCSx Write Cycle BUS (D15-D8) D7-D0 WR, WRL, WRH WrCSx Figure 15-1 External Memory Cycle: Demultiplexed Bus, With Read/Write Delay, Normal ALE Semiconductor Group t ...
Page 60
ALE t 38 CSx A23-A16 A15-A0 BHE t 6 Read Cycle BUS (D15-D8) D7-D0 RD RdCSx Write Cycle BUS (D15-D8) D7-D0 WR, WRL, WRH WrCSx Figure 15-2 External Memory Cycle: Demultiplexed Bus, With Read/Write Delay, Extended ALE Semiconductor ...
Page 61
ALE CSx A23-A16 A15-A0 BHE t 6 Read Cycle BUS (D15-D8) D7-D0 RD RdCSx Write Cycle BUS (D15-D8) D7-D0 WR, WRL, WRH WrCSx Figure 15-3 External Memory Cycle: Demultiplexed Bus, No Read/Write Delay, Normal ALE Semiconductor Group t ...
Page 62
ALE t 38 CSx A23-A16 A15-A0 BHE t 6 Read Cycle BUS (D15-D8) D7-D0 RD RdCSx Write Cycle BUS (D15-D8) D7-D0 WR, WRL, WRH WrCSx Figure 15-4 External Memory Cycle: Demultiplexed Bus, No Read/Write Delay, Extended ALE Semiconductor ...
Page 63
... CLKOUT and READY +70 ˚C for SAB-C167CR- -40 to +85 ˚C for SAF-C167CR- -40 to +125 ˚C for SAK-C167CR- (for PORT0, PORT1, Port 4, ALE, RD, WR, BHE, CLKOUT) = 100 (for Port 6, CS) = 100 pF L Parameter CLKOUT cycle time ...
Page 64
... MTTC waitstate this delay is zero. 7) The next external bus cycle may start here. Semiconductor Group READY 1) waitstate order to be safely synchronized. This is guaranteed C167CR 6) MUX/Tristate see 6) ...
Page 65
... ˚C for SAB-C167CR- – ˚C for SAF-C167CR- – 125 ˚C for SAK-C167CR- (for PORT0, PORT1, Port 4, ALE, RD, WR, BHE, CLKOUT) = 100 (for Port 6, CS) = 100 pF L Parameter HOLD input setup time ...
Page 66
CLKOUT t 61 HOLD HLDA 1) BREQ CSx (On P6.x) Other Signals Figure 17 External Bus Arbitration, Releasing the Bus Notes 1) The C167CR will complete the currently running bus cycle before granting bus access. 2) This is the first ...
Page 67
CLKOUT HOLD HLDA t 62 BREQ CSx (On P6.x) Other Signals Figure 18 External Bus Arbitration, (Regaining the Bus) Notes 1) This is the last chance for BREQ to trigger the indicated regain-sequence. Even if BREQ is activated earlier, the ...