M30624MGM-437FP MITSUBISHI, M30624MGM-437FP Datasheet

M30624MGM-437FP
Related parts for M30624MGM-437FP
M30624MGM-437FP Summary of contents
Page 1
... NMI pin) 5 (built-in feedback resistor, and external ceramic or quartz oscillator) Timer ............................................................. 82 Serial I/O ..................................................... 112 A-D Converter ............................................. 152 D-A Converter ............................................. 162 CRC Calculation Circuit .............................. 164 Programmable I/O Ports ............................. 166 Electrical characteristic ............................... 181 Flash memory version ................................. 234 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group = 3V ...
Page 2
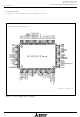
... Figure 1.1.1. Pin configuration (top view M16C/62 Group Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER /CS0 /CS1 /CS2 6 48 ...
Page 3
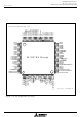
... Figure 1.1.2. Pin configuration (top view M16C/62 Group Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER /CS0 48 ...
Page 4
... R1L R1H R1L Vector table INTB R3 A0 Stack pointer ISP FB FB USP Flag register SB FLG Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Port P4 Port P5 Port P6 System clock generator OUT X -X CIN COUT Clock synchronous SI/O (8 bits 2 channels) ...
Page 5
... Mask ROM, flash memory 5V version 2.7 to 5.5V (f(X )=7MH IN : One-time PROM version 25.5mW (f 10MH IN 5V 5mA Available (to 1.2M bytes or 4M bytes) CMOS high performance silicon gate 100-pin plastic mold QFP Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group , V =5V) CC =3V, with software one-wait =3V, with software one-wait without software wait without software wait) ...
Page 6
... Description Mitsubishi plans to release the following products in the M16C/62 group: (1) Support for mask ROM version, external ROM version, one-time PROM version, EPROM version, and Flash memory version (2) ROM capacity (3) Package 100P6S-A : Plastic molded QFP (mask ROM, one-time PROM, and flash memory versions) ...
Page 7
... Description Type No – Figure 1.1.5. Type No., memory size, and package Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Package type Package 100P6S 100P6Q 100D0 ROM No. Omitted for blank one-time PROM version,and EPROM version, and flash memory version ...
Page 8
... They also output address (A Input/output This is an 8-bit I/O port equivalent to P0. Output These pins output CS 0 select signals used to specify an access space. A Output order address bits. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Function pin. Supply the V pin pin when starting ...
Page 9
... A-D converter extended input pins, or A-D trigger input pins as selected by software. Input/output This is an 8-bit I/O port equivalent to P6. Pins in this port also function as A-D converter input pins. Furthermore, P10 input pins for the key input interrupt function. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Function or a clock selected by software ...
Page 10
... Note 2: In memory expansion mode, can not be used. C0000 16 Note 3: These memory maps show an instance in which PM13 is set to 0; but in the case of M30624MG/FG, they show an instance in which PM13 is set to 1. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER . If the starting addresses of subroutines 16 ...
Page 11
... INTB H b15 b0 USP b15 b0 ISP Address registers b15 b0 SB b15 b0 FLG Frame base registers IPL U Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER b0 Program counter b0 Interrupt table L register b0 User stack pointer b0 Interrupt stack pointer b0 Static base register b0 Flag register ...
Page 12
... Bit 6: Interrupt enable flag (I flag) This flag enables a maskable interrupt. An interrupt is disabled when this flag is “0”, and is enabled when this flag is “1”. This flag is cleared to “0” when the interrupt is acknowledged. 12 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER ...
Page 13
... Carry flag Debug flag Zero flag Sign flag Register bank select flag Overflow flag Interrupt enable flag Stack pointer select flag Reserved area Processor interrupt priority level Reserved area Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER 13 ...
Page 14
... RD WR CS0 Single chip mode Address Figure 1.6.2. Reset sequence RESET 24cycles FFFFC FFFFD 16 16 FFFFC FFFFE 16 FFFFC Content of reset vector 16 FFFFE 16 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER 4.0V 0.8V Content of reset vector FFFFE 16 Content of reset vector 16 ...
Page 15
... RD output (“H” level is output) BCLK output HLDA output (The output value depends on the input to the HOLD pin) HOLD input (floating) ALE output (“L” level is output) RDY input (floating) Input port (floating) Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER CNV = BYTE = V SS ...
Page 16
... SS 16 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER (0053 )··· (0054 )··· (0055 )··· ...
Page 17
... The content of other registers and RAM is undefined when the microcomputer is reset. The initial values must therefore be set. Note1: When the V level is applied to the CNV pin Note2: This register is only exist in flash memory version. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER (03D7 )··· (03DC )· ...
Page 18
... INT1 interrupt control register (INT1IC) 005E 16 INT2 interrupt control register (INT2IC) 005F 16 0060 16 0061 16 0062 16 0063 16 0064 16 0065 16 032A 16 032B 16 032C 16 032D 16 032E 16 032F 16 0330 16 0331 16 0332 16 0333 16 0334 16 0335 16 0336 16 0337 16 0338 16 0339 16 033A 16 033B 16 033C 16 033D 16 033E 16 033F 16 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group ...
Page 19
... Flash memory control register 0 (FMR0) (Note1) 03B7 16 DMA0 request cause select register (DM0SL) 03B8 16 03B9 16 DMA1 request cause select register (DM1SL) 03BA 16 03BB 16 03BC 16 CRC data register (CRCD) 03BD 16 CRC input register (CRCIN) 03BE 16 03BF 16 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER 19 ...
Page 20
... Port P9 (P9) Port P8 direction register (PD8) Port P9 direction register (PD9) Port P10 (P10) Port P10 direction register (PD10) Pull-up control register 0 (PUR0) Pull-up control register 1 (PUR1) Pull-up control register 2 (PUR2) Port control register (PCR) Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER ...
Page 21
... Address YYYYY 16 16 F8000 16 16 F0000 16 16 E8000 16 16 E0000 16 16 F0000 16 16 E8000 16 16 E0000 16 16 C0000 16 16 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Accessible memory space byte Up to 1.2M bytes bytes (16K bytes) (128K bytes) (32K bytes) 21 ...
Page 22
... E8000 16 16 E0000 16 16 F0000 16 16 E8000 16 16 E0000 16 16 C0000 16 16 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER through 16 ________ _______ 04000 16 176K bytes to = the extent of memory expanded 2FFFF 16 CS0:active in fetching a program CS1, CS2, CS3:active in accessing data 30000 16 to ...
Page 23
... DQ0 to DQ7 AD0 to AD16 Flash ROM (1M byte) SRAM (128K bytes) Usable for Usable for data only programs only CS2 (128K bytes) Usable both for programs and Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER _______ CS0 (1008K bytes) for data 23 ...
Page 24
... E0000 16 16 F0000 16 16 E8000 16 16 E0000 16 16 C0000 16 16 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER When reset 00 16 Description Not offset 1: Offset Bank Bank Bank Bank 3 ...
Page 25
... CS0 W R Note: If only one chip select terminal (S1 or S2) is present, decoding by use of an external circuit is required. Figure 1.8.6. An example of connecting the MCU with external memories in expansion mode 2 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER . for the area from 40000 ...
Page 26
... Bank 5 2C0000 300000 Data area Bank 6 340000 380000 Program/ data area Bank 7 3C0000 Program/ data area 3FFFFF Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER M16C address Offset bit = 1 40000 40000 BFFFF Bank 0 40000 BFFFF 40000 BFFFF Bank 1 40000 BFFFF ...
Page 27
... SS ”. 2 pin, changing the processor mode bits selects the mode. Therefore, SS pin ” to the processor mode is selected bits. 2 pin Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER ) applies a (software) reset to the 16 27 ...
Page 28
... M bytes, expansion mode bytes) For details, see “Memory space expansion functions”. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER R ...
Page 29
... F8000 16 External area : Accessing this area allows the user to F0000 16 E8000 16 E0000 16 F0000 16 E8000 16 E0000 16 C0000 16 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER SFR area Internal RAM area Internally reserved area External area access a device connected externally to the microcomputer. 29 ...
Page 30
... FFFFF 16 After reset, and set the nternal reserved area expansion bit to "1" I Note: The reset vector lies in an area between D0000 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Microprocessor mode SFR area (1K bytes) Internal RAM area ...
Page 31
... Bit 6 of processor mode register 0 BYTE pin Bits 4 and 5 of processor mode register are multiplexed with Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER ) are used to change the bus settings. 16 Switching factor to P4 become part of the 0 3 ...
Page 32
... HLDA HLDA HLDA HOLD HOLD HOLD ALE ALE ALE RDY RDY RDY Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Memory expansion mode “00” “11” (Note 1) multiplexed bus for the (separate bus) entire space 16 bits 8 bit “ ...
Page 33
... BFFFF 16 (512K bytes 28000 256K bytes) (96K bytes) 40000 to 16 FFFFF 16 (512K bytes X 8) Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER function as the data bus Bits the chip select control 4 7 Chip select signal CS1 ...
Page 34
... CS2 output enable bit CS3 CS3 output enable bit CS0W CS0 wait bit CS1W CS1 wait bit CS2W CS2 wait bit CS3W CS3 wait bit Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Chip select signal CS1 CS2 When PM13=0 04000 07FFF 28000 to ...
Page 35
... Read 1 byte of data When BYTE pin = “L” ALE Data (Note Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER ) select the 16 ________ Status of external data bus Status of external data bus A Address 0 /A Address Data (Note 1) ...
Page 36
... The RDY signal is invalid when setting “1” _____ Maintain status when RDY signal received On tsu(RDY - BCLK) Accept timing of RDY signal tsu(RDY - BCLK) Accept timing of RDY signal ________ Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER ________ ________ ), but the RDY pin should be treated as Status ________ ...
Page 37
... Undefined SFR accessed Address output Floating Output data RD, WR, WRL, WRH output BHE output Output "H" Output "L" Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER __________ Status Internal ROM/RAM accessed Maintain status before accessed address of external area Floating Undefined Output " ...
Page 38
... Invalid Invalid 0 Invalid 1 Invalid (Note (Note) Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER ) (Note Bus cycle 2 BCLK cycles 1 BCLK cycle 2 BCLK cycles 1 BCLK cycle 2 BCLK cycles 2 BCLK cycles 3 BCLK cycles 3 BCLK cycles ...
Page 39
... Figure 1.12.5. Typical bus timings using software wait Bus cycle(Note) Bus cycle(Note) Output Address Bus cycle(Note) Output Address Bus cycle(Note) Address Data output Address Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Input Address Bus cycle(Note) Input Address Bus cycle(Note) Address Address Input ...
Page 40
... Externally derived clock can be input OUT (Note OUT (Note COUT Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Sub-clock generating circuit • CPU’s operating clock source • Timer A/B’s count clock source Crystal oscillator CIN COUT Available ...
Page 41
... X CIN COUT 1/32 CM04 Sub clock OUT R Main clock CM02 CM05 1/2 1/2 a CM06=0 CM17,CM16=01 CM06=0 CM17,CM16= Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER f C32 SIO2 SIO2 SIO2 CM07 Divider ...
Page 42
... COUT 1SIO2 8SIO2 ) to “1” and then executing a WAIT instruction. 16 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER ). Stopping the 16 ), the sub-clock can However, be sure the memory expan changes to “1” when shifting from high- ,f ...
Page 43
... Division by 2 mode Division by 4 mode Division by 16 mode ) to “1” before writing to this register. 16 turns “H”, and the built-in feedback resistor is cut off. X OUT Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Function R 7 generation COUT ...
Page 44
... Retains status before stop mode “H” “H” “H” Retains status before stop mode Retains status before stop mode Valid only in single-chip mode Valid only in single-chip mode Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER ) enable stops all oscillation and the microcom- ...
Page 45
... Retains status before wait mode Valid only in single-chip mode selected Valid only in single-chip mode 32 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Single-chip mode Retains status before wait mode Does not stop Does not stop when the WAIT peripheral function clock stop bit is “ ...
Page 46
... Invalid 0 0 Invalid Invalid 0 1 Invalid 1 1 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group or vice versa, the clock to which CIN Operating mode of BCLK Division by 2 mode Division by 4 mode Division by 8 mode Division by 16 mode No-division mode Low-speed mode Low power dissipation mode ...
Page 47
... All oscillators stop. The CPU and all built-in peripheral functions stop. This mode, among the three modes listed here, is the most effective in decreasing power consumption. Figure 1.13.5 is the state transition diagram of the above modes. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER ...
Page 48
... CM06 = “0” (Note 3) (divided-by-16 mode) CM04 = “1” )/4 BCLK : f(X )/ CM07 = “0” CM06 = “0” CM17 = “1” CM16 = “1” Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER CPU operation stopped WAIT instruction Wait mode Interrupt CPU operation stopped WAIT ...
Page 49
... Note: Writing a value to an address after “1” is written to this bit returns the bit to “0” . Other bits do not automatically return to “0” and they must therefore be reset by the program. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER ), system clock control reg- ...
Page 50
... Peripheral I/O (Note) An interrupt which can be enabled (disabled) by the interrupt enable flag (I flag) or whose interrupt priority can be changed by priority level. (I flag) or whose interrupt priority cannot be changed by priority level. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Undefined instruction (UND instruction) Overflow (INTO instruction) ...
Page 51
... When returning from the interrupt routine, the U flag is returned to the state it was before the acceptance of interrupt re- quest. So far as software numbers 32 through 63 are concerned, the stack pointer does not make a shift. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER 51 ...
Page 52
... These are interrupts that timer B generates. ________ • INT0 interrupt through INT5 interrupt ______ An INT interrupt occurs if either a rising edge or a falling edge or a both edge is input to the INT pin. 52 ____________ _______ ___ ________ Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER ______ ...
Page 53
... There is an address-matching interrupt enable bit FFFEF Do not use FFFF3 FFFF7 Do not use FFFFB External interrupt by input to NMI pin FFFFF 16 16 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER LSB High address Remarks , program execution starts from 16 _______ 53 ...
Page 54
... UART1 receive +84 to +87 (Note 1) Timer A0 +88 to +91 (Note 1) Timer A1 +92 to +95 (Note 1) Timer A2 +96 to +99 (Note 1) Timer A3 Timer A4 Timer B0 Timer B1 Timer B2 INT0 INT1 INT2 to Software interrupt Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Remarks Cannot be masked I flag Cannot be masked I flag ). 16 ...
Page 55
... The interrupt request bit and the interrupt priority level selection bit are located in the interrupt control register of each interrupt. Also, the interrupt enable flag (I flag) and the IPL are located in the flag register (FLG). Figure 1.14.3 shows the memory map of the interrupt control registers. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER 55 ...
Page 56
... Reserved bit Nothing is assigned attempt to write to these bits, write “0”. The value, if read, turns out to be indeterminate. interrupt request for that register. For details, see the precautions for interrupts. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER When reset XXXXX000 ...
Page 57
... High Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group Enabled interrupt priority levels Interrupt levels 1 and above are enabled Interrupt levels 2 and above are enabled Interrupt levels 3 and above are enabled Interrupt levels 4 and above are enabled Interrupt levels 5 and above are enabled ...
Page 58
... Instructions : AND, OR, BCLR, BSET 58 ; Disable interrupts. ; Four NOP instructions are required when using HOLD function. ; Enable interrupts. ; Disable interrupts. ; Dummy read. ; Enable interrupts. ; Push Flag register onto stack ; Disable interrupts. ; Enable interrupts. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER ...
Page 59
... Time from interrupt request is generated to when the instruction then under execution is completed. (b) Time in which the instruction sequence is executed. Figure 1.14.4. Interrupt response time Interrupt request acknowledged Interrupt sequence (a) (b) Interrupt response time Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Time Instruction in interrupt routine 59 ...
Page 60
... Odd 20 cycles (Note 1) ________ Indeterminate SP-2 SP-2 Indeterminate contents Indeterminate Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER 8-Bit bus, without wait 20 cycles (Note 1) 20 cycles (Note 1) 20 cycles (Note 1) 20 cycles (Note SP-4 vec ...
Page 61
... Stack pointer m value before interrupt occurs Stack status after interrupt request is acknowledged Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Stack area LSB [SP] New stack Program counter ( pointer value Program counter (PC ...
Page 62
... H H Finished saving registers in two operations. Stack area Sequence in which order registers are saved ) ( (4) Saved simultaneously, all 8 bits Flag register (FLG ) L (1) Program (2) counter ( Finished saving registers in four operations. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER ...
Page 63
... Figure 1.14.8. Hardware interrupts priorities Interrupt resolution circuit When two or more interrupts are generated simultaneously, this circuit selects the interrupt with the highest priority level. Figure 1.14.9 shows the circuit that judges the interrupt priority level. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER 63 ...
Page 64
... DBC NMI Reset Figure 1.14.9. Maskable interrupts priorities (peripheral I/O interrupts) 64 SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Level 0 (initial value) High Priority of peripheral I/O interrupts (if priority levels are same) Low Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group Interrupt request level judgment output To clock generating circuit (Fig.1.13.3) Interrupt request accepted ...
Page 65
... IFSR4 INT4 interrupt polarity switching bit IFSR5 INT5 interrupt polarity switching bit IFSR6 Interrupt request cause select bit IFSR7 Interrupt request cause select bit Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER ________ ________ When reset Function 0 : One edge ...
Page 66
... Key input interrupt control register Port P10 direction 7 register direction register 7 direction 6 Interrupt control circuit direction 5 direction 4 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER ______ register (bit 5 at address 5 (address 004D ) 16 Key input interrupt request to 4 ...
Page 67
... RMAD0 RMAD1 Function Address setting register for address match interrupt Nothing is assigned attempt to write to these bits, write “0”. The value, if read, turns out to be indeterminated. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER When reset XXXXXX00 2 Function Interrupt disabled ...
Page 68
... Reading the contents of the P8 register 5 _______ _______ _______ ________ to INT pins is changed, the interrupt request bit is sometimes set to “1” Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER will then be set to “0” Accepting an interrupt 16 _______ ________ 0 ...
Page 69
... Set the interrupt enable flag to “1” (Enable interrupt) ______ ; Disable interrupts. ; Four NOP instructions are required when using HOLD function. ; Enable interrupts. ; Disable interrupts. ; Dummy read. ; Enable interrupts. ; Push Flag register onto stack ; Disable interrupts. ; Enable interrupts. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER 69 ...
Page 70
... X watchdog timer count (32768) BCLK ). 16 Prescaler “CM07 = 0” “WDC7 = 0” 1/16 “CM07 = 0” “WDC7 = 1” 1/128 “CM07 = 1” 1/2 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER is selected for the IN ) selects the prescaler division ratio (by 16 BCLK ) and when 16 Watchdog timer Watchdog timer interrupt request Set to “ ...
Page 71
... Symbol Address WDTS 000E 16 Function The watchdog timer is initialized and starts counting after a write instruction to this register. The watchdog timer value is always initialized to “7FFF regardless of whatever value is written. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER When reset 000XXXXX 2 Function R W Must always be set to “0” ...
Page 72
... DMA1 destination pointer DAR1 (20) DMA1 forward address pointer (20) (Note) , 0038 ) 16 16 DMA latch high-order bits Data bus low-order bits Data bus high-order bits Note: Pointer is incremented by a DMA request. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER (addresses 0022 to 0020 ) 16 16 (addresses 0026 to 0024 ...
Page 73
... DMA enable bit is “0”. Can be read at any time. However, when the DMA enable bit is “1”, reading the register set up as the forward register is the same as reading the value of the forward address pointer. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER to 003F ...
Page 74
... Expanded cause If software trigger is selected, a Software DMA DSR DMA request is generated by request bit setting this bit to “1” (When read, the value of this bit is always “0”) Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER When reset 00 16 Function R W ...
Page 75
... Source address direction 0 : Fixed DSD select bit (Note Forward Destination address 0 : Fixed DAD direction select bit (Note Forward cannot be set to “1” simultaneously. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER When reset 00 16 Function R W /serial I/O3 (DMS=1) /serial I/O4 (DMS=1) ...
Page 76
... In an attempt to write to these bits, write “0”. The value, if read, turns out to be “0”. b0 Symbol TCR0 TCR1 Function • Transfer counter Set a value one less than the transfer count Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group Address When reset 0022 to 0020 Indeterminate 16 ...
Page 77
... For example (2) in Figure 1.16.5, if data is being transferred in 16-bit units on an 8-bit bus, two bus cycles are required for both the source read cycle and the destination write cycle. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER ...
Page 78
... Dummy Source Destination cycle Dummy Source Destination cycle Source Source + 1 Destination Source Source + 1 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER CPU use CPU use CPU use CPU use CPU use CPU use Dummy CPU use cycle Dummy Destination CPU use ...
Page 79
... Odd 1 Even — Odd — Even 1 Odd 2 Even — Odd — SFR area Separate bus With wait No wait 2 2 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Memory expansion mode Microprocessor mode cycles cycles cycles — 1 — — ...
Page 80
... INTi pin, for example). With an external factor selected, the DMA request bit is timed to turn to "0" immediately before data transfer starts similarly to the state in which an internal factor is selected. 80 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER ...
Page 81
... DMA transmission request signals due to external factors concurrently occur. BCLK DMA0 DMA1 CPU INT0 DMA0 request bit INT1 DMA1 request bit Figure 1.16.6. An example of DMA transfer effected by external factors Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Obtainm ent of the bus right 81 ...
Page 82
... Event counter mode • Timer mode • One-shot mode • PWM mode • Event counter mode ) is shared with RxD and the TB5 pin careful Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Clock prescaler f C32 1/32 Reset Timer A0 interrupt Timer A0 Timer A1 interrupt ...
Page 83
... Event counter mode • Timer mode • Pulse width measuring mode Noise filter • Event counter mode and the TA0 pin careful Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Clock prescaler f 1/32 C32 Reset ) set to “1” Timer B0 interrupt ...
Page 84
... Operation mode select bit TMOD1 MR0 Function varies with each operation mode MR1 MR2 MR3 TCK0 Count source select bit (Function varies with each operation mode) TCK1 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER ”. 16 Low-order High-order 8 bits 8 bits Reload register (16) Counter (16) ...
Page 85
... Timer A4 up/down flag TA2P Timer A2 two-phase pulse signal processing select bit TA3P Timer A3 two-phase pulse signal processing select bit TA4P Timer A4 two-phase pulse signal processing select bit Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Address When reset 0387 ,0386 Indeterminate 16 16 ...
Page 86
... Bit symbol Bit name Nothing is assigned attempt to write to these bits, write “0”. The value, if read, turns out to be indeterminate. CPSR Clock prescaler reset flag Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Function 1 : Timer start When read, the value is “0” ...
Page 87
... Note 1: The settings of the corresponding port register and port direction register are invalid. Note 2: The bit can be “0” or “1”. Note 3: Set the corresponding port direction register to “0”. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER pin’s input signal IN pin’ ...
Page 88
... Note 3: Valid only when counting an external signal. Note 4: When an “L” signal is input to the TAi OUT the upcount is activated. Set the corresponding port direction register to “0”. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER n : Set value pin’s polarity is reversed ...
Page 89
... TAi IN counts down rising and falling edges on the TAi TAi OUT Count up all edges TAi IN (i=3,4) Count up all edges Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER or TAi pin IN OUT n : Set value pin is “H” Down ...
Page 90
... For timer A2 and A4 mode registers, this bit can be “0” or “1”. Note 2: When performing two-phase pulse signal processing, make sure the two-phase pulse signal processing operation select bit (address 0384 sure to set the event/trigger select bit (addresses 0382 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER When reset ...
Page 91
... If timer overflow is selected, this bit can be “1” or “0” Note 3: Set the corresponding port direction register to “0”. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER ...
Page 92
... C32 pin is selected by the event/trigger select bit iIN (addresses 0382 and 0383 ). If timer overflow is selected, this bit can be “1” or “0” Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER m : values set to timer Ai register’s low-order address Function ...
Page 93
... – Cleared to “0” when interrupt request is accepted, or cleaerd by software , f ) C32 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER 8 93 ...
Page 94
... Function varies with each operation mode MR1 MR2 MR3 TCK0 Count source select bit (Function varies with each operation mode) TCK1 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Data bus high-order bits Data bus low-order bits High-order 8 bits Low-order 8 bits Reload register (16) ...
Page 95
... Bit name Nothing is assigned attempt to write to these bits, write “0”. The value, if read, turns out to be indeterminate effect CPSR Clock prescaler reset flag 1 : Prescaler is reset Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Address When reset , 0390 Indeterminate 16 ...
Page 96
... In an attempt to write to this bit, write “0”. The value, if read in timer mode, turns out to be indeterminate Count source select bit TCK0 TCK1 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER When reset 00XX0000 2 00XX0000 2 Function R ...
Page 97
... IN If timer's overflow is selected, this bit can be “0” or “1”. Note 2: Timer B0, timer B3. Note 3: Timer B1, timer B2, timer B4, timer B5. Note 4: Set the corresponding port direction register to “0”. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER 2 2 Function ...
Page 98
... Note Timer has overflowed b7 b6 Count source select bit C32 timer Bi mode register. This flag cannot be set to “1” by software. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Function (Note 2) (Note 3) ...
Page 99
... Cleared to “0” when interrupt request is accepted, or cleared by software. Transfer Transfer Transfer (measured value) (indeterminate (measured value) value) (Note 1) (Note 1) Cleared to “0” when interrupt request is accepted, or cleared by software. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Transfer (measured value) (Note 1) (Note 2) Transfer (measured value) (Note 1) (Note 1) (Note 2) ...
Page 100
... Three-phase mode 0 control bit 1: Three-phase mode 1 Short circuit timer count 0 : Not to be used source select bit (Note) 1 Always set to “0” Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER R W Description (Note 1) to output and W, and works the 5 R ...
Page 101
... Indeterminate 16 Function Set occurrence frequency of timer B2 interrupt request phase PWM control register 0, do not change the B2 interrupt occurrences frequency set counter to deal with the timer function for three-phase motor control. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Function ...
Page 102
... TA3S Timer A3 count start flag TA4S Timer A4 count start flag TB0S Timer B0 count start flag TB1S Timer B1 count start flag TB2S Timer B2 count start flag Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Address When reset ,0388 Indeterminate 16 16 ,038A Indeterminate ...
Page 103
... Invalid in timer mode. MR3 This bit can neither be set nor reset. When read in timer mode, its content is indeterminate Count source select bit TCK0 TCK1 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Function ...
Page 104
... U phase, V phase and V phase, and W phase and W phase concurrently go to “L” result, the port become the state of set by port direction register. 104 0 ). Setting “0” in this bit causes the ports to be the state 16 _______ ___ ___ Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER ___ , and P7 ...
Page 105
... Timers’ functions for three-phase motor control Figure 1.18.5. Block diagram for three-phase waveform mode Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER 105 ...
Page 106
... DU0 (bit 0 at 034A 16 16 ___ , the timer A4 counter starts counting the 16 , 0346 ), and starts outputting one-shot pulses. When timer A4 fin Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER ). In this mode, each 16 ) for setting the 16 0). ) provides the means to choose 16 ...
Page 107
... U phase output signal U phase U phase Dead time Note: Set to triangular wave modulation mode and to three-phase mode 1. Figure 1.18.6. Timing chart of operation ( Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER ___ ___ The three-phase shift register p o shifts in synchronization with the falling edge of the A4 output ...
Page 108
... DUB0 (bit 1 at 034A 16 ) allows the user to output the waveforms as shown in Figure 1.18.7, that is, to ___ Timer B2 interrupt occurres. Rewriting three-phase buffer register Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER ), and to DU1 (bit 0 at 034B 16 ___ ...
Page 109
... DUB0 (bit 1 at 034A 16 ) and set “1” in DUB1 (bit 1 at 034A 16 , timer B2 generates an interrupt, and timer A4 16 ___ ___ ___ ___ Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER ). In this mode, the 16 ) and the effective interrupt addition ...
Page 110
... Data transfer is made from the three- phase buffer register to the three- Interrupt occurres. phase shift register in step with the Rewriting the value of timer A4. timing of the timer B overflow Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER The three-phase p shift register shifts in synchronization with the falling edge of timer A4 ...
Page 111
... Figure 1.18.9. Timing chart of operation (4) Interrupt occurres. Rewriting the value of timer A4. Rewriting three-phase output buffer register n Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Data transfer is made from the three- phase buffer register to the three- phase shift register in step with the timing of the timer B overflow. ...
Page 112
... Possible Impossible Possible Possible Impossible Impossible Impossible Possible (Note 3) Possible Impossible Impossible CMOS output CMOS output Impossible Impossible Impossible Impossible Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group UART2 (Note 1) Possible (Note 1) (Note 1) Possible (Note 2) (Note 1) Possible (Note 1) (Note 1) Impossible Impossible Possible (Note 4) (Note 3) Impossible ...
Page 113
... Vcc CTS/RTS disabled CTS Values set to UART0 bit rate generator (BRG0 Values set to UART1 bit rate generator (BRG1 Values set to UART2 bit rate generator (BRG2) Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Receive Reception clock Transmit/ control circuit receive ...
Page 114
... Clock synchronous UART (9 bits) type PAR UART enabled PAR Clock UART (7 bits) synchronous disabled type UART (7 bits) UART (8 bits) “0” Clock synchronous type Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER UARTi receive register UARTi receive ...
Page 115
... PAR UART UART(7 bits) synchronous disabled (7 bits) type UART (8 bits) “0” Clock synchronous type Error signal output disable Error signal output enable Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER UART2 receive register UART2 receive ...
Page 116
... Indeterminate 16 U1BRG 03A9 Indeterminate 16 U2BRG 0379 Indeterminate 16 Function Assuming that set value = n, BRGi divides the count source Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER R W Function R W (During UART mode) Receive data Invalid overrun error 1 : Overrun error found ...
Page 117
... TxD, RxD I/O polarity reverse reverse bit 1 : Reverse Usually set to “0” 2 ” when I C mode is used. 2 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Function R W (During UART mode Transfer data 7 bits long Transfer data 8 bits long ...
Page 118
... Transmit data is output at rising edge of transfer clock and receive data is input at falling edge 0 : LSB first 1 : MSB first (Note 3) Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Function R W (During UART mode selected ...
Page 119
... Continuous receive mode enabled Data logic select bit reverse 1 : Reverse Must be fixed to “0” enable bit Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Function R W (During UART mode Transmission disabled 1 : Transmission enabled 0 : Data present in ...
Page 120
... Auto clear function Must always be “0” select bit of transmit enable bit Must always be “0” Transmit start condition select bit Always set to “0” Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER 2 Function R (During UART mode Transmit buffer empty ( ...
Page 121
... UARTi receive buffer register is completed This error occurs when the next data is ready before contents of UARTi receive buffer register are read out to FF that is set to the UART bit rate generator Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Specification , 03A8 16 16 ...
Page 122
... UART0 CTS and RTS pins each can be assigned to separate pins Whether to reverse data in writing to the transmission buffer register or reading the reception buffer register can be selected. This function is reversing TxD port output and RxD port input. All I/O data level is reversed. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Specification _______ _______ ...
Page 123
... PRY Invalid in clock synchronous serial I/O mode PRYE IOPOL TxD, RxD I/O polarity reverse bit (Note 1) Note 1: Usually set to “0”. Note 2: Set the corresponding port direction register to “0”. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER When reset Function ...
Page 124
... CTS/RTS disable bit (bit 4 at address 03A4 CTS/RTS function select bit (bit 2 at address 03A4 CTS/RTS disable bit (bit 4 at address 03A4 _______ _______ Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group _______ , 16 , 03A8 , 0378 ) = “0” ...
Page 125
... Meet the following conditions are met when the CLK input before data reception = “H” • Transmit enable bit • Receive enable bit • Dummy data write to UARTi transmit buffer register Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Stopped pulsing because transfer enable bit = “0” D ...
Page 126
... Note: This applies when the CLK polarity select bit = “0”. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER , 03AC 16 Note 1: The CLK pin level when not 7 transferring data is “H”. 7 Note 2: The CLK pin level when not transferring data is “ ...
Page 127
... CLK ) = “1”, and writing to transmit buffer register Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER ). (See Figure 1.19.13 CLK , bit 5 at address 037D 127 ...
Page 128
... This flag is set (= 1) when any of the overrun, framing, and parity errors is encountered to FF that is set to the UARTi bit rate generator Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER , 03A8 , 0378 16 16 ...
Page 129
... This function is reversing logic value of transferring data. Start bit, parity bit and stop bit are not reversed I/O polarity switch X X This function is reversing T D port output and R X level is reversed. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER D port input. All I/O data X 129 ...
Page 130
... Stop bit length select bit PRY Odd / even parity select bit PRYE Parity enable bit IOPOL TxD, RxD I/O polarity reverse bit (Note) Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER When reset Function Transfer data 7 bits long ...
Page 131
... CTS/RTS disable bit (bit 4 at address 03A4 CTS/RTS function select bit (bit 2 at address 03A4 CTS/RTS disable bit (bit 4 at address 03A4 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER , 16 , 03A8 , 0378 ) = “0” ...
Page 132
... frequency of BRGi count source ( frequency of BRGi count source (external clock) EXT n : value set to BRGi Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Stopped pulsing because transmit enable bit = “0” ...
Page 133
... Cleared to “0” when interrupt request is accepted, or cleared by software frequency of BRG2 count source ( value set to BRG2 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Note ...
Page 134
... RTS0 ( CTS0 ( _______ _______ Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Stop bit _______ ) to "1" inputs/outputs the CTS signal and 16 _______ _______ _______ _______ _______ ). OUT CTS RTS ...
Page 135
... pin output and R D pin input. The level of any data to be input or output pin and the input level of the Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Start bit P : Even parity ...
Page 136
... On the transmission side, a parity error is detected by the level of input to the R D pin when a transmission interrupt occurs that is set to the UARTi bit rate generator Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER = “101 16 = “0” “1” and “1” respectively “0”). ...
Page 137
... Read to receive buffer Cleared to “0” when interrupt request is accepted, or cleared by software frequency of BRG2 count source ( value set to BRG2 and RxD are connected Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Note ...
Page 138
... D5 Hi you choose the inverse format Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER ) assigned “1”, you can output an “L” Start bit P : Even Parity SP : Stop bit data is inverted ...
Page 139
... Clock asynchronous serial I/O (UART) mode Figure 1.19.25 shows the example of connecting the SIM interface. Connect T pull-up. Figure 1.19.25. Connecting the SIM interface Microcomputer TxD 2 RxD 2 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER D and R D and apply SIM card 139 ...
Page 140
... Reading the terminal when 0 is assigned to the direction register H level (when 0 is assigned to the CLK polarity select bit mode is in use. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER 16 Function (During UART mode) Must always be “0” Must always be “0” ...
Page 141
... SDA, clock input respectively. A delay circuit is added to the SDA transmission output staying “H”. The stop condition detection interrupt 1 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER 2 C bus) interface are explained mode selection bit. ...
Page 142
... Bit 3 of the UART2 special mode register is used as SCL- and L-synchronous output enable bit. Setting this bit to “1” goes the P7 1 142 ) is used as the arbitration loss detecting flag control bit. 16 data register to “0” in synchronization with the SCL terminal level going to “L”. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER ...
Page 143
... In normal state CLK TxD Enabling transmission With "1: falling edge of RxD " selected 2 CLK TxD RxD Figure 1.19.28. Some other functions added SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER level and TxD level do not match, but the nonconfor Timer A0 overflow Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group 143 ...
Page 144
... SCL wait output bit 2 0: UART2 clock 1: 0 output 0: Enabled SDA output disable bit 1: Disabled (high impedance) Start/stop condition Set this bit to "1" control bit (refer to Table 1.19.11) Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER 2 C mode. Figure Function 2 ...
Page 145
... The rising edge of the final bit of the reception clock ) of the main clock. IN Duration for Duration for setting up holding Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group 2 C mode selection bit mode IICM2 = 1 of the final bit of the clock) UART2 reception (the falling edge ...
Page 146
... With IICM set to 1, the port terminal readable * IICM=0 even assigned I/0 Timer 2 C mode used as the SCL wait output bit. Setting this bit to 16 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER To DMA0, DMA1 IICM=0 UART2 transmission/ or IICM2=1 NACK interrupt request IICM=1 and IICM2=0 To DMA0 ...
Page 147
... UART2 transfer clock. There can be instances in which arbitration lost detection flag is turned on. SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER ) is used as the UART2 initialization bit used as the SCL pin wait output bit 2. Setting this used as the SDA output disable bit. Setting this bit 16 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group 147 ...
Page 148
... A value set in the S I/O transfer rate register i (0363 Figure 1.19.31. S I/O3, 4 block diagram 148 SMi1 SMi0 Synchronous 1/2 circuit SMi3 Transfer rate register (8) SMi6 SMi6 S I/O counter i (3) SMi2 SMi3 SMi5 LSB MSB S I/Oi transmission/reception register (8) , 0367 ). 16 16 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Data bus 1/(ni+1) S I/Oi interrupt request 8 ...
Page 149
... Symbol Address S3BRG 0363 16 S4BRG 0367 16 Indeterminate Symbol Address S3TRR 0360 16 S4TRR 0364 16 Indeterminate Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER 40 16 Description output i output disable (high impedance) i output, CLK function ) in advance to write to the 16 . “1” ...
Page 150
... OUTi through FF set in the S I/Oi transfer rate register ( 4). 16 initial value set bit), make sure the CLKi pin input is held high. OUTi Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER , 0366 = “1”): f1/2(ni+1 0366 = 0):Input from the CLKi terminal (Note 2) ...
Page 151
... OUT port select bit ="1". OUT Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER pin output level during a non-transfer OUTi S I/Oi port select bit SMi3 = 0 SOUTi initial value select bit ...
Page 152
... AD 8-bit resolution: 28 cycles, 10-bit resolution exceeds 10MH , and make IN Z frequency to 250kH AD frequency to 1MH AD Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER ) when the A-D REF , reducing the power REF to connect V 16 /divide-by =f ...
Page 153
... A-D control register 0 (address 03D6 16 Decoder CH2,CH1,CH0=000 CH2,CH1,CH0=001 CH2,CH1,CH0=010 CH2,CH1,CH0=011 OPA1,OPA0=0,0 CH2,CH1,CH0=100 CH2,CH1,CH0=101 CH2,CH1,CH0=110 CH2,CH1,CH0=111 OPA1,OPA0=1,1 OPA0=1 OPA1,OPA0=0,1 OPA1=1 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group AD A-D conversion rate selection ) ) V ref Comparator V IN OPA1, OPA0 Normal operation ANEX0 ANEX1 External op-amp mode ...
Page 154
... External op-amp b7 b6 OPA0 ANEX0 and ANEX1 are not used connection mode bit ANEX0 input is A-D converted ANEX1 input is A-D converted OPA1 External op-amp connection mode indeterminate. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER 2 Function R is selected 0 is selected 1 ...
Page 155
... Two high-order bits of A-D conversion result • During 8-bit mode When read, the content is indeterminate Nothing is assigned attempt to write to these bits, write “0”. The value, if read, turns out to be “0”. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER When reset 0000XXX0 2 ...
Page 156
... ANEX0 and ANEX1 are not used connection mode bit ANEX0 input is A-D converted ANEX1 input is A-D converted OPA1 External op-amp connection mode Note: If the A-D control register is rewritten during A-D conversion, the conversion result is indeterminate. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER 2 Function selected ...
Page 157
... ANEX0 and ANEX1 are not used connection mode bit ANEX0 input is A-D converted ANEX1 input is A-D converted OPA1 External op-amp connection mode Note: If the A-D control register is rewritten during A-D conversion, the conversion result is indeterminate. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER 2 Function selected ...
Page 158
... External op-amp OPA0 ANEX0 and ANEX1 are not used connection mode ANEX0 input is A-D converted bit (Note ANEX1 input is A-D converted OPA1 External op-amp connection mode is indeterminate. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER pins ...
Page 159
... External op-amp OPA0 ANEX0 and ANEX1 are not used connection mode ANEX0 input is A-D converted bit (Note ANEX1 input is A-D converted OPA1 External op-amp connection mode is indeterminate. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER pins ...
Page 160
... External op-amp connection mode Note 1: If the A-D control register is rewritten during A-D conversion, the conversion result is indeterminate. Note 2: Neither ‘01’ nor ‘10’ can be selected with the external op-amp connection mode bit. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER AN ...
Page 161
... AN 16 Resistor ladder Successive conversion register ANEX0 ANEX1 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER ) to “1”. When 16 cycle Comparator is 7 161 ...
Page 162
... Figure 1.21.1. Block diagram of D-A converter 162 X n/ 256 ( 255) REF V : reference voltage REF Performance R-2R method 8 bits 2 channels D-A register0 (8) (Address 03D8 D-A0 output enable bit D-A register1 (8) (Address 03DA D-A1 output enable bit Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER ) ...
Page 163
... DA1E D-A1 output enable bit 1 : Output enabled Symbol Address DAi (i = 0,1) 03D8 03DA Indeterminate Function Output value of D-A conversion Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER When reset 00 16 Function R W When reset ...
Page 164
... Symbol Address b0 CRCD 03BD Function CRC calculation result output register Symbo CRCIN Function Data input register Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER generate CRC code. (Addresses 03BD , 03BC ) 16 16 When reset , 03BC Indeterminate 16 16 Values that ...
Page 165
... LSB CRC input register After CRC calculation is complete b0 CRC data register 0A41 16 Stores CRC code Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER [03BD , 03BC ] 16 16 CRCIN [03BE ] 16 CRCD [03BD , 03BC ] ...
Page 166
... This register is valid in the following: • External bus width is 8 bits in microprocessor mode or memory expansion mode. • Port P1 can be used as a port in multiplexed bus for the entire space. 166 SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER ). Each port can be set independently for Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group is 5 ...
Page 167
... Input to respective peripheral functions Pull-up selection Direction register Data bus Port latch Input to respective peripheral functions Note :1 symbolizes a parasitic diode. Do not apply a voltage higher than Vcc to each port. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER "1" Output (Note) (Note) (Note) (Note) ...
Page 168
... Port latch Pull-up selection Direction register Port latch Pull-up selection "1" Output Port latch NMI interrupt input "1" Output Port latch symbolizes a parasitic diode. symbolizes a parasitic diode. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER (Note1) (Note1) (Note1) (Note1) (Note2) ...
Page 169
... Pull-up selection Direction register "1" Output Port latch Input to respective peripheral functions Analog input symbolizes a parasitic diode. Do not apply a voltage higher than Vcc to each port. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER (Note) (Note) D-A output enabled (Note) (Note) 169 ...
Page 170
... Pull-up selection Direction register Port latch Pull-up selection Direction register "1" Output Port latch symbolizes a parasitic diode. symbolizes a parasitic diode. side is added to the mask ROM version. CC Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER (Note (Note) (Note2) (Note1) (Note2) (Note1) ...
Page 171
... Port P8 direction register Input mode Port P8 direction register 6 (Functions as an input port Output mode Port P8 direction register 7 (Functions as an output port) Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Address When reset , 03E6 , 03E7 , 03EA 03EF ...
Page 172
... Port P8 register “L” level data Port P8 register “H” level data Port P8 register 5 Port P8 register 6 Port P8 register 7 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Address When reset , 03E4 , 03E5 , 03E8 Indeterminate 03ED , 03F1 , 03F4 Indeterminate ...
Page 173
... Pulled high pull- pull- P10 to P10 pull- P10 to P10 pull- Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER When reset 00 16 Function R W When reset 00 (Note 2) 16 Function R W terminal, this register becomes SS When reset 00 16 ...
Page 174
... Bit symbol Bit name PCR0 Port P1 control register Nothing is assigned attempt to write to these bits, write “0”. The value, if read, turns out to be “0”. Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER When reset Function 0 : When input port, read port input level ...
Page 175
... Port P4 / CS1 CS3 Open BCLK (Note memory expansion mode or in microprocessor mode ) is set to “1”, connect Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER or V via via via a resistor (pull-up (Input mode) · ...
Page 176
... Bi register after setting a value in the timer Bi register with a count halted but before the counter starts counting gets a proper value. 176 pin is outputting an “H” level in this instance, the output level goes to “L”, and OUT Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER ”. Reading the 16 ” ...
Page 177
... Do not get either into stop mode with the NMI pin set to “L”. ____________ 16 by software sets enabled highest priority interrupt source request bit to “0” software. 16 _______ Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER will then be set to “0” Accepting an 16 _______ ...
Page 178
... Disable interrupts. ; Enable interrupts. line is long, you should insert an approximately 5K ohm SS pin and connect and V pin for noise and latch up countermeasure Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER should be a short line for improve and ...
Page 179
... Cover the transparent glass window with a shield or others during the read mode because exposing to sun light or fluorescent lamp can cause erasing the information. A shield to cover the transparent window is available from Mitsubishi Electric Corp. Be careful that the shield does not touch the EPROM lead pins. ...
Page 180
... Mask ROM confirmation form (2) Mark specification sheet (3) ROM data : EPROMs or floppy disks *: In the case of EPROMs, there sets of EPROMs are required per pattern the case of floppy disks, 3.5-inch double-sided high-density disk (IBM format) is required per pattern. 180 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER ...
Page 181
... P10 to P10 , Ta=25 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Rated value =AV -0.3 to 6.5 CC =AV CC -0.3 to 6.5 -0.3 to Vcc+0.3 -0.3 to 6.5(Note 1) -0.3 to Vcc+0.3 -0.3 to 6.5 C 300 - -40 to 85(Note 2) -65 to 150 Unit ...
Page 182
... One-time PROM No wait) 16.0 16.0 7. 14.791MH 7.0 5.0 0.0 0.0 2.7 4.2 5.5 2.7 Supply voltage [V] (BCLK: no division) CC =4.2V to 5.5V and f(BCLK) CC Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER = 2. – Standard Min Typ. Max. 2.7 5.0 5.5 Vcc 0 0 0.8Vcc Vcc 0.8Vcc 6.5 0.8Vcc Vcc 0.5Vcc Vcc 0 ...
Page 183
... CIN version Square wave, in flash memory f(X )=32kHz CIN When a WAIT instruction is executed (Note) Ta=25°C when clock is stopped Ta=85°C when clock is stopped . C32 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER 5V f(X SS Standard Unit Typ Min 3 ...
Page 184
... REF REF CC ) exceeds 10 MHz, and make ØAD equal to or lower than 10 MHz 16MH unless otherwise specified Measuring condition Note ( ) Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER 5V, Vss = REF SS Standard Min. Typ. Max. 10 ±3 input ± ...
Page 185
... ac3(RD – DB) = f(BCLK 5V Parameter Parameter 9 10 – 45 [ns] 9 – 45 [ns] 9 – 45 [ns] Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER unless otherwise specified) Standard Unit Min. Max ...
Page 186
... IN OUT t TAi input hold time h(T UP) OUT IN- 186 SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Parameter Parameter Parameter Parameter Parameter Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group unless otherwise specified) Standard Unit Min. Max. ns 100 Standard Unit Min. Max. ns 400 ...
Page 187
... INTi input HIGH pulse width t w(INL) INTi input LOW pulse width = 5V Parameter Parameter Parameter Parameter Parameter _______ Parameter Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER unless otherwise specified) Standard Unit Min. Max. 100 ns ns ...
Page 188
... Measuring condition Parameter 9 10 – 40 [ns 0. 30pF hold time Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER CM15 = “1” unless Standard Min. Max Figure 1.26.1 – ...
Page 189
... Measuring condition Parameter Figure 1.26.1 9 – 40 [ns 0. 30pF hold time Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER CM15 = “1” unless Standard Unit Min. Max ...
Page 190
... Measuring condition Figure 1.26.1 9 [ns] 9 [ns] 9 [ns] 9 [ns – 40 [ns] 9 [ns] 9 – 25 [ns] Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER CM15 = “1” unless Standard Unit Min. Max (Note) ns (Note ...
Page 191
... Timing Figure 1.26.1. Port P0 to P10 measurement circuit SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER 30pF P10 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group 191 ...
Page 192
... INTi input Figure 1.26.2. V =5V timing diagram (1) CC 192 SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER t c(TA) t w(TAH) t w(TAL) t c(UP) t w(UPH) t w(UPL) t h(T –UP c(TB) t w(TBH) t w(TBL) t c(AD) t w(ADL) t c(CK) t w(CKH) t w(CKL su(D–C) d(C–Q) t w(INL) t w(INH) Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group su(UP– h(C–Q) t h(C–D) ...
Page 193
... V =5V CC • Input timing voltage : Determined with V • Output timing voltage : Determined with V Figure 1.26.3. V =5V timing diagram (2) CC tsu(RDY–BCLK) t h(BCLK–HOLD) t d(BCLK–HLDA) Hi– =1.0V Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER th(BCLK–RDY) =4.0V IH =2.5V, V =2.5V OH 193 ...
Page 194
... Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER ...
Page 195
... V IL =0.8V Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER 4ns.min t h(RD–CS) 0ns.min 4ns.min t h(BCLK–ALE) –4ns.min 0ns.min t h(RD–DB) 0ns.min 4ns.min t h(WR–CS) 0ns ...
Page 196
... Data output Address t d(DB–WR) (tcyc*3/2–40)ns.min t t h(BCLK–ALE) d(AD–WR) –4ns.min 0ns.min t d(BCLK–WR) 25ns.max =5V CC Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER h(BCLK–CS) h(RD–CS) 4ns.min (tcyc/2)ns.min Data input Address t h(RD–DB) 0ns.min t SU(DB– ...
Page 197
... Ta=25°C when clock is stopped Ta=85°C when clock is stopped . C32 Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER 3V f(X SS ...
Page 198
... IN Z Measuring condition REF REF REF ) = 7MH (Note2) unless otherwise specified Measuring condition (Note1) Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER 3V REF SS Standard Min. Typ. Max 3V, = f(X )/2 ...
Page 199
... EPROM, One-time PROM Mask ROM, Flash memory (5V version) EPROM, One-time PROM Mask ROM, Flash memory (5V version) Parameter 9 – 90 [ns] 9 – 90 [ns] 9 – 90 [ns] Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER unless otherwise specified) Standard Unit Min. Max. ns 143 ...
Page 200
... IN t TAi input hold time h(T UP) OUT IN- 200 SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER Parameter Parameter Parameter Parameter Parameter Mitsubishi microcomputers M16C / 62 Group unless otherwise specified) Standard Unit Min. Max. 150 Standard Unit Min. Max. 600 ...