ATmega128A Atmel Corporation, ATmega128A Datasheet - Page 4

ATmega128A
Manufacturer Part Number
ATmega128A
Description
Manufacturer
Atmel Corporation
Specifications of ATmega128A
Flash (kbytes)
128 Kbytes
Pin Count
64
Max. Operating Frequency
16 MHz
Cpu
8-bit AVR
# Of Touch Channels
16
Hardware Qtouch Acquisition
No
Max I/o Pins
53
Ext Interrupts
8
Usb Speed
No
Usb Interface
No
Spi
1
Twi (i2c)
1
Uart
2
Graphic Lcd
No
Video Decoder
No
Camera Interface
No
Adc Channels
8
Adc Resolution (bits)
10
Adc Speed (ksps)
15
Analog Comparators
1
Resistive Touch Screen
No
Temp. Sensor
No
Crypto Engine
No
Sram (kbytes)
4
Eeprom (bytes)
4096
Self Program Memory
YES
Dram Memory
No
Nand Interface
No
Picopower
No
Temp. Range (deg C)
-40 to 85
I/o Supply Class
2.7 to 5.5
Operating Voltage (vcc)
2.7 to 5.5
Fpu
No
Mpu / Mmu
no / no
Timers
4
Output Compare Channels
8
Input Capture Channels
2
Pwm Channels
7
32khz Rtc
Yes
Calibrated Rc Oscillator
Yes
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
ATmega128A XC6SLXFGG484CTV BCM7366ZBK W2SG0008I-T
Manufacturer:
XILINX
0
Company:
Part Number:
ATmega128A-16AU
Manufacturer:
ATMEL
Quantity:
6
Part Number:
ATmega128A-16AU
Manufacturer:
ATMEL/爱特梅尔
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
ATmega128A-AU
Manufacturer:
ATMEL
Quantity:
9 000
Company:
Part Number:
ATmega128A-AU
Manufacturer:
ATMEL
Quantity:
3 480
Part Number:
ATmega128A-AU
Manufacturer:
ATMEL/爱特梅尔
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
ATmega128A-AUR
Manufacturer:
ATMEL
Quantity:
3 000
Part Number:
ATmega128A-AUR
Manufacturer:
ATMEL/爱特梅尔
Quantity:
20 000
®
®
The Atmel
AVR
core combines a rich instruction set with 32 general purpose working registers.
All the 32 registers are directly connected to the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), allowing two inde-
pendent registers to be accessed in one single instruction executed in one clock cycle. The
resulting architecture is more code efficient while achieving throughputs up to ten times faster
than conventional CISC microcontrollers.
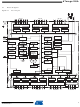
The ATmega128A provides the following features: 128Kbytes of In-System Programmable
Flash with Read-While-Write capabilities, 4Kbytes EEPROM, 4Kbytes SRAM, 53 general pur-
pose I/O lines, 32 general purpose working registers, Real Time Counter (RTC), four flexible
Timer/Counters with compare modes and PWM, 2 USARTs, a byte oriented Two-wire Serial
Interface, an 8-channel, 10-bit ADC with optional differential input stage with programmable
gain, programmable Watchdog Timer with Internal Oscillator, an SPI serial port, IEEE std.
1149.1 compliant JTAG test interface, also used for accessing the On-chip Debug system and
programming and six software selectable power saving modes. The Idle mode stops the CPU
while allowing the SRAM, Timer/Counters, SPI port, and interrupt system to continue function-
ing. The Power-down mode saves the register contents but freezes the Oscillator, disabling all
other chip functions until the next interrupt or Hardware Reset. In Power-save mode, the asyn-
chronous timer continues to run, allowing the user to maintain a timer base while the rest of the
device is sleeping. The ADC Noise Reduction mode stops the CPU and all I/O modules except
Asynchronous Timer and ADC, to minimize switching noise during ADC conversions. In Standby
mode, the Crystal/Resonator Oscillator is running while the rest of the device is sleeping. This
allows very fast start-up combined with low power consumption. In Extended Standby mode,
both the main Oscillator and the Asynchronous Timer continue to run.
The device is manufactured using Atmel’s high-density nonvolatile memory technology. The On-
chip ISP Flash allows the program memory to be reprogrammed in-system through an SPI serial
interface, by a conventional nonvolatile memory programmer, or by an On-chip Boot program
running on the AVR core. The boot program can use any interface to download the application
program in the application Flash memory. Software in the Boot Flash section will continue to run
while the Application Flash section is updated, providing true Read-While-Write operation. By
combining an 8-bit RISC CPU with In-System Self-Programmable Flash on a monolithic chip,
the Atmel ATmega128A is a powerful microcontroller that provides a highly flexible and cost
effective solution to many embedded control applications.
The ATmega128A AVR is supported with a full suite of program and system development tools
including: C compilers, macro assemblers, program debugger/simulators, in-circuit emulators,
and evaluation kits.
2.2
ATmega103 and ATmega128A Compatibility
The ATmega128A is a highly complex microcontroller where the number of I/O locations super-
sedes the 64 I/O locations reserved in the AVR instruction set. To ensure backward compatibility
with the ATmega103, all I/O locations present in ATmega103 have the same location in
ATmega128A. Most additional I/O locations are added in an Extended I/O space starting from
$60 to $FF, (i.e., in the ATmega103 internal RAM space). These locations can be reached by
using LD/LDS/LDD and ST/STS/STD instructions only, not by using IN and OUT instructions.
The relocation of the internal RAM space may still be a problem for ATmega103 users. Also, the
increased number of interrupt vectors might be a problem if the code uses absolute addresses.
To solve these problems, an ATmega103 compatibility mode can be selected by programming
the fuse M103C. In this mode, none of the functions in the Extended I/O space are in use, so the
internal RAM is located as in ATmega103. Also, the Extended Interrupt vectors are removed.
ATmega128A
4
8151HS–AVR–02/11