ATmega165P Atmel Corporation, ATmega165P Datasheet - Page 211

ATmega165P
Manufacturer Part Number
ATmega165P
Description
Manufacturer
Atmel Corporation
Specifications of ATmega165P
Flash (kbytes)
16 Kbytes
Pin Count
64
Max. Operating Frequency
16 MHz
Cpu
8-bit AVR
# Of Touch Channels
16
Hardware Qtouch Acquisition
No
Max I/o Pins
54
Ext Interrupts
17
Usb Speed
No
Usb Interface
No
Spi
2
Twi (i2c)
1
Uart
1
Graphic Lcd
No
Video Decoder
No
Camera Interface
No
Adc Channels
8
Adc Resolution (bits)
10
Adc Speed (ksps)
15
Analog Comparators
1
Resistive Touch Screen
No
Temp. Sensor
No
Crypto Engine
No
Sram (kbytes)
1
Eeprom (bytes)
512
Self Program Memory
YES
Dram Memory
No
Nand Interface
No
Picopower
Yes
Temp. Range (deg C)
-40 to 85
I/o Supply Class
1.8 to 5.5
Operating Voltage (vcc)
1.8 to 5.5
Fpu
No
Mpu / Mmu
no / no
Timers
3
Output Compare Channels
4
Input Capture Channels
1
Pwm Channels
4
32khz Rtc
Yes
Calibrated Rc Oscillator
Yes
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
ATmega165PV-8AU
Manufacturer:
ATMEL/爱特梅尔
Quantity:
20 000
- Current page: 211 of 364
- Download datasheet (8Mb)
21.7
21.7.1
8019K–AVR–11/10
ADC Noise Canceler
Analog Input Circuitry
The ADC features a noise canceler that enables conversion during sleep mode to reduce noise
induced from the CPU core and other I/O peripherals. The noise canceler can be used with ADC
Noise Reduction and Idle mode. To make use of this feature, the following procedure should be
used:
Note that the ADC will not be automatically turned off when entering other sleep modes than Idle
mode and ADC Noise Reduction mode. The user is advised to write zero to ADEN before enter-
ing such sleep modes to avoid excessive power consumption.
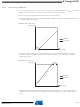
The analog input circuitry for single ended channels is illustrated in
source applied to ADCn is subjected to the pin capacitance and input leakage of that pin, regard-
less of whether that channel is selected as input for the ADC. When the channel is selected, the
source must drive the S/H capacitor through the series resistance (combined resistance in the
input path).
The ADC is optimized for analog signals with an output impedance of approximately 10 kΩ or
less. If such a source is used, the sampling time will be negligible. If a source with higher imped-
ance is used, the sampling time will depend on how long time the source needs to charge the
S/H capacitor, with can vary widely. The user is recommended to only use low impedant sources
with slowly varying signals, since this minimizes the required charge transfer to the S/H
capacitor.
Signal components higher than the Nyquist frequency (f
kind of channels, to avoid distortion from unpredictable signal convolution. The user is advised
to remove high frequency components with a low-pass filter before applying the signals as
inputs to the ADC.
Figure 21-8. Analog Input Circuitry
a. Make sure that the ADC is enabled and is not busy converting. Single Conversion
b. Enter ADC Noise Reduction mode (or Idle mode). The ADC will start a conversion
c. If no other interrupts occur before the ADC conversion completes, the ADC interrupt
mode must be selected and the ADC conversion complete interrupt must be enabled.
once the CPU has been halted.
will wake up the CPU and execute the ADC Conversion Complete interrupt routine. If
another interrupt wakes up the CPU before the ADC conversion is complete, that
interrupt will be executed, and an ADC Conversion Complete interrupt request will be
generated when the ADC conversion completes. The CPU will remain in active mode
until a new sleep command is executed.
ADCn
I
IH
I
IL
1..100 kΩ
ADC
/2) should not be present for either
C
S/H
= 14 pF
ATmega165P
Figure
V
CC
/2
21-8. An analog
211
Related parts for ATmega165P
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
INTERVAL AND WIPE/WASH WIPER CONTROL IC WITH DELAY
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Low-Voltage Voice-Switched IC for Hands-Free Operation
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MONOLITHIC INTEGRATED FEATUREPHONE CIRCUIT
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AM-FM Receiver IC U4255BM-M
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Monolithic Integrated Feature Phone Circuit
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Multistandard Video-IF and Quasi Parallel Sound Processing
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
High-performance EE PLD
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
8-bit Flash Microcontroller
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
2-Wire Serial EEPROM
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
U6046BREAR WINDOW HEATING TIMER / LONG-TERM TIMER
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet: