ATmega48 Automotive Atmel Corporation, ATmega48 Automotive Datasheet - Page 123

ATmega48 Automotive
Manufacturer Part Number
ATmega48 Automotive
Description
Manufacturer
Atmel Corporation
Specifications of ATmega48 Automotive
Flash (kbytes)
4 Kbytes
Pin Count
32
Max. Operating Frequency
16 MHz
Cpu
8-bit AVR
# Of Touch Channels
12
Hardware Qtouch Acquisition
No
Max I/o Pins
23
Ext Interrupts
24
Usb Speed
No
Usb Interface
No
Spi
2
Twi (i2c)
1
Uart
1
Graphic Lcd
No
Video Decoder
No
Camera Interface
No
Adc Channels
8
Adc Resolution (bits)
10
Adc Speed (ksps)
15
Analog Comparators
1
Resistive Touch Screen
No
Temp. Sensor
No
Crypto Engine
No
Sram (kbytes)
0.5
Eeprom (bytes)
256
Self Program Memory
NO
Dram Memory
No
Nand Interface
No
Picopower
No
Temp. Range (deg C)
-40 to 125
I/o Supply Class
2.7 to 5.5
Operating Voltage (vcc)
2.7 to 5.5
Fpu
No
Mpu / Mmu
no / no
Timers
3
Output Compare Channels
6
Input Capture Channels
1
Pwm Channels
6
32khz Rtc
Yes
Calibrated Rc Oscillator
Yes
- Current page: 123 of 225
- Download datasheet (4Mb)
16.3
16.3.1
7701E–AVR–02/11
Functional Descriptions
Three-wire Mode
The 4-bit counter can be both read and written via the data bus, and can generate an overflow
interrupt. Both the serial register and the counter are clocked simultaneously by the same
clock source. This allows the counter to count the number of bits received or transmitted and
generate an interrupt when the transfer is complete. Note that when an external clock source
is selected, the counter counts both clock edges. In this case, the counter counts the number
of edges, and not the number of bits. The clock can be selected from three different sources:
the USCK pin, timer/counter 0 compare match, or from software.
The two-wire clock control unit can generate an interrupt when a start condition is detected on
the two-wire bus. It can also generate wait states by holding the clock pin low after a start con-
dition is detected, or after the counter overflows.
The USI three-wire mode is compliant with the serial peripheral interface (SPI) mode 0 and 1,
but does not have the slave select (SS) pin functionality. However, this feature can be imple-
mented in software if necessary. Pin names used by this mode are: DI, DO, and USCK.
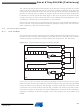
Figure 16-2. Three-wire Mode Operation, Simplified Diagram
Figure 16-2 on page 123
and one as slave. The two shift registers are interconnected in such way that after eight USCK
clocks, the data in each register are interchanged. The same clock also increments the USI's
4-bit counter. The counter overflow (interrupt) flag, or USIOIF, can therefore be used to deter-
mine when a transfer is completed. The clock is generated by the master device software by
toggling the USCK pin via the PORT register, or by writing a logical one to the USITC bit in
USICR.
SLAVE
MASTER
Bit7
Bit7
Bit6
Bit6
Bit5
Bit5
Bit4
Bit4
Bit3
Bit3
shows two USI units operating in three-wire mode, one as master
Atmel ATtiny24/44/84 [Preliminary]
Bit2
Bit2
Bit1
Bit1
Bit0
Bit0
PORTxn
USCK
USCK
DO
DO
DI
DI
123
Related parts for ATmega48 Automotive
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 4K 5V 20MHZ 32-TQFP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 4K 20MHZ 5V 32TQFP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 4K 20MHZ 5V 28DIP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 4K 20MHZ 5V 32-QFN
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Atmel Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 4K 5V 20MHZ 32-TQFP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 4K 5V 20MHZ 32-QFN
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 4K 5V 20MHZ 32-QFN
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 4K 5V 20MHZ 28-DIP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 4K 5V 20MHZ 28-DIP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 4K FLASH 20MHZ 28QFN
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MCU AVR 4KB FLASH 20MHZ 32QFN
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet: