AD9634 Analog Devices, AD9634 Datasheet - Page 21

AD9634
Manufacturer Part Number
AD9634
Description
12-Bit, 170 MSPS/210 MSPS/250 MSPS, 1.8 V Analog-to-Digital Converter
Manufacturer
Analog Devices
Datasheet
1.AD9634.pdf
(32 pages)
Specifications of AD9634
Resolution (bits)
12bit
# Chan
1
Sample Rate
250MSPS
Interface
LVDS
Analog Input Type
Diff-Uni
Ain Range
1.75 V p-p
Adc Architecture
Pipelined
Pkg Type
CSP
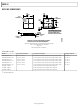
An alternative to using a transformer-coupled input at
frequencies in the second Nyquist zone is to use an amplifier
with variable gain. The
(DVGA) provides good performance for driving the AD9634.
Figure 50 shows an example of the
through a band-pass antialiasing filter.
VOLTAGE REFERENCE
A stable and accurate voltage reference is built into the AD9634.
The full-scale input range can be adjusted by varying the reference
voltage via SPI. The input span of the ADC tracks reference
voltage changes linearly.
CLOCK INPUT CONSIDERATIONS
For optimum performance, the
CLK+ and CLK−, should be clocked with a differential signal.
The signal is typically ac-coupled into the CLK+ and CLK− pins by
means of a transformer or a passive component configuration.
These pins are biased internally (see Figure 51) and require no
external bias. If the inputs are floated, the CLK− pin is pulled low
to prevent spurious clocking.
Clock Input Options
The
can be a CMOS, LVDS, LVPECL, or sine wave signal. Regardless
of the type of signal being used, clock source jitter is of the most
concern, as described in the Jitter Considerations section.
Figure 52 and Figure 53 show two preferable methods for clocking
the
source is converted from a single-ended signal to a differential
signal using an RF balun or RF transformer.
AD9634
AD9634
CLK+
(at clock rates of up to 625 MHz). A low jitter clock
has a very flexible clock input structure. Clock input
Figure 51. Equivalent Clock Input Circuit
4pF
AD8375
AVDD
0.9V
AD9634
NOTES
1. ALL INDUCTORS ARE COILCRAFT 0603CS COMPONENTS
2. FILTER VALUES SHOWN ARE FOR A 20MHz BANDWIDTH FILTER CENTERED AT 140MHz.
digital variable gain amplifier
WITH THE EXCEPTION OF THE 1µH CHOKE INDUCTORS (0603LS).
AD8375
AD8375
sample clock inputs,
Figure 50. Differential Input Configuration Using the
driving the
1µH
1µH
4pF
1000pF
1000pF 180nH
VPOS
CLK–
1nF
301Ω
180nH
AD9634
Rev. 0 | Page 21 of 32
5.1pF
220nH
220nH
3.9pF
165Ω
165Ω
The RF balun configuration is recommended for clock frequencies
between 125 MHz and 625 MHz, and the RF transformer is
recommended for clock frequencies from 10 MHz to 200 MHz.
The back-to-back Schottky diodes across the secondary windings
of the transformer limit clock excursions into the
approximately 0.8 V p-p differential. This limit helps prevent the
large voltage swings of the clock from feeding through to other
portions of the AD9634, while preserving the fast rise and fall times
of the signal, which are critical for low jitter performance.
If a low jitter clock source is not available, another option is to
ac couple a differential PECL signal to the sample clock input pins
as shown in Figure 54. The AD9510, AD9511,AD9512, AD9513,
AD9514, AD9515, AD9516, AD9517, AD9518, AD9520, AD9522,
AD9523, AD9524, ADCLK905, ADCLK907, and
clock drivers offer excellent jitter performance.
CLOCK
CLOCK
CLOCK
INPUT
VCM
INPUT
INPUT
15pF
1nF
CLOCK
Figure 52. Transformer Coupled Differential Clock (Up to 200 MHz)
INPUT
50kΩ
Figure 53. Balun-Coupled Differential Clock (Up to 625 MHz)
Figure 54. Differential PECL Sample Clock (Up to 625 MHz)
68nH
50Ω
390pF
390pF
2.5kΩ║2pF
AD8375
AD9634
1nF
0.1µF
0.1µF
50kΩ
100Ω
ADT1-1WT, 1:1Z
Mini-Circuits
AD95xx,
ADCLKxxx
PECL DRIVER
XFMR
25Ω
25Ω
240Ω
390pF
390pF
390pF
®
390pF
SCHOTTKY
HSMS2822
DIODES:
SCHOTTKY
HSMS2822
DIODES:
240Ω
0.1µF
0.1µF
100Ω
CLK+
CLK–
AD9634
ADCLK925
ADC
CLK+
CLK–
CLK+
CLK–
AD9634
ADC
ADC
to