AD7985 Analog Devices, AD7985 Datasheet - Page 22

AD7985
Manufacturer Part Number
AD7985
Description
16-Bit, 2.5 MSPS PulSAR 11 mW ADC in QFN
Manufacturer
Analog Devices
Datasheet
1.AD7985.pdf
(28 pages)
Specifications of AD7985
Resolution (bits)
16bit
# Chan
1
Sample Rate
2.5MSPS
Interface
Ser,SPI
Analog Input Type
SE-Uni
Ain Range
(Vref) p-p,Uni (Vref)
Adc Architecture
SAR
Pkg Type
CSP
AD7985
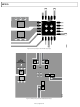
CS MODE, 4-WIRE WITH BUSY INDICATOR
This mode is usually used when a single AD7985 is connected
to an SPI-compatible digital host with an interrupt input and
when it is desired to keep CNV, which is used to sample the
analog input, independent of the signal used to select the data
reading. This independence is particularly important in applica-
tions where low jitter on CNV is desired. This mode is available
only in normal conversion mode (TURBO is low). The connection
diagram is shown in Figure 32, and the corresponding timing is
given in Figure 33.
With SDI high, a rising edge on CNV initiates a conversion,
selects CS mode, and forces SDO to high impedance. In this
mode, CNV must be held high during the conversion phase and
the subsequent data readback. (If SDI and CNV are low, SDO is
driven low.) Prior to the minimum conversion time, SDI can be
TURBO = 0
ACQUISITION
SDO
CNV
SCK
SDI
t
SSDICNV
t
HSDICNV
CONVERSION
t
CONV
Figure 33. CS Mode, 4-Wire with Busy Indicator Serial Interface Timing
Figure 32. CS Mode, 4-Wire with Busy Indicator Connection Diagram
t
EN
SDI
AD7985
CNV
SCK
1
Rev. A | Page 22 of 28
t
t
HSDO
DSDO
TURBO
SDO
D15
2
VIO
t
47kΩ
CYC
D14
used to select other SPI devices, such as analog multiplexers, but
SDI must be returned low before the minimum conversion time
elapses and then held low for the maximum possible conversion
time to guarantee the generation of the busy signal indicator.
When the conversion is complete, SDO goes from high imped-
ance to low impedance. With a pull-up on the SDO line, this
transition can be used as an interrupt signal to initiate the data
readback controlled by the digital host. The AD7985 then enters
the acquisition phase and powers down. The data bits are then
clocked out, MSB first, by subsequent SCK falling edges. The
data is valid on both SCK edges. Although the rising edge can
be used to capture the data, a digital host using the SCK falling
edge allows a faster reading rate, provided that it has an accept-
able hold time. After the optional 17
SDI goes high (whichever occurs first), SDO returns to high
impedance.
3
ACQUISITION
CONVERT
DATA IN
CLK
CS1
IRQ
DIGITAL HOST
t
ACQ
t
SCKL
t
SCKH
15
t
SCK
16
D1
17
D0
(I/O QUIET
TIME)
t
th
DIS
SCK falling edge or when
t
QUIET