AD9280 Analog Devices, AD9280 Datasheet - Page 6

AD9280
Manufacturer Part Number
AD9280
Description
8-Bit, Complete, 32 MSPS A/D Converter
Manufacturer
Analog Devices
Datasheet
1.AD9280.pdf
(24 pages)
Specifications of AD9280
Resolution (bits)
8bit
# Chan
1
Sample Rate
32MSPS
Interface
Par
Analog Input Type
Diff-Uni,SE-Uni
Ain Range
1 V p-p,2 V p-p
Adc Architecture
Pipelined
Pkg Type
SOP
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
AD9280AR
Manufacturer:
ADI/亚德诺
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
AD9280ARS
Manufacturer:
PANASONIC
Quantity:
2 600
Part Number:
AD9280ARS
Manufacturer:
ADI/亚德诺
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
AD9280ARSZ
Manufacturer:
ADI/亚德诺
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
AD9280ARSZRL
Manufacturer:
ADI/亚德诺
Quantity:
20 000
AD9280
DEFINITIONS OF SPECIFICATIONS
Integral Nonlinearity (INL)
Integral nonlinearity refers to the deviation of each individual
code from a line drawn from “zero” through “full scale.” The
point used as “zero” occurs 1/2 LSB before the first code transi-
tion. “Full scale” is defined as a level 1 1/2 LSB beyond the last
code transition. The deviation is measured from the center of
each particular code to the true straight line.
Differential Nonlinearity (DNL, No Missing Codes)
An ideal ADC exhibits code transitions that are exactly 1 LSB
apart. DNL is the deviation from this ideal value. It is often
specified in terms of the resolution for which no missing codes
(NMC) are guaranteed.
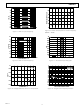
Typical Characterization Curves
–0.5
–1.0
–0.5
–1.0
1.0
0.5
1.0
0.5
0
0
0
0
32
32
Figure 3. Typical DNL
Figure 4. Typical INL
64
64
96
96
CODE OFFSET
CODE OFFSET
128
128
160
160
192
192
224
224
(AVDD = +3 V, DRVDD = +3 V, F
Span from 0.5 V to 2.5 V, External Reference, unless otherwise noted)
240
240
–6–
Offset Error
The first transition should occur at a level 1 LSB above “zero.”
Offset is defined as the deviation of the actual first code transi-
tion from that point.
Gain Error
The first code transition should occur for an analog value 1 LSB
above nominal negative full scale. The last transition should
occur for an analog value 1 LSB below the nominal positive full
scale. Gain error is the deviation of the actual difference be-
tween first and last code transitions and the ideal difference
between the first and last code transitions.
Pipeline Delay (Latency)
The number of clock cycles between conversion initiation and
the associated output data being made available. New output
data is provided every rising edge.
1.00E+05
1.00E+05
60
55
50
45
40
35
30
25
20
60
55
50
45
40
35
30
25
20
S
Figure 6. SINAD vs. Input Frequency
Figure 5. SNR vs. Input Frequency
= 32 MHz (50% Duty Cycle), MODE = AVDD, 2 V Input
1.00E+06
1.00E+06
INPUT FREQUENCY – Hz
INPUT FREQUENCY – Hz
–20.0 AMPLITUDE
–6.0 AMPLITUDE
–0.5 AMPLITUDE
–20.0 AMPLITUDE
–0.5 AMPLITUDE
–6.0 AMPLITUDE
1.00E+07
1.00E+07
1.00E+08
1.00E+08
REV. E