AD8016 Analog Devices, AD8016 Datasheet

AD8016
Specifications of AD8016
Available stocks
Related parts for AD8016
AD8016 Summary of contents
Page 1
... The low power dissipation, high output current, high output voltage swing, flexible power-down, and robust thermal packaging enable the AD8016 to be used as the Central Office (CO) terminal driver in ADSL, HDSL2, VDSL, and proprietary xDSL systems. One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A. ...
Page 2
... AD8016–SPECIFICATIONS Parameter DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE –3 dB Bandwidth Bandwidth for 0.1 dB Flatness Large Signal Bandwidth Peaking Slew Rate Rise and Fall Time Settling Time Input Overdrive Recovery Time NOISE/DISTORTION PERFORMANCE Distortion, Single-Ended Second Harmonic Third Harmonic Multitone Power Ratio* IMD IP3 Voltage Noise (RTI) ...
Page 3
... Full Temperature Range) CC Typ Max V CC 0.8 AD8016 Unit MHz MHz MHz MHz dB V/µ dBc dBc dBc dBc dBm nV/√Hz pA√Hz mV µA µA kΩ mA/Amp ...
Page 4
... The output stage of the AD8016 is designed for maximum load current capability result, shorting the output to common can cause the AD8016 to source or sink 2000 mA. To ensure proper operation necessary to observe the maximum power derating curves. Direct connection of the output to either power supply rail can destroy the device ...
Page 5
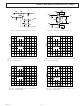
... –V S Figure 6. Differential Test Circuit +10 = ± Figure 7. 100 mV Step Response + Ω , Single-Ended ± Figure Step Response + Ω , Single-Ended R L –5– AD8016 0 49.9 O 499 111 R 499 L –V O 0 – ...
Page 6
... AD8016 – 499 F – + p-p O –50 –60 –70 –80 –90 –100 –110 0.01 0.1 1 FREQUENCY (MHz) Figure 9. Distortion vs. Frequency; Second Harmonic, = ± Ω , Differential – 499 F – + p-p O –50 –60 –70 –80 –90 –100 –110 0.01 0.1 FREQUENCY (MHz) Figure 10. Distortion vs. Frequency; Second Harmonic, = ± ...
Page 7
... PWDN1, PWDN0 = (1,1) – DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT (V p-p) = ± +10 MHz –30 –40 (0,0) –50 (0,1) –60 –70 PWDN1, PWDN0 = (1,1) –80 – DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT (V p- Ω , Differential L AD8016 500 600 Ω (1,0) 20 ...
Page 8
... AD8016 3 0 – 40mV p-p IN – 100 –9 L –12 –15 –18 –21 –24 – FREQUENCY (MHz) Figure 21. Frequency Response PWDN1, PWDN0 Codes 100 499 –1 –4 –7 –10 –13 –16 – FREQUENCY (MHz) Figure 22. Output Voltage vs. Frequency; V ...
Page 9
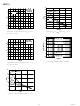
... Figure 30. Open-Loop Transimpedance and Phase vs. Frequency OUT STEP R = 100 L – ± 1000 100 10 0.1 0.01 100 500 –9– AD8016 PHASE TRANSIMPEDANCE 0.001 0.01 0 100 FREQUENCY (MHz OUT STEP R = 100 L +2mV (–0.1 –2mV (–0.1%) V ...
Page 10
... AD8016 V OUT –100 0 100 200 300 400 500 TIME (ns) Figure 33a. Overload Recovery 100 Ω + OUT –100 0 100 200 300 400 500 TIME (ns) Figure 33b. Overload Recovery 100 Ω + PWDN1, PWDN0 = (1, [1,0] [0,1] ...
Page 11
... V of either power supply rail. This enables full CO ADSL performance on only 12 V rails, an immediate 20% power saving. The AD8016 is also unique in that it has a power management system included on-chip. It features four user programmable power levels (all of which provide a low output impedance of the driver), as well as the provision for complete shutdown (high impedance state) ...
Page 12
... In the event of thermal overload, the AD8016 was designed to shut down at a junction temperature of 165°C and return to normal operation at a junction temperature 140°C. The AD8016 continues to operate, cycling on and off, as long as the thermal overload condition remains. The frequency of the protection cycle depends on the ambient environment, severity of the thermal overload condition, the power being dissipated, and the thermal mass of the PCB beneath the AD8016 ...
Page 13
... AD8016. The dc power dissipation for V –75.3 dBc (V – V –57.2 dBc CC EE N/A For the AD8016 powered on +12 V and –12 V supplies (± V the number is 0 differential driver circuit (Figure 6), –13– AD8016 ® , buffered by an AD8002 ), or 2 × I × ...
Page 14
... DUT Power: Typical DSL DMT signal produces about 1 power dissipation in the AD8016 package. The fully biased (PWDN0 and PWDN1 = Logic 1) quiescent current of the AD8016 is ~25 mA MHz differential sine wave at an amplitude p-p/amplifier into an R (50 Ω per side) produces the 1 power typical in the AD8016 device ...
Page 15
... LFM of air flow. If the target maximum junction temperature of the AD8016ARB is 125°C, a 4-layer PCB with 1 oz. copper covering the outer layers and measuring 9 square inches is required with 0 LFM of air flow. ...
Page 16
... AD8016 Figure 45. DMT Signal Generator Schematic –16– REV. B ...
Page 17
... C26 0.1 F 0.1 F R10 C16 C25 0.1 F 0.1 F +VL –VT TP20 3 P2 TP21 C23 0.1 F C22 0.1 F –VR TP22 TP12 TP24 +VL C18 0.1 F Figure 46b. Schematic AD8016ARB-EVAL –17– AD8016 TP13 PR1 TP14 TP1 ...
Page 18
... AD8016 LAYOUT AD8016ARB-EVAL Figure 47. Assembly Figure 48. Layer 1 Figure 49. Power/Ground Plane Figure 50. Layer 1 Figure 51. Silkscreen Bottom –18– REV. B ...
Page 19
... AMP# 555154-1 MOD. JACK (SHIELDED 3-Pin Gold Male Header Waldom #WM 2723-ND 3 3-Pin Gold Male Locking Header Waldom #WM 2701-ND 1 AD8016 ARB 1 AD8016 SOIC REV. B Evaluation PC Board No. 4 –40 × 1/4" Panhead SS Machine Screw 4 No. 4 –40 × 1/2" Threaded Alum. Standoffs 4 OPTION 2 1:1.4 Turns Ratio RF Transformer from CoEv 24-Lead Batwing SOIC, Thermally Enhanced w/Fused Leads [SOIC/W/BAT] 0 ...
Page 20
... AD8016 20-Lead Power SOIC, Thermally Enhanced Package [PSOP3] 11.00 BSC 3.60 3.35 3.10 SEATING PLANE 28-Lead Thin Shrink Small Outline With Exposed Pad [TSSOP-EP PIN 1 1.20 MAX 0.15 0.00 Revision History Location 11/03—Data Sheet changed from REV REV. B. Changes to ORDERING GUIDE ....................................................................................................................................................4 Changes to TPC 21 .........................................................................................................................................................................8 Updated OUTLINE DIMENSIONS........................................................................................................................................19-20 ...