E-TDA7402 STMicroelectronics, E-TDA7402 Datasheet

E-TDA7402
Specifications of E-TDA7402
Available stocks
Related parts for E-TDA7402
E-TDA7402 Summary of contents
Page 1
... The digital control allows a programming in a wide range of all the filter characteristics. The stereo decoder part also offers several possibilities of programming, especially for the adaptation to different IF devices ...
Page 2
... Contents Contents 1 Pin connections and block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 2 Electrical specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 3 Audioprocessor part . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15 3.1 Audioprocessor part features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15 3.2 Input stages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16 3.2.1 3.2.2 3.2.3 3.2.4 3.2.5 3.3 AutoZero . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17 3.3.1 3.3.2 3.4 Pause detector / MUX-output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18 3.4.1 3.4.2 3.4.3 3.4.4 3.4.5 3.5 Soft Mute . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20 3 ...
Page 3
... Multipath detector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37 4.5.1 5 Functional description of stereo decoder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38 5.1 Stereo decoder mute . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38 5.2 InGain + infilter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39 5.3 Demodulator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39 5.4 De-emphasis and highcut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40 5.5 PLL and pilot tone detector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40 5.6 Fieldstrength control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40 5.7 EVEL input and gain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40 5.8 Stereo blend control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41 5.9 Highcut control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41 6 Functional description of the noise blanker ...
Page 4
... Transmitted data (send mode 8.4 Subaddress (receive mode 8.5 Data byte specification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49 9 Application information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66 10 Package information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67 11 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68 4/69 Automatic threshold control by the stereo blend voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . 44 Over deviation detector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44 Multipath level . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44 AM mode of the noiseblanker . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44 Feature description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46 Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46 TDA7402 ...
Page 5
... Thermal data Table 5. Supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14 Table 6. Attack times vs. soft-step times . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26 Table 7. Stereo decoder electrical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31 Table 8. Noise blanker electrical characteristics Table 9. Multipath detector electrical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37 Table 10. Transmitted data (send mode Table 11. Reset condition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47 Table 12. Subaddress (receive mode Table 13. Main selector ( Table 14. ...
Page 6
... Bass control @ fC = 80Hz Figure 10. Bass center frequencies @ gain = 14dB Figure 11. Bass quality factors @ Gain = 14dB 80Hz Figure 12. Bass normal and DC Mode @ Gain = 14dB 80Hz . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22 Figure 13. Treble control @ fC = 17.5kHz . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 Figure 14. Treble center frequencies @ gain = 14dB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 Figure 15. Subwoofer application with LPF 80/120/160Hz and HPF 90/135/180Hz . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24 Figure 16 ...
Page 7
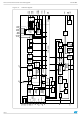
... TDA7402 1 Pin connections and block diagram Figure 1. Pin connections (top view SE1L 1 SE1R 2 FD1L+/SE3L 3 FD1L-/SE2L 4 FD1R+/SE3R 5 FD1R-/SE2R 6 7 FD2L+ FD2L- 8 FD2R+ 9 FD2R Pin connections and block diagram ACINLR 33 ACINRF 32 ACINRR 31 OUTLF 30 OUTLR 29 OUTRF 28 OUTRR 27 OUTSWL 26 OUTSWR 25 OUTSSL ...
Page 8
... Pin connections and block diagram Figure 2. Block diagram ACINLF ACINLR ACINRF ACINRR SWINL SWINR ACOUTR ACOUTL 8/69 TDA7402 ...
Page 9
... TDA7402 2 Electrical specifications 25° 10kΩ; all gains = 0dB 1kHz; unless otherwise specified. S amb L Table 2. Electrical characteristics Symbol Parameter Input selector R Input resistance in V Clipping level CL S Input separation IN G Min. input gain IN MIN G Max. input gain IN MAX G Step resolution ...
Page 10
... Step resolution STEP E Attenuation set error A E Tracking error steps DC Soft mute A Mute attenuation MUTE T Delay time D V Low threshold for SM Pin TH low V High threshold for SM Pin TH high 10/69 Test condition Main / mix source -20 to +20dB G = -80 to -20dB Adjacent attenuation steps ...
Page 11
... Bass control C Control range RANGE A Step resolution STEP f Center frequency C Q Quality factor BASS DC Bass-DC-gain GAIN Treble control C Control range RANGE A Step resolution STEP f Center frequency C (3) Pause detector V Zero crossing threshold TH I Pull-up current DELAY V Pause threshold THP Test condition ...
Page 12
... Symbol Parameter Speaker attenuator R Input impedance in G Max. gain MAX A Max. attenuation MAX A Step resolution STEP A Output mute attenuation MUTE E Attenuation set error steps DC Audio outputs V Clipping level CLIP R Output load resistance L C Output load capacitance L R Output impedance OUT V DC voltage level ...
Page 13
... Symbol Parameter Subwoofer lowpass f Lowpass corner frequency LP (4) Differential outputs R load resistance at each output L R load resistance differential DL C Capacitive load at each output LMAX C Capacitive load differential DLMAX V DC offset at pins Offset R Output impedance OUT V DC voltage level DC e Output noise ...
Page 14
... Output noise NO S/N Signal to noise ratio d distortion S Channel separation left/right C E Total tracking error configured as multiplexer-output 2. The SM Pin is active low (mute = configured as pause-output 4. If programmed as subwoofer diff. output Table 3. Absolute maximum ratings Symbol V Operating supply voltage S T Operating temperature range amb T ...
Page 15
... Voice bandpass – 2nd order butterworth highpass filter with programmable cut off frequency – 2nd order butterworth lowpass filter with programmable cut off frequency – selectable flat mode Audioprocessor part 15/69 ...
Page 16
... Input stages In the basic configuration two full differential, two mono differential, one single ended stereo and one single ended mono input are available. In addition a dedicated input for the stereo decoder MPX signal is present. Figure 3. Input-stages SE2 FD1- ...
Page 17
... Single ended stereo input (SE1), single ended mono input (AM) and FM-MPX input All single ended inputs offer an input impedance of 100kΩ. The AM pin can be connected by software to the input of the stereo-decoder in order to use the AM noiseblanker and AM High Cut feature. 3.3 ...
Page 18
... For such applications the TDA7402 could be switched in the AutoZero Remain Mode (Bit 6 of the subaddress byte). If this bit is set to high, the DATABYTE 0 could be loaded without invoking the AutoZero and the old adjustment value remains. ...
Page 19
... Different shapes of 1st and 2nd-order loudness st Figure 6. 1 and 2 0.0 -5.0 dB -10.0 -15.0 -20.0 10.0 3.4.5 Flat mode In flat mode the loudness stage works as a 0dB to -19dB attenuator. 100 order loudness @ Attn. = 15dB, f 100.0 Hz Audioprocessor part 1.0K 10.0K =400Hz P 1.0K 10.0K ...
Page 20
... DC offset before the volume stage or the sudden change of the envelope of the audio signal. With the Soft Step feature both kinds of clicks could be reduced to a minimum and are no more audible. The blend time from one step to the next is programmable in four steps. ...
Page 21
... Bass control @ f 15.0 10.0 5.0 dB 0.0 -5.0 -10.0 -15.0 10.0 3.7.2 Center frequency Figure 10 shows the eight possible center frequencies 60, 70, 80, 90, 100, 130, 150 and 200Hz. Figure 10. Bass center frequencies @ gain = 14dB 15.0 12.5 10.0 7.5 dB 5.0 2.5 0.0 10.0 = 80Hz 100 ...
Page 22
... DC mode In this mode the DC-gain is increased by 4.4dB. In addition the programmed center frequency and quality factor is decreased by 25% which can be used to reach alternative center frequencies or quality factors. Figure 12. Bass normal and DC Mode @ Gain = 14dB, f 15.0 12.5 10.0 7.5 5 ...
Page 23
... TDA7402 3.8 Treble There are two parameters programmable in the treble stage: 3.8.1 Attenuation Figure 13. shows the attenuation as a function of frequency at a center frequency of 17.5kHz. Figure 13. Treble control @ f 15.0 10.0 5.0 0.0 -5.0 -10.0 -15.0 10.0 3.8.2 Center frequency Figure 14. shows the four possible center frequencies 10k, 12.5k, 15k and 17.5kHz. ...
Page 24
... Both filters, the lowpass and the highpass-filter, have butterworth characteristics so that their cut off frequencies are not equal, but shifted by the factor 1.125 to get a flat frequency response. 3.10 Voice band application Figure 16. Voiceband application with HPF 300/450/600/750Hz and LPF 3k/6kHz ...
Page 25
... The low pass output-voltage then is A/D converted an added to the current volume-word defined by the I input, the output of the ADC lower levels the voltage is increasing with 1Bit/dB obvious that with this configuration and a 0.5dB-step volume stage the compression rate is fixed to 2:1 (1dB less at the input leads to 0.5dB less at the output). ...
Page 26
... I C bus timing While the compander is working, a volume word coming from this stage is added to the I bus volume word, and the volume is changed with a soft slope between adjacent steps (Soft Step stage). As mentioned in the description of this stage not recommended to change the volume during this slope. To avoid this while the compander is working and the volume has to be changed, the compander hold-bit is implemented (Bit 7 in the subaddress byte) ...
Page 27
... Output selector The output-selector allows to connect the main- or the second-source to the front, rear and subwoofer speaker attenuator, respectively example of this programming the device is able to connect via software the main source to the back (rear) and the second source to the front (see Figure ...
Page 28
... Center speaker mode (filtered mono signal at SWL, unfiltered mono signal at SWR) In all applications the phase of the output-signal can be configured to be 0° or 180°. In the center speaker mode only at the filtered output the phase is changed. Figure 20. Application 1 using internal highpass and mono low pass filter ...
Page 29
... TDA7402 Figure 21. Application 2 using internal highpass and external stereo low pass filter MAIN SOURCE LEFT CHANNEL MAIN SOURCE RIGHT CHANNEL SECOND SOURCE LEFT CHANNEL SECOND SOURCE Figure 22. Application 3 using pure external filtering (e.g. DSP) MAIN SOURCE LEFT CHANNEL MAIN SOURCE RIGHT CHANNEL ...
Page 30
... Audioprocessor part 3.15 Speaker attenuator and mixing A mixing-stage is placed after each speaker attenuator and can be set independently to mixing mode. Having a full volume for the mix signal the stage offers a wide flexibility to adapt the mixing levels. Figure 23. Output selector FROM OUTPUT SELECTOR ...
Page 31
... Multipath-detector with programmable internal/external influence 2 ● I C-bus control of all necessary functions 4.2 Stereo decoder electrical characteristics V = 9V, de-emphasis time constant = 50µs, MPX input voltage V S deviation), modulation frequency = 1kHz, input gain = 6dB, T specified. Table 7. Stereo decoder electrical characteristics Symbol Parameter V ...
Page 32
... VHCL Min. voltage for FULL high cut min VHCL Max. voltage for FULL high cut max VHCL Step resolution step Carrier and harmonic suppression at the output α19 Pilot signal f=19kHz α38 Subcarrier f=38kHz α57 Subcarrier f=57kHz α76 Subcarrier f=76kHz 32/69 Test condition Min ...
Page 33
... Traffic radio (V.F.) suppression measured with: 91% stereo signal; 9% pilot signal; fm=1kHz; 5% subcarrier (f=57kHz, fm=23Hz AM, m=60%) 4.3.3 SCA (subsidiary communications authorization) α67 measured with: 81% mono signal; 9% pilot signal; fm=1kHz; 10%SCA - subcarrier (f = 67kHz, unmodulated). S Test condition ( ) at1kHz ( ...
Page 34
... Stereo decoder part 4.3.4 ACI (adjacent channel interference) α114 α190 measured with: 90% mono signal; 9% pilot signal; fm=1kHz; 1% spurious signal (f = 110kHz or 186kHz, unmodulated). S 4.4 Noise blanker part 4.4.1 Noise blanker part features ● AM and FM mode ● internal 2nd order 140kHz high-pass filter for MPX path ● ...
Page 35
... AM IF AMIF,min c f max AMIF,max c 1. All thresholds are measured using a pulse with µs, THIGH= 2 µs and µs. The repetition rate must not increase the PEAK voltage design/characterization functionally guaranteed through dedicated test mode structure Test condition V =0mV MPX V =50mV, f=150kHz ...
Page 36
... Figure 26. Deviation controlled trigger adjustment Figure 27. Field strength controlled trigger adjustment V PEAK » 3V 36/ HIGH PEAK OLD 65m 30m MONO STEREO NOISE ATC_SB OFF (11) noisy signal 260m V (00) 220m V (01 (10 (11 ISE OLLE 1. etector o ff (11 TIO N [KH z] 2.3V (00) 1.8V (01) 1.3V (10) 0.9V good signal E' TDA7402 ...
Page 37
... Multipath detector 4.5.1 Multipath detector features ● internal 19kHz band pass filter ● programmable band pass and rectifier gain ● selectable internal influence on stereo blend and/or Highcut Table 9. Multipath detector electrical characteristics Symbol Center frequency of f CMP multipath-bandpass G Bandpass gain ...
Page 38
... This influence of Soft Mute on the stereo decoder mute can be switched off by setting bit 3 of the Soft Mute byte to "0". A stereo decoder mute command (bit 0, stereo decoder byte set to "1") will also set the stereo decoder independently to the high-ohmic mute state. ...
Page 39
... InGain + infilter The InGain stage allows adjustment of the MPX-signal to a magnitude of about 1V internally, which is the recommended value. The 4 of 80kHz and is used to attenuate spikes and noise, and acts as an anti-aliasing filter for the following switch capacitor filters. 5.3 Demodulator In the demodulator block, the left and the right channels are separated from the MPX signal. ...
Page 40
... The setup of the highcut characteristics is described in 5.5 PLL and pilot tone detector The PLL has the task to lock on the 19kHz pilot tone during a stereo transmission to allow a correct demodulation. The included pilot tone-detector enables the demodulation if the pilot tone reaches the selected pilot tone threshold V available ...
Page 41
... VMO 5.9 Highcut control The highcut control set-up is similar to the stereo blend control set up: the starting point VHCH can be set with 2 bits to be 42, 50 66% of REF5V whereas the range can be set to be 17, 22 33% of VHCH (see Functional description of stereo decoder Figure 31 Figure 32) ...
Page 42
... Functional description of stereo decoder Figure 33. Highcut characteristics 42/69 LOWPASS TIME CONSTANT τ ' • 3.7 DEEMPHASIS SHIFT ON Deemp τ 3 • Deemp OFF τ Deemp τ ' Deemp VHCL D00AU1169 TDA7402 VHCH FIELDSTRENGHT ...
Page 43
... The aim of the noiseblanker part is to cancel the audible influence of the spikes. Therefore the output of the stereo decoder is held at the actual voltage for a time between 22 and 38µ (370 and 645µ mode). The block diagram of the noise blanker is given in Figure 34 ...
Page 44
... Over deviation detector If the system is tuned to stations with a high deviation the noiseblanker can trigger on the higher frequencies of the modulation or distortion. To avoid this behavior, which causes audible noise in the output signal, the noiseblanker offers a deviation-dependent threshold adjustment. By rectifying the MPX signal a further signal representing the actual deviation is obtained ...
Page 45
... Noise The noise-signal is the PEAK signal without additional influences (see the noiseblanker description). The factor 'a' can by programmed to 0.7 .... 1.15. The output is a low impedance output able to drive external circuitry as well as simply fed converter for RDS applications. Functional description of the multipath detector Figure 34) ...
Page 46
... In this mode the stereo decoder high ohmic-mute mutes both inputs in parallel. Figure 36. Dual MPX input diagram MPX/ MPX1 MD2G/ MPX2 MD2/ CONTROL 7.3.2 Configuration The Dual MPX mode can be easily configured by setting bit 3 of subaddress 30 to LOW (see Byte 30 description and application diagram of 46/69 1 100K 40K 40K 1 100K CONTROL ...
Page 47
... R/W = "0" -> Receive-Mode (Chip could be programmed by µP) "1" -> Transmission-Mode (Data could be received by µP) ACK = Acknowledge P = Stop Max clock speed 500kbits/s 8.2 Auto increment If bit I in the subaddress byte is set to "1", the auto increment of the subaddress is enabled. 8.3 Transmitted data (send mode) Table 10. Transmitted data (send mode) MSB X ...
Page 48
... Main Source Selector Main Loudness Volume Treble Bass Mixing Programming Soft Mute Voice-Band Second Source Selector Second Source Loudness Subwoofer Config. / Bass Compander Configuration Audioprocessor Configuration Audioprocessor Subwoofer attenuator Subwoofer attenuator Speaker attenuator Speaker attenuator Speaker attenuator Speaker attenuator Mixing Level Control ...
Page 49
... TDA7402 8.5 Data byte specification The status after power on reset is marked bold face / underlined in the programming tables. Table 13. Main selector (0) MSB Table 14. Main loudness (1) MSB LSB Source selector FD1 / SE2 SE3 FD2 SE1 MD2 MD1 / SE4 Stereo decoder Input gain 0 0 0dB ...
Page 50
... C bus interface Table 15. Volume (2) MSB Note not recommended to use a gain more than 20dB for system performance reason. In general, the maximum gain should be limited by software to the maximum value, which is needed for the system. Table 16. Treble filter (3) MSB 50/69 LSB Gain/attenuation (+32.0dB (+31.5dB ...
Page 51
... Mixing 0 Mute 1 enable Mixing source 0 0 Beep 0 1 MD1 1 0 MD2 mono Mixing target 0 Speaker LF off 1 Speaker Speaker RF off 1 Speaker RF on Speaker LR off Speaker LR on Speaker RR off Speaker RR on Stereo subw. using internal highpass filter On Off bus interface Function Function 51/69 ...
Page 52
... On (Mute) 1 Off 0 0 Mutetime = 0.48ms 0 1 Mutetime = 0.96ms 1 0 Mutetime = 123ms 1 1 Mutetime = 324 ms Influence on stereo decoder highohmic mute off Influence on pilot detector hold and MP hold off Influence on Soft Mute on off Beep frequencies 600 Hz 780 Hz 1.56 kHz 2.4 kHz LSB ...
Page 53
... Table 21. Second source selector (8) MSB LSB High pass cut off frequency 0 0 90Hz 0 1 135Hz 1 0 180Hz 1 1 215Hz 0 0 300Hz 0 1 450Hz 1 0 600Hz 1 1 750Hz Anti clipping enable on off Anti clipping input MP-In AM LSB Source selector FD1 / SE2 SE3 ...
Page 54
... I C bus interface Table 22. Second loudness (9) MSB Table 23. Subwoofer configuration / Bass (10) MSB 54/69 LSB Attenuation - - - not allowed Center frequency 200Hz 400Hz 600Hz 800Hz Loudness order First order Second order LSB Subwoofer filter 0 0 off 0 1 80Hz 1 0 120Hz 1 1 160Hz Subwoofer outputs ...
Page 55
... TDA7402 Table 24. Compander (11) MSB Note: The Soft Step times are only programmable while the compander is not in use. Table 25. Configuration audioprocessor I (12) MSB LSB Activity / reference level 0 0 off RMS RMS Attack-times 0 0 6ms 0 1 12ms 1 0 24ms 1 1 49ms Release-times ...
Page 56
... I C bus interface Table 25. Configuration audioprocessor I (12) (continued) MSB Table 26. Configuration audioprocessor II (13) MSB 56/69 LSB Main loudness 0 flat 1 Filter ON Second loudness 0 flat 1 Filter ON Front speaker 0 not allowed 1 Second source internal coupled 0 Main source AC coupled 1 Main source internal coupled Rear speaker not allowed ...
Page 57
... TDA7402 Table 26. Configuration audioprocessor II (13) (continued) MSB Table 27. Speaker, subwoofer and mixer level-control (14-20) MSB The programming of all speaker, subwoofer and mixing level controls are the same. LSB FD2 attenuation -6dB 0dB MD1 mode single ended differential LSB + - - - - Mute bus interface ...
Page 58
... I C bus interface Table 28. Testing Audioprocessor (21) MSB Note: This byte is used for testing or evaluation purposes only and must not set to other values than "11101110" in the application! Table 29. Stereo decoder (22) MSB 58/69 LSB Audioprocessor testmode 0 off 1 on Test-multiplexer Compander log amp. output Compander low pass output ...
Page 59
... TDA7402 Table 29. Stereo decoder (22) (continued) MSB De-emphasis-Shift enabled (Subaddr.26/Bit7 = 0) Table 30. Noise blanker I (23) MSB LSB Forced MONO 1 MONO/STEREO switch automatically Pilot threshold HIGH Pilot threshold LOW De-emphasis 50µs De-emphasis 62.5µs (46.9µs De-emphasis 75µs De-emphasis 100µs (75µs LSB Noise blanker off ...
Page 60
... Fieldstrength adjust OFF Blank Time 38µs / 1.2ms 0 1 25.5µs / 800µ 32µ 22µs / 640µs Noise rectifier discharge resistor R = infinite Strong multipath influence on PEAK 18k off on (18k discharge if V LSB Stereo decoder mode rectifier gain 6dB 8dB 10dB 0 1 ...
Page 61
... TDA7402 Table 32 noiseblanker (25) (continued) MSB Table 33. High cut (26) MSB LSB Rectifier cut off frequency 0 14.0kHz 1 18.5kHz 0 28.0kHz 1 56.0kHz must be "1" LSB High cut 0 off 1 on max. high cut 0 0 2dB 0 1 5dB 1 0 7dB 1 1 10dB VHCH 42% REF5V 0 1 50% REF5V 1 0 58% REF5V ...
Page 62
... REF5V 60.0% REF5V 63.3% REF5V 66.6% REF5V 70.0% REF5V Quality detector co-efficient 0 a=0.7 1 a=0.85 0 a=1.0 1 a=1.15 HCC level shift (only level through MPD) 0.0V 500mV 1.0 V 1.5 V LSB Fast Load off Bandpass Gain 0 0 6dB 0 1 12dB 1 0 16dB 1 ...
Page 63
... Rectifier gain 0 0 Gain = 7.6dB 0 1 Gain = 4.6dB 1 0 Gain = 0dB 1 1 disabled Charge current at MP out 0.25µA 0.50µA Multipath on high cut decay time 2ms 10ms Multipath influence on PEAK discharge off -1V/ms LSB Roll off compensation not allowed 7.2% ...
Page 64
... I C bus interface Table 37. Stereo decoder configuration (30) MSB Using the multipath time-constants for stereo bland and high cut 64/69 LSB Multipath influence on high cut Off Multipath influence on stereo blend Off Level input over multipath detector Off Dual MPX mode Off 1 1 must be "1" ...
Page 65
... TDA7402 Table 38. Testing stereo decoder (31) MSB Note: This byte is used for testing or evaluation purposes only and must not set to other values than "11111100" in the application! LSB Main testmode 0 off 1 on Stereo decoder testmode 0 off 1 on Test signals F228 threshold Level for stereo blend ...
Page 66
... FD1R+ 220nF FD1R- 220nF FD2L+ 220nF FD2L- 220nF FD2R+ 220nF FD2R- 220nF AM 220nF MPX1 470nF MPOUT Figure 38. Application diagram (Dual MPX mode) 100nF SEL 100nF SER 220nF FD1L+ FD1L+ 220nF FD1L- FD1L- 220nF FD1R+ FD1R+ 220nF FD1R- FD1R- 220nF FD2L+ ...
Page 67
... Package information In order to meet environmental requirements, ST (also) offers these devices in ECOPACK packages. ECOPACK is marked on the package and on the inner box label, in compliance with JEDEC Standard JESD97. The maximum ratings related to soldering conditions are also marked on the inner box label. ECOPACK trademark. ECOPACK specifications are available at: www.st.com. ...
Page 68
... Revision history Table 39. Document revision history Date 26-Apr-2002 21-Jun-2004 26-Apr-2004 26-Apr-2006 23-Mar-2007 18-Sep-2008 68/69 Revision 1 Initial release 2 Technical migration from ST-PRESS to EDOCS 3 Revalidation 4 Minor text changes. Document reformatted. 5 Package change, text modifications. Content of the Table 6 readability, no technical changes. Changes 18, Table 19 and ...
Page 69
... The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics. All other names are the property of their respective owners. Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan - Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America Please Read Carefully: © ...