CD2231 Intel Corporation, CD2231 Datasheet - Page 46

CD2231
Manufacturer Part Number
CD2231
Description
CD2231 Intelligent Two-channel Lan And Wan Communications Controller
Manufacturer
Intel Corporation
Datasheet
1.CD2231.pdf
(178 pages)
- Current page: 46 of 178
- Download datasheet (3Mb)
CD2231 — Intelligent Two-Channel LAN and WAN Communications Controller
5.4.5
46
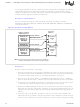
Table 3.
A and B Buffers Chaining (Sheet 2 of 2)
Transmit DMA Transfer
As in receive data transfers, two buffers are available for DMA transmit transfers. The ATBADR/
BTBADR and ATBCNT/BTBCNT (Transmit Buffer Address and Transmit Buffer Count
registers) contain the start address of and the byte count in the buffers. These registers are set by the
host when initiating a transfer. The CD2231 makes a copy of the registers to perform the transfer,
leaving the originals unchanged. The transfer of buffers between the host and the CD2231 is
controlled by the ATBSTS/BTBSTS (Transmit Buffer Status) registers.
Buffers can contain either complete frames or blocks of data, linked together to form a complete
frame or a block, or used in an Append mode to transmit data as it arrives from another process.
The first two transfer types are Block mode transfers, the last is the Append mode. Both are
described further below. The management of the buffers reduces the processor overhead associated
with short data transfers and increases the minimum response time requirements for frame-based
transmissions.
Chain Mode Transfer
In Chain mode, the frame should be complete in buffers in memory before transmission is started.
The Append Status bit should not be set; the Start of Frame bit must be set to begin transmission,
and the Last Buffer bit must be set if this buffer is the last in a chained block or is a complete frame
or block.
When the CRC bit is set, the CD2231 generates and transmits a cyclic redundancy check word for
the frame using the polynomial selected by the CPSR (CRC Polynomial Select register). If the
Interrupt Required bit is set, a host interrupt is generated after the buffer is transmitted.
Transmit buffers can be chained to support large frames. To minimize bus usage, the first buffer of
the chain should begin on an even address in host memory. The CD2231 begins fetching a frame
from a buffer performing DMA transfer, reading two bytes at a time. The CD2231 cannot realign
data between external memory and the FIFO. If one buffer of the chain ends on an odd address, the
next buffer in the chain should begin on an odd address. Otherwise, only single-byte transfers are
made for the rest of the buffer.
Append Mode Transfer (Buffer A Only)
Append mode transfers are available for Buffer A in Asynchronous mode only. If Buffer A is set to
Append mode, the host can enable the CD2231 to transmit data in the buffer before it is completely
filled. The CD2231 starts transmitting new data when it is appended to the buffer.
This mode is useful for terminal echo routines that do not wait for a complete block to be formed
before starting transmission. In this mode, transmission is started when the buffer is made available
to the CD2231 by the host; ATBADR[0–3] and ATBCNT[l, h] are initialized. Subsequent
triggering of DMA transfer occurs by programming the ATBCNT[l, h] with the accumulated byte
Ntbuf
0
1
1
2231own
Buffer A
1
1
0
2231own
Buffer B
1
0
0
Host sets up Buffer A
CD2231 completes B Tx, passes to host, accepts A and
marks B as next
CD2231 completes A Tx and passes it to host
Transmit Action
Datasheet
Related parts for CD2231
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
CD-ROM, DVD Multimedia IC
Manufacturer:
China Hua Jing Electronics Group Co.

Part Number:
Description:
Cd-rom
Manufacturer:
ROHM Electronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
CD-ROM spindle motor driver
Manufacturer:
Rohm
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
CD Digital Signal Processor
Manufacturer:
Silan
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
CD Digital Servo Signal Processor
Manufacturer:
Silan
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
CD Digital Signal Processor
Manufacturer:
Silan
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
CD Servo Controller
Manufacturer:
Silan
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Cd Electronic Shockproof Controller
Manufacturer:
Silan
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Cd Servo Controller With Mcu With Interface Supporting Sc9831 Wma/mp3 Encoding/decoding
Manufacturer:
Silan
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Cd Digital Servo Signal Processor Slave Mode
Manufacturer:
Silan
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Cd Digital Servo Signal Processor With Mcu 2/4 Digits Lcd Display And Remote Control
Manufacturer:
Silan
Datasheet: