AD9832 Analog Devices, AD9832 Datasheet - Page 8

AD9832
Manufacturer Part Number
AD9832
Description
CMOS Complete DDS
Manufacturer
Analog Devices
Datasheet
1.AD9832.pdf
(16 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
AD9832AST
Manufacturer:
ADI
Quantity:
217
Company:
Part Number:
AD9832BRU
Manufacturer:
AD
Quantity:
5 510
Part Number:
AD9832BRU
Manufacturer:
ADI/亚德诺
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
AD9832BRUZ
Manufacturer:
ADI
Quantity:
860
Part Number:
AD9832BRUZ
Manufacturer:
ADI/亚德诺
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
AD9832BRUZ-REEL7
Manufacturer:
KOA
Quantity:
400 000
AD9832
TERMINOLOGY
Integral Nonlinearity
This is the maximum deviation of any code from a straight line
passing through the endpoints of the transfer function. The end-
points of the transfer function are zero scale, a point 0.5 LSB be-
low the first code transition (000 . . . 00 to 000 . . . 01) and full
scale, a point 0.5 LSB above the last code transition (111 . . . 10
to 111 . . . 11). The error is expressed in LSBs.
Differential Nonlinearity
This is the difference between the measured and ideal 1 LSB
change between two adjacent codes in the DAC.
Signal to (Noise + Distortion)
Signal to (Noise + Distortion) is measured signal to noise at the
output of the DAC. The signal is the rms magnitude of the
fundamental. Noise is the rms sum of all the nonfundamental
signals up to half the sampling frequency (f
ing the dc component. Signal to (Noise + Distortion) is depen-
dent on the number of quantization levels used in the digitization
process; the more levels, the smaller the quantization noise. The
theoretical Signal to (Noise + Distortion) ratio for a sine wave
input is given by
where N is the number of bits. Thus, for an ideal 10-bit con-
verter, Signal to (Noise + Distortion) = 61.96 dB.
Total Harmonic Distortion
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) is the ratio of the rms
sum of harmonics to the rms value of the fundamental. For
the AD9832, THD is defined as:
where V
V
sixth harmonic.
Output Compliance
The output compliance refers to the maximum voltage that can
be generated at the output of the DAC to meet the specifica-
tions. When voltages greater than those specified for the output
compliance are generated, the AD9832 may not meet the speci-
fications listed in the data sheet.
Spurious Free Dynamic Range
Along with the frequency of interest, harmonics of the fundamental
frequency and images of the MCLK frequency are present at the
output of a DDS device. The spurious free dynamic range (SFDR)
refers to the largest spur or harmonic present in the band of
interest. The wide band SFDR gives the magnitude of the larg-
est harmonic or spur relative to the magnitude of the fundamental
frequency in the bandwidth 2 MHz about the fundamental fre-
quency. The narrow band SFDR gives the attenuation of the
largest spur or harmonic in a bandwidth of 50 kHz about the
fundamental frequency.
Clock Feedthrough
There will be feedthrough from the MCLK input to the analog
output. Clock feedthrough refers to the magnitude of the MCLK
signal relative to the fundamental frequency in the AD9832’s out-
put spectrum.
4
, V
5
and V
Signal to (Noise + Distortion) = (6.02N + 1.76) dB
THD
1
is the rms amplitude of the fundamental and V
6
are the rms amplitudes of the second through the
20 log
V
2
2
V
3
2
V
V
1
4
2
MCLK
V
5
2
/2) but exclud-
V
6
2
2
, V
3
,
–8–
A3
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Register
FREQ0 REG
FREQ1 REG
PHASE0 REG 12 Bits
PHASE1 REG 12 Bits
PHASE2 REG 12 Bits
PHASE3 REG 12 Bits
8
4
H
M
- 8
M
S
B
A2
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
S
B
t i
B
6 1
s
W
s
(
T
M
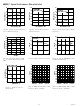
Table II. Addressing the Registers
o
Table III. 32-Bit Frequency Word
Table IV. 12-Bit Frequency Word
h
r
S
e
d
Size
32 Bits
32 Bits
B
8
A1
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
Table I. Control Registers
4
L
s
L
o
M
a
M
S
d
B
S
e
d
B
s
=
s
f o
A0
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
Description
Frequency Register 0. This de-
fines the output frequency, when
FSELECT = 0, as a fraction of
the MCLK frequency.
Frequency Register 1. This de-
fines the output frequency, when
FSELECT = 1, as a fraction of
the MCLK frequency.
Phase Offset Register 0. When
PSEL0 = PSEL1 = 0, the contents
of this register are added to the
output of the phase accumulator.
Phase Offset Register 1. When
PSEL0 = 1 and PSEL1 = 0, the
contents of this register are added to
the output of the phase accumulator.
Phase Offset Register 2. When
PSEL0 = 0 and PSEL1 = 1, the con-
tents of this register are added to
the output of the phase accumulator.
Phase Offset Register 3. When
PSEL0 = PSEL1 = 1, the contents
of this register are added to the
output of the phase accumulator.
) 0
h t
e
8
H
Destination Register
FREQ0 REG 8 L LSBs
FREQ0 REG 8 H LSBs
FREQ0 REG 8 L MSBs
FREQ0 REG 8 H MSBs
FREQ1 REG 8 L LSBs
FREQ1 REG 8 H LSBs
FREQ1 REG 8 L MSBs
FREQ1 REG 8 H MSBs
PHASE0 REG 8 LSBs
PHASE0 REG 8 MSBs
PHASE1 REG 8 LSBs
PHASE1 REG 8 MSBs
PHASE2 REG 8 LSBs
PHASE2 REG 8 MSBs
PHASE3 REG 8 LSBs
PHASE3 REG 8 MSBs
L
S
B
6 1
s
L
8
S
L
B
8
S
s
B
L
s
L
S
REV. A
B
s