LCMXO2280 Lattice Semiconductor, LCMXO2280 Datasheet - Page 12
LCMXO2280
Manufacturer Part Number
LCMXO2280
Description
(LCMXOxxx) MachXO Family
Manufacturer
Lattice Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.LCMXO2280.pdf
(95 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
LCMXO2280-4FTN324C-3I
Manufacturer:
LATTICE
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
LCMXO2280C
Manufacturer:
Lattice
Quantity:
650
Company:
Part Number:
LCMXO2280C-3B256C
Manufacturer:
Lattice Semiconductor Corporation
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
LCMXO2280C-3B256I
Manufacturer:
Lattice Semiconductor Corporation
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
LCMXO2280C-3BN256C
Manufacturer:
Lattice Semiconductor Corporation
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
LCMXO2280C-3BN256I
Manufacturer:
Lattice Semiconductor Corporation
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
LCMXO2280C-3FT256C
Manufacturer:
Lattice Semiconductor Corporation
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
LCMXO2280C-3FTN256C
Manufacturer:
SIPEX
Quantity:
1 508
Company:
Part Number:
LCMXO2280C-3FTN324C
Manufacturer:
LATTICE
Quantity:
175
Part Number:
LCMXO2280C-3FTN324C
Manufacturer:
LATTICE
Quantity:
20 000
Lattice Semiconductor
sysCLOCK Phase Locked Loops (PLLs)
The MachXO1200 and MachXO2280 provide PLL support. The source of the PLL input divider can come from an
external pin or from internal routing. There are four sources of feedback signals to the feedback divider: from
CLKINTFB (internal feedback port), from the global clock nets, from the output of the post scalar divider, and from
the routing (or from an external pin). There is a PLL_LOCK signal to indicate that the PLL has locked on to the input
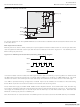
clock signal. Figure 2-10 shows the sysCLOCK PLL diagram.
The setup and hold times of the device can be improved by programming a delay in the feedback or input path of
the PLL which will advance or delay the output clock with reference to the input clock. This delay can be either pro-
grammed during configuration or can be adjusted dynamically. In dynamic mode, the PLL may lose lock after
adjustment and not relock until the t
allows the user to adjust the phase and duty cycle of the CLKOS output.
The sysCLOCK PLLs provide the ability to synthesize clock frequencies. Each PLL has four dividers associated
with it: input clock divider, feedback divider, post scalar divider, and secondary clock divider. The input clock divider
is used to divide the input clock signal, while the feedback divider is used to multiply the input clock signal. The post
scalar divider allows the VCO to operate at higher frequencies than the clock output, thereby increasing the fre-
quency range. The secondary divider is used to derive lower frequency outputs.
Figure 2-10. PLL Diagram
Figure 2-11 shows the available macros for the PLL. Table 2-5 provides signal description of the PLL Block.
Figure 2-11. PLL Primitive
CLKFB
(from Post Scalar
Divider output,
clock net,
routing/external
pin or CLKINTFB
port
(from routing or
external pin)
CLKI
RST
Input Clock
Divider
(CLKI)
Feedback
(CLKFB)
Divider
Dynamic Delay Adjustment
DDAIDEL[2:0]
LOCK
DDA MODE
Adjust
Delay
DDAILAG
DDAIZR
CLKFB
parameter has been satisfied. Additionally, the phase and duty cycle block
CLKI
RST
Controlled
Oscillator
Voltage
VCO
EHXPLLC
2-9
Post Scalar
(CLKOP)
Divider
CLKOP
CLKOS
CLKOK
LOCK
CLKINTFB
MachXO Family Data Sheet
Phase/Duty
Secondary
(CLKOK)
Divider
Select
Clock
LOCK
CLKOS
CLKOP
CLKOK
CLKINTFB
(internal feedback)
www.DataSheet4U.com
Architecture