MC145408 Motorola, MC145408 Datasheet - Page 6

MC145408
Manufacturer Part Number
MC145408
Description
(MC145403 - MC145408) DRIVER / RECEIVERS
Manufacturer
Motorola
Datasheet
1.MC145408.pdf
(9 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
MC145408DW
Manufacturer:
FREESCALE
Quantity:
1 831
www.DataSheet4U.com
DataSheet
4
DI1 – DI n
Data Input Pins
ers. Input voltage levels on these pins are LSTTL compatible
and must be between V CC and GND. A weak pull–up on
each input sets all unused DI pins to V CC , causing the corre-
sponding unused driver outputs to be at V SS .
Tx1 – TX n
Transmit Data Output Pins
which swing from V DD to V SS . A logic 1 at the DI input causes
the corresponding Tx output to swing to V SS . A logic 0 at the
DI input causes the corresponding Tx out to swing to V DD .
The actual levels and slew rate achieved will depend on the
output loading (R L
POWER SUPPLY CONSIDERATIONS
vice current.
through an internal diode from the V CC pin to the V DD pin
when V DD < V CC by approximately 0.6 V or greater. This high
current condition can exist for a short period of time during
power up/down. Additionally, if the + 12 V supply is switched
MC145403 MC145404 MC145405 MC145408
6
U
.com
These are the high impedance digital input pins to the driv-
These are the EIA–232–E transmit signal output pins,
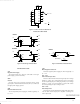
Figure 4 shows a technique to guard against excessive de-
The diode D1 prevents excessive current from flowing
APPLICATION INFORMATION
ø
C L ).
MMBZ15VDLT1 x 10
Figure 4.
C3
C1
1N4001
– 12 V
off while the + 5 V is on and the off supply is a low impedance
to ground, the diode D1 will prevent current flow through the
internal diode.
from drifting positive to V CC , in the event that power is re-
moved from V SS (Pin 12). If V SS power is removed, and the
impedance from the V SS pin to ground is greater than
approximately 3 k , this pin will be pulled to V CC by internal
circuitry causing excessive current in the V CC pin.
exist, then the diodes D1 and D2 are not required.
ESD PROTECTION
ble to the outside world is essential. High static voltages ap-
plied to the pins when someone touches them either directly
or indirectly can cause damage to gate oxides and transistor
junctions by coupling a portion of the energy from the I/O pin
to the power supply buses of the IC. This coupling will usually
occur through the internal ESD protection diodes. The key to
protecting the IC is to shunt as much of the energy to ground
as possible before it enters the IC. Figure 4 shows a tech-
nique which will clamp the ESD voltage at approximately
appears on the supply pins is shunted to ground through the
capacitors C1 – C3. This scheme has provided protection to
the interface part up to 10 kV, using the human body model
test.
D1
15 V using the MMBZ15VDLT1. Any residual voltage which
The diode D2 is used as a voltage clamp, to prevent V SS
If by design, neither of the above conditions are allowed to
ESD protection on IC devices that have their pins accessi-
+ 12 V
V DD
V SS
Rx1
Rx2
Rx3
Rx4
Rx5
Tx1
Tx2
Tx3
Tx4
Tx5
1N4001
10
12
11
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1N5818
R
R
R
R
R
D
D
D
D
D
D2
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
V CC
DO1
DI1
DO2
DI2
DO3
DI3
DO4
DI4
DO5
DI5
GND
+ 5 V
C2
MOTOROLA