S2009TB Applied Micro Circuits Corporation, S2009TB Datasheet

S2009TB
Related parts for S2009TB
S2009TB Summary of contents
Page 1
DEVICE SPECIFICATION 1.6 GBPS QUAD SERIAL BACKPLANE DEVICE 1.6 GBPS QUAD SERIAL BACKPLANE DEVICE FEATURES • CMOS Technology • Broad operating rate range (1.3 - 1.6 Gbps) - 1.6 Gbps - 1/2 Rate Operation • Quad Transmitter with Phase-Lock Loop ...
Page 2
S2009 Figure 2. Typical Serial Backplane Application MAC (ASIC) MAC ATM (ASIC) Gigabit S2009 Ethernet Etc. MAC (ASIC) MAC (ASIC) MAC (ASIC) ATM MAC Gigabit (ASIC) Ethernet S2009 Etc. MAC (ASIC) MAC (ASIC) 2 1.6 GBPS QUAD SERIAL BACKPLANE DEVICE ...
Page 3
GBPS QUAD SERIAL BACKPLANE DEVICE Figure 3. S2009 Input/Output Diagram RESET_N RATE REFCLK TCLKO TCLKO2 SYNC DINA[0:7] 10 DNA, KGENA TCLKA SQLA_N DINB[0:7] 10 DNB, KGENB TCLKB SQLB_N DINC[0:7] 10 DNC, KGENC TCLKC SQLC_N DIND[0:7] 10 DND, KGEND TCLKD ...
Page 4
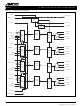
S2009 Figure 4. Transmitter Block Diagram RATE REFCLK CH_LOCK 8 DINA[0:7] FIFO SYNC (input) DNA KGENA 0 1 TCLKA 8 DINB[0:7] FIFO (input) DNB KGENB 0 1 TCLKB 8 DINC[0:7] FIFO (input) DNC KGENC 0 1 TCLKC 8 DIND[0:7] FIFO ...
Page 5
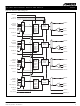
GBPS QUAD SERIAL BACKPLANE DEVICE Figure 5. Receiver Block Diagram CMODE RATE REFCLK EOFA FIFO KFLAGA (output) ERRA 8 Q DOUTA[0:7] RCAP/N LOLA EOFB FIFO KFLAGB (output) ERRB 8 DOUTB[0:7] RCBP/N LOLB EOFC FIFO KFLAGC (output) ERRC 8 DOUTC[0:7] ...
Page 6
S2009 TRANSMITTER DESCRIPTION The transmitter section of the S2009 contains a single PLL which is used to generate the serial rate transmit clock for all transmitters. Four channels are provided with a variety of options regarding input clocking and loopback. ...
Page 7
GBPS QUAD SERIAL BACKPLANE DEVICE Figure 6. DINx Data Clocking with TCLK TCLKO DINx[0:7] TCLKx MAC ASIC Figure 6 demonstrates the flexibility afforded by the S2009. A low jitter reference is provided directly to the S2009 at 1/20 the ...
Page 8
S2009 In order to provide interface compatibility to non- AMCC serial backplane transceivers, the S2009 can also generate a unique sync character consisting of 16 consecutive K28.5 characters. This event is initi- ated by the simultaneous assertion of SYNC and ...
Page 9
GBPS QUAD SERIAL BACKPLANE DEVICE Table 4. Data to 8B/10B Alphabetic Representation Table 5. Operating Rates ...
Page 10
S2009 RECEIVER DESCRIPTION Each receiver channel is designed to implement a Serial Backplane receiver function through the physi- cal layer. A block diagram showing the basic func- tion is provided in Figure 5. Whenever a signal is present, the receiver ...
Page 11
GBPS QUAD SERIAL BACKPLANE DEVICE When operating in independent mode, PLL “Loss of Lock” status for each channel is indicated by a continu- ous 1-0-1 on its respective ERR, EOF, and KFLAG outputs. LOLx will report a logic 1 ...
Page 12
S2009 TCLKD is used to reset the Channel Lock state machine and initialize the FIFOs in the receive data path. Assertion of TCLKD Low does not interrupt the transmit data path. When not in Channel Lock Mode, the linkage between ...
Page 13
GBPS QUAD SERIAL BACKPLANE DEVICE Figure 8. Channel Lock Synchronization Timing (Internal) RESYNC A (Internal) RESYNC B (Internal) RESYNC C (Internal) RESYNC D (internal) deskewed RESYNC A (internal) deskewed RESYNC B (internal) deskewed RESYNC C (internal) deskewed RESYNC D ...
Page 14
S2009 Table 7. Error and Status Reporting, Channel Lock and Independent Mode ...
Page 15
GBPS QUAD SERIAL BACKPLANE DEVICE CHANNEL LOCKING/RE-LOCKING PROCEDURE The channel locking/relocking procedures are sum- marized below. Following these procedures will in- sure proper Channel Lock operation of the device. When powered up, the S2009 will lock to the re- ...
Page 16
S2009 Table 8. Output Clock Mode Table 8A. S2009 Data Clocking 1.6 GBPS QUAD SERIAL BACKPLANE DEVICE ...
Page 17
GBPS QUAD SERIAL BACKPLANE DEVICE OTHER OPERATING MODES Operating Frequency Range The S2009 is designed to operate at serial baud rates of 1.3 to 1.6 GHz (1.04 – 1.28 Gbps user data rate). Loopback Mode When loopback mode is ...
Page 18
S2009 The following table provides a list of the pins that are JTAG tested. Each port has a Boundary Scan Register (BSR), unless otherwise noted. The following features are described: the JTAG mode of each register (input, output2, or internal ...
Page 19
GBPS QUAD SERIAL BACKPLANE DEVICE Table 9. JTAG Pin Assignments (Continued ...
Page 20
S2009 Table 10. Transmitter Input Pin Assignment and Descriptions ...
Page 21
GBPS QUAD SERIAL BACKPLANE DEVICE Table 10. Transmitter Signal Input Pin Assignment and Descriptions (Continued ...
Page 22
S2009 Table 11. Transmitter Output Signals ...
Page 23
GBPS QUAD SERIAL BACKPLANE DEVICE Table 12. Mode Control Signals ...
Page 24
S2009 Table 13. Receiver Output Pin Assignment and Descriptions ...
Page 25
GBPS QUAD SERIAL BACKPLANE DEVICE Table 13. Receiver Output Pin Assignment and Descriptions (Continued ...
Page 26
S2009 Table 13. Receiver Output Pin Assignment and Descriptions (Continued ...
Page 27
GBPS QUAD SERIAL BACKPLANE DEVICE Table 14. Receiver Input Pin Assignment and Descriptions ...
Page 28
S2009 Table 16. Power and Ground Signals ...
Page 29
GBPS QUAD SERIAL BACKPLANE DEVICE Table 16. Power and Ground Signals (Continued ...
Page 30
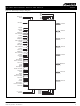
S2009 Figure 10. S2009 Pinout (Bottom View ...
Page 31
GBPS QUAD SERIAL BACKPLANE DEVICE Figure 11. S2009 Pinout (Top View ...
Page 32
S2009 Figure 12. Compact 208 Pin TBGA Package Thermal Management Note: The S2009 requires an airflow ...
Page 33
GBPS QUAD SERIAL BACKPLANE DEVICE Figure 13. Transmitter Timing (Independent or Channel Lock Mode) TCLKx, TCLKA DINx[0:7], DNx, KGENx, SYNC SERIAL DATA OUT Table 18. S2009 Transmitter Timing (Independent or Channel Lock Mode ...
Page 34
S2009 Table 20. S2009 Receiver Timing (Full and Half Clock Mode ...
Page 35
GBPS QUAD SERIAL BACKPLANE DEVICE Figure 14. Receiver Timing (Full Clock Mode, CMODE = 1) SERIAL DATA IN RCxN RCxP DOUTx[0:7], EOFx, KFLAGx, ERRx Figure 15. Receiver Timing (Half Clock Mode, CMODE = 0) SERIAL DATA IN RCxN RCxP ...
Page 36
S2009 Table 21. Absolute Maximum Ratings ...
Page 37
GBPS QUAD SERIAL BACKPLANE DEVICE Table 24. Serial Data Timing, Transmit Outputs ...
Page 38
S2009 Figure 16. Differential Input Voltage V IN (+) V IN (– (+) – (–) (Note: V (+) – V (-) is the algebraic difference of the input signals Table 27. Differential LVPECL Characteristics ...
Page 39
GBPS QUAD SERIAL BACKPLANE DEVICE Figure 17. Differential Output Voltage V OUT (+) V OUT (–) V OUT (+) – V OUT (–) (Note: V (+) – V (-) is the algebraic difference of the input signals.) OUT OUT ...
Page 40
S2009 OUTPUT LOAD The S2009 serial outputs do not require output pulldown resistors. ACQUISITION TIME With the input eye diagram shown in Figure 23, the S2009 will recover data with a 1E-9 BER within the time specified ...
Page 41
GBPS QUAD SERIAL BACKPLANE DEVICE Figure 24. Loop Filter Capacitor Connections February 9, 2001 / Revision C 270 CAP1 22 nF CAP2 270 S2009 S2009 41 ...
Page 42
... Applied Micro Circuits Corporation • 6290 Sequence Dr., San Diego, CA 92121 Phone: (858) 450-9333 • (800) 755-2622 • Fax: (858) 450-9885 AMCC reserves the right to make changes to its products or to discontinue any semiconductor product or service without notice, and advises its customers to obtain the latest version of relevant information to verify, before placing orders, that the information being relied on is current ...