TDA5142 Philips Semiconductors, TDA5142 Datasheet - Page 11
TDA5142
Manufacturer Part Number
TDA5142
Description
Brushless DC motor drive circuit
Manufacturer
Philips Semiconductors
Datasheet
1.TDA5142.pdf
(20 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
TDA5142
Manufacturer:
NXP
Quantity:
5 510
Company:
Part Number:
TDA5142
Manufacturer:
NXP
Quantity:
5 510
Company:
Part Number:
TDA5142T
Manufacturer:
NXPLIPS
Quantity:
5 510
Part Number:
TDA5142T
Manufacturer:
SOP-24
Quantity:
20 000
Philips Semiconductors
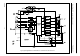
Introduction (see Fig.6)
Full-wave driving of a three phase motor requires three
push-pull output stages. In each of the six possible states
two outputs are active, one sourcing (H) and one sinking
(L). The third output presents a high impedance (Z) to the
motor, which enables measurement of the motor
back-EMF in the corresponding motor coil by the EMF
comparator at each output. The commutation logic is
responsible for control of the output transistors and
selection of the correct EMF comparator. In Table 1 the
sequence of the six possible states of the external
connected output transistors has been depicted and the
corresponding output levels on the NA, PA, NB, PB, NC
and PC outputs of the TDA5142T.
The zero-crossing in the motor EMF (detected by the
comparator selected by the commutation logic) is used to
calculate the correct moment for the next commutation,
that is, the change to the next output state. The delay is
calculated (depending on the motor loading) by the
adaptive commutation delay block.
The output stages are also protected by a current limiting
circuit and by thermal protection.
The detected zero-crossings are used to provide speed
information. The information has been made available on
the FG output pin. This output provides an output signal
with a frequency equal to the commutation frequency.
The system will only function when the EMF voltage from
the motor is present. Therefore, a start oscillator is
provided that will generate commutation pulses when no
zero-crossings in the motor voltage are available.
A timing function is incorporated into the device for internal
timing and for timing of the reverse rotation detection.
Table 1 Output states.
Note
1. H = HIGH state; L = LOW state; Z = high-impedance OFF-state.
June 1994
STATE
Brushless DC motor drive circuit
1
2
3
4
5
6
MOT1
H
H
Z
Z
L
L
(1)
OUT-
NA
H
H
L
L
L
L
(1)
OUT-
PA
H
H
H
H
L
L
(1)
MOT2
H
H
L
L
Z
Z
(1)
11
The TDA5142T also contains an uncommitted
transconductance amplifier (OTA) that can be used as a
control amplifier. The output is capable of directly driving
an external power transistor.
The TDA5142T is designed for systems with low current
consumption: use of I
output transistors (patented).
Adjustments
The system has been designed in such a way that the
tolerances of the application components are not critical.
However, the approximate values of the following
components must still be determined:
T
This capacitor determines the frequency of the start
oscillator. It is charged and discharged, with a current of
2 A, from 0.05 to 2.2 V and back to 0.05 V. The time
taken to complete one cycle is given by:
t
The start oscillator is reset by a commutation pulse and so
is only active when the system is in the start-up mode. A
pulse from the start oscillator will cause the outputs to
change to the next state (torque in the motor).
start
OUT-
NB
HE START CAPACITOR
The start capacitor; this determines the frequency of the
start oscillator.
The two capacitors in the adaptive commutation delay
circuit; these are important in determining the optimum
moment for commutation, depending on the type and
loading of the motor.
The timing capacitor; this provides the system with its
timing signals.
H
H
L
L
L
L
(1)
= (2.15
OUT-
PB
C) s (with C in F)
H
H
H
H
L
L
(1)
2
(CAP-ST)
L logic, adaptive base drive for the
MOT3
H
H
Z
L
L
Z
(1)
Product specification
OUT-
NC
TDA5142T
H
H
L
L
L
L
(1)
OUT-
PC
H
H
H
H
L
L
(1)