TDA5146T Philips Semiconductors, TDA5146T Datasheet - Page 14
TDA5146T
Manufacturer Part Number
TDA5146T
Description
Brushless DC motor drive circuit
Manufacturer
Philips Semiconductors
Datasheet
1.TDA5146T.pdf
(18 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
TDA5146T
Manufacturer:
PHILIPS/飞利浦
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
TDA5146TC1D
Manufacturer:
PHILIPS/飞利浦
Quantity:
20 000
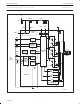
1. If the chosen value of CAP–TI is too small, then oscillations can occur in certain positions of a blocked rotor. If the chosen value is too large,
Philips Semiconductors
NOTE:
The External Damping Components
Flyback pulses from the motor windings may cause H F interference and acoustic noise. The flyback pulses can be damped by
RC–combinations in parallel with the motor windings. This reduces the HF interference; it also reduces the acoustic noise by several dB,
depending on the motor construction.
These damping components also have negative effects. They not only dissipate energy from the flyback pulses, but also contribute to the
overall energy consumption. Other negative effects are discussed below.
One negative effect is the distortion of the motor EMF sensed by the comparators in the TDA5146T. This distortion may influence the correct
functioning of the TDA5146T, for example, an (damped) oscillation occurring after the winding has been switched off. This oscillation must be
critically (or over critically) damped, so that:
A second requirement is that the effect of the damping components must be negligible by the time that the zero–crossing of the EMF is
expected. This is because the remainder of the step (due to RC components) causes shifting of the zero–crossing. For a critically damped
combination the voltage can be calculated as a negative exponential with ws
Example: Commutation frequency = 900 Hz, so t = 1100 ms, the time taken from the end of the diode pulse to the zero–crossing of the EMF will
be approximately t = 440 ms. If a damping voltage from 9 V to 3 mV is required, then the reduction is 3000–fold, or e exp–8 = e exp – ws
This gives ws = 18180 rad/s. With L = 3 mH, C is found to be 1.01 mF (use 1 mF) and R is found to be 109.1 W (use 100 W).
A motor voltage of 7 V (peak–to–peak) at 150 Hz gives 3300 V/s, thus a 3 mV remainder shifts the zero–crossing 1 ms. Eddy currents will also
contribute to this phase shift. A shift of 20 ms corresponds with 0.18 degrees (mechanically) for a 1500 rpm motor, or 0.1 mm on a VHS scanner
drum.
Other Design Aspects
There are other design aspects concerning the application of the TDA5146T besides the commutation function. They are:
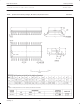
FG Signal
The FG signal is generated in the TDA5146T by using the zero–crossing of the motor EMF from the three motor windings. Every zero–crossing
in a (star connected) motor winding is used to toggle the FG output signal. The FG frequency is therefore half the commutation frequency. All
transitions indicate the detection of a zero–crossing (except for PG). The negative–going edges are called FG pulses because they generate an
interrupt in a controlling microprocessor.
The accuracy of the FG output signal (jitter) is very good. This accuracy depends on the symmetry of the motor’s electromagnetic construction,
which also effects the satisfactory functioning of the motor itself.
Example: A three phase motor with 6 magnetic pole–pairs at 1500 rpm and with a full–wave drive has a commutation frequency of 25
= 900 Hz, and generates a tacho signal of 450 Hz.
DIRECTION Input
If the voltage on pin 24 is less than 0.8 V, the motor is running in one direction (depending of the motor connections). If the voltage on pin 24 is
higher than 2.0V, the motor is running in the other direction.
BRAKE function
If the voltage on pin 23 is higher than 2.0V , the motor brakes. In that condition, the 3 outputs MOT1, MOT2, and MOT3 are forced at a low level
and the current limitation is done internally by the sink drivers.
TEST function
It is possible to turn off the three outputs by forcing in pin 16 a current of 600 mA.
1994 May 18
Generation of the tacho signal FG
Possibilities of motor control
Preposition input
Direction input
Brake input
Reliability
Brushless DC motor drive circuit
then it is possible that the motor may run in the reverse direction (synchronously with little torque).
R
2
C = 4
L (L = inductance of one coil, R and C for damping)
14
t.
TDA5146T
Product specification
6
t.
6