LTC4269-1 Linear Technology Corporation, LTC4269-1 Datasheet - Page 26

LTC4269-1
Manufacturer Part Number
LTC4269-1
Description
IEEE 802.3 At PD And Synchronous No-Opto Flyback Controller
Manufacturer
Linear Technology Corporation
Datasheet
1.LTC4269-1.pdf
(44 pages)
www.DataSheet4U.com
APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
LTC4269-1
Note the use of the external feedback resistive divider
ratio to set output voltage provides the user additional
freedom in selecting a suitable transformer turns ratio.
Turns ratios that are the simple ratios of small integers;
e.g., 1:1, 2:1, 3:2 help facilitate transformer construction
and improve performance.
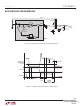
When building a supply with multiple outputs derived
through a multiple winding transformer, lower duty cycle
can improve cross regulation by keeping the synchronous
rectifi er on longer, and thus, keep secondary windings
coupled longer. For a multiple output transformer, the turns
ratio between output windings is critical and affects the
accuracy of the voltages. The ratio between two output
voltages is set with the formula V
N21 is the turns ratio between the two windings. Also
keep the secondary MOSFET R
cross regulation.
The feedback winding usually provides both the feedback
voltage and power for the LTC4269-1. Set the turns ratio
between the output and feedback winding to provide a
rectifi ed voltage that under worst-case conditions is greater
than the 11V maximum V
Leakage Inductance
Transformer leakage inductance (on either the primary or
secondary) causes a spike after the primary-side switch
turn-off. This is increasingly prominent at higher load
currents, where more stored energy is dissipated. Higher
fl yback voltage may break down the MOSFET switch if it
has too low a BV
One solution to reducing this spike is to use a clamp circuit
to suppress the voltage excursion. However, suppressing
the voltage extends the fl yback pulse width. If the fl yback
26
For our example: N
where
We
N
V
F
SF
will choose
=
:
>
Diode Forward V
11
V
OUT
+
V
DSS
F
3
1
rating.
SF
>
CC
o o ltage
11 0 7
turn-off voltage.
+
5
OUT2
DS(ON)
.
=
= V
2 34
small to improve
.
1
OUT1
• N21 where
pulse extends beyond the enable delay time, output
voltage regulation is affected. The feedback system has a
deliberately limited input range, roughly ±50mV referred
to the FB node. This rejects higher voltage leakage spikes
because once a leakage spike is several volts in amplitude,
a further increase in amplitude has little effect on the
feedback system. Therefore, it is advisable to arrange the
clamp circuit to clamp at as high a voltage as possible,
observing MOSFET breakdown, such that leakage spike
duration is as short as possible. Application Note 19
provides a good reference on clamp design.
As a rough guide, leakage inductance of several percent
(of mutual inductance) or less may require a clamp, but
exhibit little to no regulation error due to leakage spike
behavior. Inductances from several percent up to, perhaps,
ten percent, cause increasing regulation error.
Avoid double digit percentage leakage inductances. There
is a potential for abrupt loss of control at high load current.
This curious condition potentially occurs when the leakage
spike becomes such a large portion of the fl yback waveform
that the processing circuitry is fooled into thinking that the
leakage spike itself is the real fl yback signal!
It then reverts to a potentially stable state whereby the
top of the leakage spike is the control point, and the
trailing edge of the leakage spike triggers the collapse
detect circuitry. This typically reduces the output voltage
abruptly to a fraction, roughly one-third to two-thirds of
its correct value.
Once load current is reduced suffi ciently, the system snaps
back to normal operation. When using transformers with
considerable leakage inductance, exercise this worst-case
check for potential bistability:
1. Operate the prototype supply at maximum expected
2. Temporarily short-circuit the output.
3. Observe that normal operation is restored.
If the output voltage is found to hang up at an abnormally
low value, the system has a problem. This is usually evident
by simultaneously viewing the primary-side MOSFET drain
voltage to observe fi rsthand the leakage spike behavior.
load current.
42691f