pcf8814 NXP Semiconductors, pcf8814 Datasheet
pcf8814
Related parts for pcf8814
pcf8814 Summary of contents
Page 1
... DATA SHEET PCF8814 65 96 pixels matrix LCD driver Objective specification INTEGRATED CIRCUITS 2003 Mar 13 ...
Page 2
... Objective specification PCF8814 Set Y address of RAM Set X address of RAM Set display start line Bias levels LCD drive voltage LCD drive voltage generation Temperature measurement Temperature compensation N-line inversion Orthogonal functions Voltage monitor Bottom Row Swap LIMITING VALUES ...
Page 3
... The can be interfaced to microcontrollers via a serial bus. (1) Type PCF8814MU/2DB/2 is sold under a Motif agreement. Motif Group in the US and other countries. Type PCF8814U/2DB/2 is not covered by a Philips/Motif License agreement. For further information on Motif licensed and unlicensed LCD drivers from Philips, please contact your local Philips office. ...
Page 4
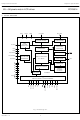
... DATA PROCESSING DISPLAY DATA RAM 65 96 bits ADDRESS COUNTER COMMAND DECODER I/O BUFFER 2 PARALLEL / SERIAL / I C-BUS INTERFACE Fig.1 Block diagram. 4 Objective specification R0 to R64 65 ROW DRIVERS ORTHOGONAL FUNCTIONS GENERATOR RESET OSCILLATOR TIMING GENERATOR DISPLAY ADDRESS COUNTER PCF8814 MBL539 PCF8814 RES OSC ...
Page 5
... These two logic inputs are used for interface selection. Horizontal mirroring input. External reset input, active LOW. This signal will reset the device and must be applied to initialize the chip. 5 Objective specification PCF8814 . SS is used as the supply voltage DD1 and V DD2 ...
Page 6
... SDAHOUT pad to the system SDAH line can be significant, a potential divider is generated by the bus pull-up resistor and the ITO track resistance possible that during the acknowledge cycle the PCF8814 will not be able to create a valid logic 0 level. By splitting the SDAH input from the SDAHOUT output the device could be used in a mode that ignores the acknowledge bit ...
Page 7
... The PCF8814 contains 65 row and 96 column drivers which connect the appropriate LCD bias voltages in sequence to the display, in accordance with the data to be displayed. The number of simultaneously selected rows is represented by the value ‘p’. In the PCF8814, ‘p’ is set automatically, depending on the partial display mode selected. 8 ...
Page 8
... Philips Semiconductors 65 96 pixels matrix LCD driver bank 0 bank 1 bank 2 bank 3 bank 8 2003 Mar 13 DDRAM LCD Fig.2 DDRAM to display mapping (MY = 0). 8 Objective specification PCF8814 top of LCD R0 R8 R16 R24 R64 MGU686 ...
Page 9
... Philips Semiconductors 65 96 pixels matrix LCD driver bank 0 bank 1 bank 2 bank 3 bank 8 2003 Mar 13 DDRAM LCD Fig.3 DDRAM to display mapping (MY = 1). 9 Objective specification PCF8814 top of LCD R64 R56 R48 R40 R0 MGU687 ...
Page 10
... After the very last address the address pointers wrap around to address and both horizontal and vertical addressing modes 194 290 386 482 578 674 770 X address X address 10 Objective specification PCF8814 95 0 191 Y address 863 8 95 MGU688 0 Y address 863 8 95 MGU689 ...
Page 11
... The Data Order bit (DOR) defines the bit order (LSB on top or MSB on top) for writing into the RAM (see Figs 6 and 7). LSB handbook, full pagewidth MSB LSB MSB MSB handbook, full pagewidth LSB MSB LSB 2003 Mar 13 Fig.6 RAM byte organisation (DOR = 0). Fig.7 RAM byte organisation (DOR = 1). 11 Objective specification PCF8814 MGU690 MGU691 ...
Page 12
... Fig.8). When the mirroring is disabled and the address located at the top of the display (see Fig.9). handbook, full pagewidth 0 handbook, full pagewidth 0 2003 Mar 13 X address Y address Fig.8 RAM format addressing (MY = 1). X address Y address Fig.9 RAM format addressing (MY = 0). 12 Objective specification PCF8814 MGU692 MGU693 ...
Page 13
... Fig.11). handbook, full pagewidth 95 handbook, full pagewidth 0 2003 Mar 13 X address Y address Fig.10 RAM format addressing (MX = 1). X address Y address Fig.11 RAM format addressing (MX = 0). 13 Objective specification PCF8814 MGU694 MBL599 ...
Page 14
... SDIN DB7 2003 Mar 13 For the 4-line serial interface the D/C line is added. The PCF8814 is connected to the serial data I/O of the microcontroller by two pins: SDIN (data input) and SDO (data output) connected together. The timing diagrams for the 3-line and 4-line SPI are shown in Chapter 15 ...
Page 15
... Mar 13 DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0 last DB2 DB1 DB0 data data data display data string Fig.14 Transmission of several bytes. 15 Objective specification PCF8814 DB7 DB6 DB5 DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0 instruction MBL549 MBL550 ...
Page 16
... R EAD MODE In the read mode of the interface the microcontroller reads data from the PCF8814 the microcontroller first has to send the read status command, then the PCF8814 will respond by transmitting data on the SDO line. After that SCE is required to go HIGH, (see Fig.16). ...
Page 17
... Figure 17 shows the general format of the write mode and the definition of the transmission byte. Any instruction can be sent in any order to the PCF8814. The MSB is transmitted first. The serial interface is initialized when SCE is HIGH. In this state, SCLK clock ...
Page 18
... Fig.19 Write mode - transmission of several bytes. D/C DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0 Fig.20 Write mode - interrupted by reset (RES). 18 Objective specification DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0 DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0 D/C transmission byte D/C PCF8814 MBL541 MBL542 DB7 DB6 MBL543 ...
Page 19
... R EAD MODE In the read mode of the interface the microcontroller reads data from the PCF8814 so, the microcontroller first has to send a command, the read status command, and then the following byte is transmitted in the opposite direction by using SDO (see Fig.21). After that, SCE is required to go HIGH before a new command is sent ...
Page 20
... See Fig.23. data line change stable; of data data valid allowed Fig.23 Bit transfer. 20 Objective specification PCF8814 S YSTEM CONFIGURATION MASTER MASTER TRANSMITTER/ TRANSMITTER RECEIVER MGA807 MBC621 ...
Page 21
... In this event the transmitter must leave the data line HIGH to enable the master to generate a STOP condition. The acknowledge timing is shown in Fig.25 START condition Fig.25 Acknowledge on the I 21 Objective specification PCF8814 SDA SCL P STOP condition MBC622 not acknowledge acknowledge 8 9 clock pulse for acknowledgement ...
Page 22
... RAM at the address specified by the data pointer. The data pointer is automatically updated and the data is directed to the intended PCF8814 device. If the D/C bit of the last control byte was set to logic 0, these command bytes will be decoded and the setting of the device will be changed according to the received commands ...
Page 23
... Hs-mode Fig.27 Complete data transfer in Hs-mode. 23 Objective specification F/S-mode DATA A bytes ack.) Hs-mode continues Sr SLAVE ADD. MSC616 (8-bit DATA A/ PCF8814 then F/S mode If Sr (dotted lines) then Hs-mode MSC618 ...
Page 24
... PCF8814 status information slave address R/W 24 Objective specification acknowledge from PCF8814 control byte 0 A data byte D/C 1 byte n 0 bytes CO MSB . . . . . . . . . . . LSB NOT acknowledgement from Master A P STOP condition MGU699 PCF8814 ...
Page 25
... Table 6. Sending the instruction to read back the temperature sensor will select the status byte shown in Table TD5 TD4 TD3 25 Objective specification Read mode ID2 D2 D1 TD2 TD1 PCF8814 D0 ID1 D0 TD0 ...
Page 26
... I interface. Processing of the instructions does not require the display clock. Data accesses to the PCF8814 can be broken-down into two areas, those that define the operating mode of the device, and those that fill the display RAM. For the 4-line SPI interface the distinction is the D/C pad ...
Page 27
... OTP enable/disable defaults set frame frequency ( OSE CAL enter calibration mode and MM control programming write 0 to OTP shift register write 1 to OTP shift register FUNCTION NOP pad selected reserved reserved PCF8814 ...
Page 28
... These values can set by the module maker. If the factory defaults OTP bit has been set, then these values cannot be changed via the interface. Otherwise, the OTP data will only be used if the Set factory defaults instruction OTP bit is set to 1. 2003 Mar 13 DESCRIPTION 28 Objective specification PCF8814 RESET STATE ...
Page 29
... Objective specification PCF8814 DIVIDER EXTERNAL CLOCK RATIO FREQUENCY (kHz) 3264 261.1 2688 215.0 3072 245.8 2560 204.8 2560 204.8 2688 215.0 2816 225.3 2688 215.0 3264 228.5 3584 250.9 3072 215.0 3200 224 ...
Page 30
... Objective specification Display control M X IRROR M Y IRROR Set Y address of RAM Set X address of RAM PCF8814 BANK Bank 0 Bank 1 Bank 2 Bank 3 Bank 4 Bank 5 Bank 6 Bank 7 Bank 8 ...
Page 31
... VALID MODE 32 Row valid MBL588 31 Objective specification INVALID MODE MUX 32 and C = Row not valid PCF8814 ROW Row 0 Row 8 Row 16 Row 24 Row 32 Row 40 Row 48 Row 56 ...
Page 32
... Objective specification PCF8814 Display ROW 0 ROW 1 ROW 2 ROW 3 ROW 4 ROW 5 ROW ROW 7 ROW 8 ROW 9 ROW 10 ROW 11 ROW 12 ROW 13 ROW 14 ROW 15 ROW 16 ROW ROW 18 ROW 19 ROW 20 ROW 21 ...
Page 33
... Re-direct the 16th row of RAM data to the first display row (Row = 32) Fig.32 Effects of L and C address, MX, MY and partial displays. 2003 Mar (32 row partial mode) 33 Objective specification PCF8814 Move Row 0 to Row (Row = 24 MBL591 ...
Page 34
... This leads to the bias settings given in Table 19. The bias can be selected in software and also programmed by OTP. 34 Objective specification LCD = F V COL(max COL(min MCE009 -------------------------------- = --------------------- - = --- - 1 – for a given value – PCF8814 R, and the value ...
Page 35
... LCD SYMBOL VALUE b 0. CAUTION allows values above the maximum allowed V remains below 9.0 V. allows values below the minimum LCD (5 V), the user has to ensure, while setting LCD register and selecting the temperature PR remains above 5.0 V. LCD PCF8814 LCD (1) (2) UNIT V V LCD PR ...
Page 36
... Assuming MMVOPCAL = 0 and Fig.35 V LCD 2003 Mar 13 measured temperature slopes TEMPERATURE COMPENSATION MMVOPCAL [ 5 7 programming of PCF8814 shown as plots of equations (1) and (2). 36 Objective specification PCF8814 MGW833 MGT847 . . . LCD V OP ...
Page 37
... LSB for TD (1.875 K/LSB) and an LSB for V 2. Slopes of V equations (1), (2), (3) and Table Objective specification MA, MB, MC (1) and MD 111 2.50 110 1.75 101 1.25 100 1.00 011 0.75 010 0.50 001 0.25 000 0.00 (30 mV/LSB). OP are calculated from LCD D MGW834 PCF8814 (1)(2) SLOPE (mV/ ...
Page 38
... When frame inversion is OFF, the N-line inversion counter runs continuously N-line inversion invert every 2 rows : : invert every 62 rows 1 frame inversion ON; N-line counter restarted at every frame 0 frame inversion OFF; N-line counter runs continuously 38 Objective specification PCF8814 EQUATION ...
Page 39
... LCD driver 11.11 Orthogonal functions The orthogonal functions used in the PCF8814 are shown in Tables 25 and 26. SF refers to the sub-frame. All the rows will have the first function applied before the function moves on to its next state. For clarity, no N-line inversion is shown here ...
Page 40
Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ... handbook, full pagewidth NORMAL FRAME SF0 SF1 NORMAL FRAME SF0 ...
Page 41
... BIT VM CHARGE PUMP STATUS 0 indicates the charge pump is not working correctly 1 indicates the charge pump is working correctly PCF8814 MBL590 ...
Page 42
... Bottom Row Swap (BRS) allows for the possibility to route to the module in two different ways as shown by the row count in Figs 39 and 40. handbook, full pagewidth R0 handbook, full pagewidth R31 2003 Mar 13 PCF8814 R64 R31 COLUMNS DISPLAY AREA Fig.39 BRS = 0. PCF8814 R0 R32 COLUMNS DISPLAY AREA Fig.40 BRS = 1. 42 Objective specification PCF8814 R32 MGU700 R64 MGU701 ...
Page 43
... SS 13 HANDLING Inputs and outputs are protected against electrostatic discharge in normal handling. However totally safe desirable to take normal precautions appropriate to handling MOS devices (see “Handling MOS devices” ). 2003 Mar 13 PARAMETER 43 Objective specification PCF8814 MIN MAX UNIT 0.5 +6.5 V 0.5 +5 ...
Page 44
... LCD = 5 V LCD voltage that may be generated is dependent on voltage, temperature and (display) load. and TC used at the calibration and with temperature calibration disabled 2 7.5 V, voltage multiplier = 4V DD2 LCD = +25 C. amb 44 Objective specification PCF8814 MIN. TYP. MAX. 1.7 3.3 2.4 4.5 9.0 9.0 70 +70 0.1 1 ...
Page 45
... V = 1.8 V; MUX rate 1 : 65; DD1 amb note 1 note 2 SPI 3-line or 4-line interface 3-line serial interface f = 6.5 MHz SCLK including ITO track + connector resistance + PCB 45 Objective specification PCF8814 MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT 261.1 kHz 228.5 kHz 261.1 kHz ...
Page 46
... RES may be LOW before the time from the previous SCLK rising edge (irrespective of the state of SCE) to the falling edge of SCE. H5 2003 Mar 13 CONDITIONS total capacitance for one bus line goes HIGH. 46 Objective specification PCF8814 MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT 0 3.4 MHz 160 ns 160 ...
Page 47
... RES handbook, full pagewidth SCE t PWL1 SCLK t S1 SDIN 2003 Mar VHRL t RW Fig.41 Reset timing PWH1 t H1 Fig.42 3-line serial interface timing. 47 Objective specification PCF8814 t RWS MCE012 PWH2 ( cyc MGU702 ...
Page 48
... SCLK SDIN SDO Fig.44 SPI 3-line or 4-line serial interface timing - read mode. 2003 Mar PWH1 t H4 Fig.43 4-line serial interface timing Objective specification PCF8814 PWH2 ( cyc MBL552 MCE013 ...
Page 49
... Rising edge of the first SCLH clock pulse after an acknowledge bit. 2003 Mar Fig.45 3-line serial interface timing - read mode. t rDA t HD;DAT t SU;DAT t fCL t rCL1 (1) t HIGH t LOW t LOW 2 Fig.46 I C-bus timing diagram (Hs-mode). 49 Objective specification SU;STO t rCL1 (1) t HIGH PCF8814 t S1 MBL553 Sr P MGK871 ...
Page 50
... IC from light. The protection must be done on all sides of the IC, i.e. front, rear and all edges. 16.2 Chip-on-glass application The pinning of the PCF8814 has an optimal design for single-plane wiring e.g. for chip-on-glass display modules. Display size pixels. 16.3 Application capacitor values ...
Page 51
... Fig.49 Application example using external high voltage generation. 2003 Mar 13 DISPLAY 65 96 pixels 96 PCF8814 C VDD1 V DD1 C VLCD I/O C VDD2 V DD2 V SS DISPLAY 65 96 pixels 96 PCF8814 C VDD I LCDIN 51 Objective specification PCF8814 32 MBL546 sources (V and DD1 DD2 32 MBL547 ...
Page 52
... One Time Programmable (OTP) technology has been implemented on the PCF8814. It enables the module maker to program some extended features of the PCF8814 after it has been assembled on an LCD module. Programming is made under the control of the interfaces and the use of one special pad. This pad must be made available on the module glass but needs not to be accessed by the set maker ...
Page 53
... SLA [2:0] OTP DEFAULTS e.g. SLA [2:0] 1 Fig.51 Factory defaults. 53 Objective specification D EFAULT CHARGE PUMP MULTIPLICATION FACTOR D V EFAULT VALUE PR [7:0] can be pre-defined EFAULT BIAS VALUE Seal bit ACTION 0 possible to enter calibration mode 1 calibration mode disabled FACTORY DEFAULT to temperature compensation circuit MBL593 PCF8814 ...
Page 54
... LCD driver 17.4 OTP architecture The OTP circuitry in the PCF8814 contains many bits of data. The circuitry for 1 bit is called an OTP slice. Each OTP slice consists of 2 main parts: the OTP cell (a non-volatile memory cell) and the shift register cell (a flip-flop) ...
Page 55
... REGISTER FLIP-FLOP read data write data from the to the OTP cell OTP cell OTP CELL 2003 Mar 13 DATA TO THE CIRCUIT FOR CONFIGURATION AND CALIBRATION SHIFT REGISTER DATA INPUT Fig.52 Basic OTP architecture. 55 Objective specification PCF8814 SHIFT REGISTER OTP CELLs MGU289 ...
Page 56
... In this example the shift register is filled with the following data: MMVPR = 1101 0000, and the seal bit is logic assumed that the PCF8814 has just been reset. After transmitting the last bit the PCF8814 can exit or remain in CALMM mode (see step 1). from the OTPPROG After this sequence has been applied it is possible to observe the impact of the data shifted in ...
Page 57
... ACTION 1 exit power-down wait 5 ms for refresh to take effect 1 enter CALMM mode 1 shift in data, MMVPR[7] is first bit; see note 1 1 MMVPR[6] 0 MMVPR[5] 1 MMVPR[4] 0 MMVPR[3] 0 MMVPR[ MMVOPCAL[0] 0 seal bit 0 exit CALMM mode MMVPR [ 7:0 ] LSB PCF8814 MSB 1 1 MCE014 ...
Page 58
... The order for programming cells is not significant, however recommended that the seal bit is programmed last. Once this bit has been programmed it will not be possible to re-enter the CALMM mode. Prior to the sequence specified in Table 34 assumed that the PCF8814 has just been reset ...
Page 59
... V LCDIN notes 1 and 2 programming active programming inactive during when programming a single bit to logic 1 during prior to programming t su(SCLK) t su(gate Fig.54 Programming waveforms. 59 Objective specification PCF8814 MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT ; SS1 11.0 11.5 12.0 V 0 SS1 9.0 9.5 10 ...
Page 60
... Philips Semiconductors 65 96 pixels matrix LCD driver 18 CHIP INFORMATION The PCF8814 is manufactured in n-well CMOS technology. The substrate potential. SS Table 36 Bonding pad information ROWS/COLS PARAMETER SIDE Pad pitch 51.84 (min) Bump 30.04 x 99.00 dimensions 15 Wafer thickness 381 ( 25) (excl. bumps) handbook, halfpage y center x center Fig ...
Page 61
... Objective specification PCF8814 PAD NAME X V 2025.0 DD2 V 1962.0 DD2 V 1836.0 DD1 V 1773.0 DD1 V 1710.0 DD1 V 1647.0 DD1 V 1584.0 DD1 V 1521.0 DD1 SCLK 1422 ...
Page 62
... Objective specification PCF8814 PAD NAME X RES 4356.0 dummy 4437.0 dummy 4500.0 dummy 4563.0 dummy 4626.0 dummy 4689.0 dummy 4752.0 dummy 4815.0 dummy 5054 ...
Page 63
... Objective specification PCF8814 PAD NAME X C75 1107.5 C74 1055.7 C73 1003.9 C72 952.0 C71 848.3 C70 796.5 C69 744.7 C68 692.8 C67 641 ...
Page 64
... Recognition mark, right 3091.5 810.0 Bump alignment mark 3188.5 810.0 Top right corner 3247.0 810.0 Bottom left corner 3298.9 810.0 64 Objective specification PCF8814 PAD NAME X R29 3350.7 R28 3402.5 R27 3454.4 R26 3506.2 R25 3558.1 R24 3609.9 R23 3661 ...
Page 65
... Philips Semiconductors 65 96 pixels matrix LCD driver handbook, full pagewidth y 0,0 Active pads Dummy pads Fig.58 Bonding pad location (viewed from bump side). 2003 Mar 10. 1. Objective specification PCF8814 MCE015 ...
Page 66
... For test purposes only: maximum forward current = 5 mA. 2003 Mar 13 V DD2 V SS1 V SS2 V LCDIN , V LCDSENSE V SS1 V LCDIN LCD outputs V SS1 V DD1 2 I C-bus pins V SS1 SS1 Fig.59 ESD structures 66 Objective specification PCF8814 V DD3 V SS1 V LCDOUT V SS1 V DD1 SCLK, SDIN, SDO V SS1 V DD1 T3, T4, V SS1 MBL596 ...
Page 67
... IC type name on the die surface with respect to the chamfer on the upper left corner of the tray. Refer to the bonding pad location diagram for the orientating and position of the type name on the die surface. 67 Objective specification PCF8814 MBL597 Fig.61 Tray alignment. MBL598 ...
Page 68
... Objective specification PCF8814 DEFINITION These products are not Philips Semiconductors ...
Page 69
... It is the responsibility of the customer to test and qualify their application in which the die is used. C COMPONENTS 2 C components conveys a license under the Philips’ system provided the system conforms to the I 69 Objective specification PCF8814 2 C patent to use the 2 C specification defined by ...
Page 70
... Philips Semiconductors 65 96 pixels matrix LCD driver 2003 Mar 13 NOTES 70 Objective specification PCF8814 ...
Page 71
... Philips Semiconductors 65 96 pixels matrix LCD driver 2003 Mar 13 NOTES 71 Objective specification PCF8814 ...
Page 72
Philips Semiconductors – a worldwide company Contact information For additional information please visit http://www.semiconductors.philips.com. For sales offices addresses send e-mail to: sales.addresses@www.semiconductors.philips.com. © Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2003 All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited ...