pcf8833 NXP Semiconductors, pcf8833 Datasheet
pcf8833
Available stocks
Related parts for pcf8833
pcf8833 Summary of contents
Page 1
... DATA SHEET PCF8833 STN RGB - 132 Objective specification INTEGRATED CIRCUITS 132 3 driver 2003 Feb 14 ...
Page 2
... Objective specification PCF8833 LIMITING VALUES HANDLING DC CHARACTERISTICS AC CHARACTERISTICS APPLICATION INFORMATION Supply and capacitor connection configuration MODULE MAKER PROGRAMMING V calibration LCD Factory defaults Seal bit OTP architecture Interface commands Suggestion on how to calibrate V MMVOP Example of filling the shift register ...
Page 3
... Optimized layout for COF, Chip On Glass (COG) and Transformer Coupled Plasma (TCP) assembly. 2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The PCF8833 is a single chip low power CMOS LCD controller driver, designed to drive colour Super-Twisted Nematic (STN) displays of 132 rows and 132 RGB columns. All necessary functions for the display are ...
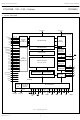
Page 4
... ROW DRIVERS ORTHOGONAL FUNCTION GENERATOR RESET OSCILLATOR TIMING GENERATOR GREYSCALE CONTROLLER COMMAND DECODER MPU INTERFACES PS2 D0/SDIN SDOUT PCF8833 496 RES 555 OSC 578 T1 577 T2 576 T3 575 T4 574 T5 573 T6 625 MGU910 ...
Page 5
... PS1 and PS2 must tied to either V V DD1 I set serial or parallel interface mode PS1 and PS2 must tied to either V V DD1 5 Objective specification PCF8833 DESCRIPTION and V DD2 DD3 is used as the supply for the rest of the DD1 and V but in this case care ...
Page 6
... LCD supply input voltage 2 O LCD bias level O LCD bias level O LCD bias level O LCD bias level 6 Objective specification DESCRIPTION ; an external clock signal, DD1 , the display is not clocked and may be left in a DD1 SS1 SS1 SS1 SS1 SS1 LCDOUT2 PCF8833 SS1 SS1 SS1 ...
Page 7
... The display clock is derived from the built-in oscillator. The PCF8833 has 2 types of accesses; those defining the operating mode of the device (instructions) and those filling the display RAM. Since writing to the RAM occurs more frequently, efficient data transfer is achieved by autoincrementing the RAM address pointers ...
Page 8
Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ... Table 1 Command table; note 1 D ...
Page 9
Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ... D ...
Page 10
Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ... D ...
Page 11
Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ... D ...
Page 12
... The MSB of data stored in RAM is evaluated only in Partial mode only pixels of partial area are inverted; INVON is not effective; when DAL or DALO are active 12 Objective specification PCF8833 CONDITIONS COMMAND Sleep_OUT Sleep_IN reset BSTRON reset BSTROFF DISPON reset ...
Page 13
... Command register set to default states; see Table 4 Interface pins are set to inputs. Table 4 Reset state after hardware and software reset COMMAND Sleep_IN PCF8833 is in Sleep_IN mode (booster and display are switched off) INVOFF display inversion is off BSTRON when Sleep_OUT is active; booster is switched on DISPON when Sleep_OUT is active ...
Page 14
... Calibration mode may not be entered if the SEAL bit has been set. Programming is only possible when in Calibration mode. 2003 Feb 14 3 driver DESCRIPTION voltage; note 1 LCD2 = 2.5; note 1 max 14 Objective specification PCF8833 RESET STATE 2DEC 129DEC 2DEC 129DEC see Section 6.2.22 0DEC 31DEC 0DEC 130DEC ...
Page 15
... BSTRON and BSTROFF with LCDIN1 DISPON and DISPOFF start send DISPOFF (28H) send BSTROFF (02H) end MGU911 Fig.2 Booster voltage off flow chart. 15 Objective specification PCF8833 SS1 DEFAULT 01H ...
Page 16
... Figure 3 shows two sequences for using the BSTRON command, assuming BSTROFF and DISPOFF were set before sending Sleep_OUT. In sequence A the command to switch the display on (DISPON) is sent to the PCF8833 before the BSTRON command is sent. Therefore the display will only be switched on when the LCD supply ...
Page 17
... D18 D17 D16 D10 BYTE REMARK RDID1 hard wired = 45H RDID2 OTP programmed; see Chapter 15 (1) RDID3 OTP programmed; see Chapter 15 PCF8833 DEFAULT 04H 0 DEFAULT 0 04H X 45H XX XX DEFAULT 04H XX 45H XX XX ...
Page 18
... EAD DISPLAY STATUS The Read Display Status (RDDST) command returns a 32-bit display status information and can be accessed when the PCF8833 is in normal Display mode (see Section 6.2.11), in partial Display mode (see Section 6.2.23 Sleep_IN mode; see Section 6.2.8. The input and output data format is as follows: After the ...
Page 19
... D14 = 0 logic 1 when INVON is selected logic 0 when INVOFF is selected logic 1 when DAL is selected logic 0 otherwise logic 1 when DALO is selected logic 0 otherwise logic 1 when DISPON is selected logic 0 when DISPOFF is selected logic 1 when TEON is selected logic 0 when TEOFF is selected D[8:0] = 0:0000:0000 PCF8833 ...
Page 20
... LEEP This command must be sent to allow the PCF8833 to power-up (see Fig.4). DISPON and BSTRON are set with a reset, the PCF8833 will start-up with Sleep_OUT following the built-in start-up sequence which generates the requested voltages and switches on the display, unless DISPOFF and/or BSTROFF was sent after the last reset ...
Page 21
... Fig.4 Start-up, when leaving Power-down mode (i.e. after sending Sleep_OUT). 2003 Feb 14 3 driver reset Sleep_IN D31 = 0 send Sleep_OUT Sleep_OUT BSTROFF booster BSTRON booster on D31 = 0 wait for D31 bit D31 = 1 DISPOFF display DISPON ready display on display off 21 Objective specification PCF8833 DEFAULT MGU913 11H ...
Page 22
... PTLAR partial area def send PTLON partial mode on send PTLAR partial area def optional send SEP scroll mode Fig.5 Sequence how PTLON can be used. 22 Objective specification PCF8833 normal display send DISPOFF display off wait until display supply ...
Page 23
... D 6.2.12 D ISPLAY INVERSION OFF The Display inversion off command (INVOFF) turns the display into a non-inverted screen without modifying the display data RAM. Display inversion off is the reset state of the PCF8833. Table 21 Display inversion off register bits D 6.2.13 D ISPLAY INVERSION ON The Display inversion on command (INVON) turns the display into an inverted screen without modifying the display data RAM ...
Page 24
... NORON exit pixel on/off normal display send DAL/DALO all pixel on/off effect in partial display mode Fig.6 Flowchart representation of DAL and DALO. 24 Objective specification PCF8833 all pixel on/off send PTLON exit pixel on/off partial mode on send DAL/DALO ...
Page 25
... The Display off command (DISPOFF) connects all rows and columns to V Since the reset state of the PCF8833 is Sleep_IN (see Section 6.2.8) the display will be in the off state after a reset. The DISPOFF command can be switched off by sending the Display on command (DISPON); see Section 6.2.18. ...
Page 26
... Initial state Sleep_OUT booster on display on Booster off send DISPOFF display off (1) send BSTROFF (2) D31 = 0 booster off Booster on send BSTRON booster on D31 = 0 wait for D31 bit D31 = 1 send DISPON display on 26 Objective specification PCF8833 DEFAULT MGU916 29H ...
Page 27
... D7 D6 2003 Feb 14 3 driver xs[5] xs[4] xs[3] xe[5] xe[4] xe[ ys[5] ys[4] ys[3] ye[5] ye[4] ye[ Objective specification PCF8833 xs[3] xs[3] xs[0] xe[2] xe[1] xe[ ys[3] ys[3] ys[0] ye[2] ye[1] ye[ DEFAULT 2AH 02H 81H DEFAULT 2BH 02H 81H DEFAULT ...
Page 28
... With the Colour set (RGBSET) command the mapping from the 256-colour interface data is translated to the 4 kbyte colour RAM data of the PCF8833 can be changed. The translation table must be changed, if necessary, before sending 256 colour data. For the red and green pixel 8 from the available 16 grey scales can be selected. For the blue pixel 4 from the 16 grey scales can be selected ...
Page 29
... AA1S AA1S 101 (AA1S must be set in multiples of 4). Figure 11 shows how the Partial mode can be used. RAM partial area Fig.8 Partial Display mode for LAO = 0. 29 Objective specification PCF8833 AA1S 32 (only 1 partial display size 131. (131 + 1) display 0 ROW 0 1 ...
Page 30
... Philips Semiconductors STN RGB - 132 132 handbook, full pagewidth AA1E [ 7 128 32 rows AA1S [ 7 2003 Feb 14 3 driver RAM partial area Fig.9 Partial Display mode for LAO = 1. 30 Objective specification PCF8833 display 0 ROW 0 1 ROW 1 2 ROW 2 3 ROW 3 ROW ROW 5 6 ...
Page 31
... STN RGB - 132 132 handbook, full pagewidth AA1E [ 7 AA1S [ 7 128 32 rows Fig.10 Partial Display mode for LAO = 0 and AA1S[7:0] = 128. 2003 Feb 14 3 driver RAM partial area 31 Objective specification PCF8833 display 0 ROW 0 1 ROW 1 ROW ROW 3 partial area 4 ROW 4 5 ...
Page 32
... PTLAR partial area def send PTLON partial mode on send PTLAR partial area def optional send SEP scroll mode 32 Objective specification PCF8833 normal display send DISPOFF display off wait until display supply voltage is settled send DISPON display on MGU920 ...
Page 33
... V ERTICAL SCROLLING DEFINITION In the PCF8833 three different scrolling modes can be used. These scrolling modes differ from each other in the way the RAM to display mapping is done. The vertical scrolling is defined as follows: Vertical scrolling definition (VSCRDEF) command TF[7:0] defines the number of lines for the top fixed area on the display, there is no top fixed area when TF[7: ...
Page 34
... SEP scroll mode on set a new scroll area send NORON normal display send VSCRDEF scroll area def send SEP scroll mode on exit scroll mode send NORON send PLTON normal display partial mode 34 Objective specification PCF8833 normal display MGU922 ...
Page 35
... The RAM-to-display mapping for the rolling Scroll mode when a 132 130 (columns rows) display is connected to the PCF8833 is illustrated in Fig.14. In this case rows 0 and 131 must be left open. When a 132 connected, there will be a one-to-one mapping between the RAM and the display, and there will be no unused rows ...
Page 36
... SEP [ 7:0 ] 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 36 Objective specification PCF8833 display (132 x 130 SEP SA = 114 120 121 8 9 SEP 1 124 125 126 127 128 ...
Page 37
... PCF8833 is illustrated in Fig.16. In this case unused rows and columns are to be left open, for instance row 0 and 131 132 connected to the PCF8833 the content of row 0 and 131 will be the same as the content which is displayed in row 1 and 130, respectively. By doing so, the display data RAM will have 1 row in the background, whose content can be updated when it is not displayed ...
Page 38
... PCF8833 is illustrated in Fig.18. In this case unused rows and columns are to be left open, for instance row 0 and 131 132 connected to the PCF8833 the content of row 0 and 131 will be the same as the content which is displayed in row 1 and 130, respectively. By doing so the display data RAM will have 2 rows in the background, whose content can be updated when they are not displayed ...
Page 39
... SEP5 SEP4 SEP3 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 39 Objective specification PCF8833 SEP2 SEP1 SEP0 display (132 x 130 7 7:0 ] 120 121 124 125 ...
Page 40
... Feb 14 3 driver SEP [ 7:0 ] 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 40 Objective specification PCF8833 display (132 x 130 SEP SA 122 123 8 9 SEP 3 124 125 126 127 128 ...
Page 41
... Effect of LAO on scroll modes An example of when the PCF8833 is working in the non-rolling Scroll mode ( 132) with the Line Address Order (LAO) bit set to logic 1, is illustrated in Fig.20. The Scroll modes described in Sections 6.2.24.1 and 6.2.24.2 also work on the same principle when the LAO bit is set to logic 1. ...
Page 42
... TE signal 2003 Feb 14 3 driver superframe period (16 frames ) 850 s Fig.21 Tearing effect line: distribution of pulses. 42 Objective specification PCF8833 DEFAULT DEFAULT MGU930 34H 35H 00H ...
Page 43
... 131 0 RAM 2 1 131 131 131 2 1 column address MGU931 Fig.22 Display data RAM access control. 43 Objective specification LOGIC 1 DISPLAY 131 131 0 0 PCF8833 0 DEFAULT 0 36H 00H ...
Page 44
... STN RGB - 132 132 6.2.28 I DLE MODE OFF The Idle mode off (IDMOFF) command turns off the Idle mode and the PCF8833 is working in the 4 kbyte colour mode. This command is similar to the Idle mode on command (IDMON); see Section 6.2.29. Table 42 Idle mode off register bits D/C 7 ...
Page 45
... Notes 1. PCF8833 is switched into 256 colour mode, 256 colours are mapped to the 4 kbyte RAM with a LUT; see Section 6.2.22. 2. PCF8833 is switched into 4 kbyte colour mode, which is also the reset state. 3. PCF8833 is switched into 64 kbyte colour mode, which is achieved by means of dithering. 6.2. ...
Page 46
... V LCD 2003 Feb 14 3 driver VALUE 0.04 3.6 VCON [ 6:0 ] MMVOPCAL [ 5:0 ] Fig.23 Setting of V programming range (05H to 19AH Fig.24 V programming range of the PCF8833. LCD 46 Objective specification UNIT 8 LCD MGU932 . OP 410DEC PCF8833 MGU933 V OP ...
Page 47
... T OP ROW SWAP The Top Row Swap (TRS) command enables the top rows of the PCF8833 to be swapped (mirrored) in order to make an optimum glass layout. The function of the TRS command in combination with BRS is illustrated in Figures 25, 26, 27 and 28. The description of BRS function can be found in Section 6.2.32. ...
Page 48
... Fig.25 Row sequence for BRS = 0 and TRS = 0. 96 131 PCF8833 95 64 columns DISPLAY 131 Fig.26 Row sequence for BRS = 0 and TRS = 1. 48 Objective specification PCF8833 rows 32 rows MGU934 rows rows 0 31 ...
Page 49
... Fig.27 Row sequence for BRS = 1 and TRS = 0. 96 131 PCF8833 64 95 columns 32 rows DISPLAY 131 Fig.28 Row sequence for BRS = 1 and TRS = 1. 49 Objective specification PCF8833 rows rows MGU936 rows rows 0 ...
Page 50
... The Super frame inversion command (FINV), which is the inversion of the row functions after all rows are written to can be switched off for the PCF8833. When switched off, the inversion of the row functions will then only be done with N-line inversion. Inversion of the row functions is needed avoid a DC component over the LCD display. A detailed description of the N-line inversion is given in Section 6 ...
Page 51
... Table 57 Temperature compensated frame frequency reset state BIT TCDFE non-segmented frame frequency 6.2.37 T EMPERATURE COMPENSATED The PCF8833 incorporates a temperature segmented V compensated V (TCVOPE) command the temperature segmented V LCD The TCVOPE control bit reset state is defined in Table 59. When the non-segmented V programming is chosen the LCD supply voltage is flat, i.e. no compensation over the ...
Page 52
... MULTIPLICATION FACTOR D AND LCD SLB SLB Objective specification PCF8833 might have to be LCD will not be changed linearly, but steps SLA SLA SLA ...
Page 53
... SLD SLD 1.250 1.000 0.875 0.750 0.625 0.500 0.375 0.250 Objective specification PCF8833 SLC SLC SLC SLOPE 53.33 mV/ C 42.66 mV/ C 37.33 mV/ C 32.00 mV/ C 26.66 mV/ C 21.33 mV/ C 16.00 mV/ C 10.66 mV MGU938 DEFAULT ...
Page 54
... A complete overview of the programming range of V can be found in Section 15.1. SLA SLB SLC SLD zero offset VCON [ 5:0 ] MMVOPCAL [ 5 8:0 ] Fig.30 Segmented temperature compensation. 54 Objective specification can be calculated by multiplying the offset LCD = 40 mV (64 34) 0.5 = 600 mV. OFFSET 8 PCF8833 LCD V LCD MGU939 ...
Page 55
... 6.2.41 F RAME FREQUENCY PROGRAMMING The PCF8833 incorporates temperature segmented Frame frequency programming (TCDF). The temperature range is split into 4 areas as shown in Fig.31. In each of the segments a Division Factor (DF) can be programmed which determines the Frame Frequency (FF). In equation (2) the frame frequency can be calculated from a given division factor ...
Page 56
... When the Idle mode is selected (see Section 6.2.29) the frame frequency is determined from division factor DF8. In the Idle mode the PCF8833 works in 8-colour mode and therefore a lower frame frequency can be chosen which will be the same over the whole temperature range. Calculation of the frame frequency and determining the division factor is the same as explained in Section 6 ...
Page 57
... Feb 14 3 driver The bias voltages needed in a MRA LCD driver depends on the number of simultaneous selected rows (P). The bias voltages of the PCF8833 are given for and see Fig.32. In the PCF8833 the maximum column (4) voltage (GMAX) is always lower or equal to the row 2a voltage F ...
Page 58
... 0.5 V – = LCD1 Limitations on bias voltages in Partial mode : 1 0.5 V – = LCD1 max PCF8833 (1) not allowed 8.0 8.5 9.0 9.5 (2) 10.0 not allowed 0 DEFAULT 1 C7H VB 0BH 0 ...
Page 59
... Philips Semiconductors STN RGB - 132 132 6.2.44 T EMPERATURE READBACK The PCF8833 has a built-in temperature readback (RDTEMP) measurement device. The measured value is provided as an 8-bit digital value TD[7:0] which can be read back via the interface. The temperature can be determined from TD[7:0] using the following formula ...
Page 60
... STN RGB - 132 132 6.2.46 R EADBACK The PCF8833 can be identified when the readback commands (RDID1, RDID2 and RDID3) are sent via the interface. When the readback command is sent, the PCF8833 will send back an 8-bit number. Depending on the SCLK speed the readback bit D7 might get corrupted ...
Page 61
... FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION 7.1 MPU interfaces The PCF8833 can interface to a microcontroller with an 8-bit parallel or a serial interface to transmit both data and commands to the PCF8833. 7.1.1 H ARDWIRED INTERFACE SELECTION The selection of a given interface is done by setting pins PS0, PS1 and PS2 as shown in Table 81. Inputs PS1 and PS2 ...
Page 62
... D ISPLAY DATA FORMATTING Different display data formats are available because different colour depths are supported by the PCF8833. The colour depths supported are as follows: 4 kbyte colours (12-bit/pixel), RGB bits input; see Table 82. The data coming from the interface is directly stored in RAM. ...
Page 63
... The address counter sets the addresses of the display data RAM for writing. Data is written pixel wise into the RAM of the PCF8833. The data for one pixel is collected (RGB bit) before it is written into the display data RAM. The RAM locations are addressed by the address pointers ...
Page 64
... Fig.35 Sequence of writing data bytes into RAM with horizontal addressing ( showing function MX and MY. 2003 Feb 14 3 driver xe MGU945 handbook, halfpage 131 131 xe MGU947 handbook, halfpage 131 ye ys 131 64 Objective specification xe xs MGU946 131 X address and 131 X address and PCF8833 MGU948 ...
Page 65
... Fig.36 Sequence of writing data bytes into RAM with vertical addressing ( showing function MX and MY. 2003 Feb 14 3 driver xe MGU949 handbook, halfpage ys ye 131 131 xe MGU951 handbook, halfpage 131 ye ys 131 65 Objective specification 131 X address and 131 X address and PCF8833 MGU950 MGU952 ...
Page 66
... Depending on the application of the VC capacitor it might be advantageous or even necessary to set the OPT bit VCBW = 1; see Table 97 and Section 15.8. CAPACITOR VALUE Objective specification PCF8833 (display off) SS1 is generated by means of LCD directly LCDIN1 LCDOUT2 VOLTAGE RANGE ...
Page 67
... PARALLEL INTERFACE The 8080-series 8-bit bidirectional interface can be used 3 column for communication between the microcontroller and the PCF8833. The selection of this interfaces is done with pins PS2, PS1 and PS0; see Section 7.1.1. The interface functions of the 8080-series parallel interface are given in Table 86. ...
Page 68
... HIGH when the command data is transferred (see Fig.38). The same is valid when RAM data is sent to the PCF8833 (see Fig.39). The PCF8833 can send data back to the microcontroller in 2 different ways. The protocol for the RDID1, RDID2, RDID3 and RDTEMP commands is illustrated in Fig.40. ...
Page 69
... Fig.41 Parallel bus protocol, read from register (PS[2:0] = XX1) for the RDDIDIF and RDDST commands. 2003 Feb 14 3 driver dummy dummy TB read read dummy RDDIDIF = 24 bits, RDDST = 32 bits read RDDIDIF = 24 bits, RDDST = 32 bits 69 Objective specification PCF8833 command command MGU956 command command MGU957 ...
Page 70
... D/C TB 2003 Feb 14 3 driver Any instruction can be sent in any order to the PCF8833; the MSB is transmitted first. The serial interface is initialized when SCE is HIGH. In this state, SCLK pulses have no effect and no power is consumed by the serial interface. A falling edge on pin SCE enables the serial interface and indicates the start of data transmission ...
Page 71
... Fig.45 Serial bus protocol, Write mode, interrupted by chip enable (SCE); (PS[2:0] = XX0). 2003 Feb 14 3 driver Objective specification PCF8833 P b0 MGU959 P b0 MGU960 P b0 MGU961 ...
Page 72
... After the read command has been sent, the SDIN line must be set to 3-state not later than the falling SCLK edge of the last bit (see Fig.46). When using the RDDIDIF (see Section 6.2.6) or RDDST (see Section 6.2.7) commands the PCF8833 sends data bits respectively back to the microcontroller ...
Page 73
Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ... S TB SCE SCLK SDIN DC SDOUT Fig.47 ...
Page 74
... Inputs and outputs are protected against electrostatic discharge in normal handling. However totally safe recommended to take normal precautions appropriate to handling MOS devices (see “Handling MOS Devices” ). 2003 Feb 14 3 driver PARAMETER ) write pins DD pins SS 74 Objective specification PCF8833 MIN. MAX. UNIT 0.5 +0.5 V 0.5 +4.0 V 0.5 +6.5 V ...
Page 75
... Normal mode; note 5 Normal mode; notes 5 and 7; see Fig.49 Normal mode; note Normal mode; note 5 DD1 DD2 0 0 DD1 SS1 75 Objective specification PCF8833 = 40 to +85 C; unless amb MIN. TYP. MAX. 1.5 3.3 2.4 4.5 2.4 3.5 16.0 20.0 3.8 10.0 3.8 20.0 70 +70 1.5 5 0.5 1 ...
Page 76
... V DD1, DD3 DD1 76 Objective specification MIN. TYP. 100 0 100 0 . DD2 V , inputs at V DD2 output is loaded by LCD1 MGU965 (4) (3) (2) ( cyc (MHz) supplies when writing data from interface to PCF8833 MAX. UNIT 100 mV 100 mV , temperature and or DD1 ...
Page 77
... MIN. TYP. tbf 600 tbf 500 150 160 pF PCF8833 MAX. UNIT Hz kHz kHz ns 100 ...
Page 78
... W(RESL) resetting t W(RESL accepted not accepted Fig.50 Reset timing. 78 Objective specification . + t (t – CYC CCLR CCHR t RT normal operation resetting normal operation t RI accepted PCF8833 t RSS MGU966 ...
Page 79
... Feb 14 3 driver t CSS T SCYC t SLW SDS t SDH t ACC t OH Fig.51 Serial interface timing. t CCLR , t CCLW ACC Fig.52 Parallel interface timing (8080 type). 79 Objective specification PCF8833 t CSH t SCC t SHW CYC t CCHR , t CCHW CHW MGU967 MGU968 ...
Page 80
... Philips Semiconductors STN RGB - 132 132 14 APPLICATION INFORMATION handbook, full pagewidth 66 Figure 54 shows a typical supply and capacitor connections for the PCF8833. 2003 Feb 14 3 driver DISPLAY 132 132 (RGB) 396 PCF8833 I/O Fig.53 Application configuration. 80 Objective specification PCF8833 66 MGU969 ...
Page 81
... V SS2 200 V DD3 DD2 30 V DD1 60 V LCDOUT2 LCDIN2 LDSENSE LCDOUT1 LCDIN1 Fig.54 I/O configuration for the PCF8833. 81 Objective specification PCF8833 MGU970 PCF8833 ...
Page 82
... MODULE MAKER PROGRAMMING The One Time Programmable (OTP) technology has been implemented in the PCF8833. It enables the module maker to perform an LCD supply voltage calibration after it has been assembled on an LCD module. The module maker can also pre-define command set registers in order to provide the setmaker with a ‘ ...
Page 83
... The operation can be thought switch that selects between two sources for the data. When the factory defaults are selected (EFD = 1), changing the values via the interface is not possible, not even by sending the SFD , LCD command. ACTION 83 Objective specification PCF8833 V OFFSET LCD +1240 mV +1200 mV +1160 mV : +80 mV +40 mV ...
Page 84
... In the PCF8833 104 OTP cells are available for the module maker. These cells are organised in a matrix of 7 rows and 15 columns, where the last row is only partially used ...
Page 85
Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ... Table 90 OTP array: content BIT SEAL DFA ...
Page 86
... Objective specification PCF8833 not used ...
Page 87
... OTP cell. This instruction takes complete. During this time all other instructions may be sent. In the PCF8833 the refresh instruction is associated with the Sleep_OUT instruction such that the shift register is automatically refreshed every time the Sleep_OUT instruction is sent. ...
Page 88
Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ... Table 95 Sequence to determine MMVOP COMMAND BYTE STEP D ...
Page 89
... X 0 for 50 ms strongly recommended to use the sequence shown in OTP(drain) 89 Objective specification PCF8833 DESCRIPTION ADDR 0 1 01H reset (may also be hardware reset) wait 1 ms for refresh to take effect 0 F0H enter CALMM mode 1 01H ORA = 000; OPE = 0; ...
Page 90
Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ... Table 97 Sequence to program OTP cells COMMAND BYTE STEP D ...
Page 91
Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ... COMMAND BYTE STEP D ...
Page 92
... OTP(gate) during per programmed OTP OTP(drain) cell V and OTP(gate) V > OTP(drain) V and OTP(gate) V > OTP(drain) 92 Objective specification PCF8833 MIN. TYP. MAX. tbf 8 tbf tbf 0 tbf tbf 8 tbf tbf 0 tbf tbf 100 tbf tbf 500 tbf ...
Page 93
... OPE V OTP(gate) V OTP(drain) OPE V OTP(gate) V OTP(drain) Fig.57 Programming waveforms, OPE rises after V 2003 Feb 14 3 driver t OPESU t WRITEPW (a) V OTP(drain) applied before V OTP(gate) t OPESU t WRITEPW (b) V OTP(gate) applied before V OTP(drain) 93 Objective specification PCF8833 t OPEHD t OPEHD MGU973 and V . OTP(gate) OTP(drain) ...
Page 94
... V SS1 2003 Feb 14 3 driver V DD2 V SS1 V SS2 V LCDIN1 V LCDIN1 V SS1 V LCDOUT2, V LCDSENSE V LCDOUT2 V LCDSENSE SS1 V2H, V1H LCDIN2 V SS1 Fig.58 Protection circuit diagram; part 1. 94 Objective specification PCF8833 V DD3 V SS1 V LCDOUT1 V LCDOUT1 V SS1 T7 V LCDIN2 V SS1 MGU977 ...
Page 95
... – V SS1 2003 Feb 14 3 driver RES, V DD(tieoff), V SS(tieoff) V DD1 V SS1 C1 – – – – V DD1 V SS1 Fig.59 Protection circuit diagram; part 2. 95 Objective specification PCF8833 V OTP(gate OTP(drain) 200 k V SS1 C0 to C395 R131 V LCDIN2 V SS1 MGU978 ...
Page 96
... C336 C335 LCDOUT1 V LCDIN1 C288 C5 C287 C5 V LCDOUT2 V LCDSENSE V LCDIN2 V2L V1L C240 VC C239 V1H V2H R96 C192 R131 pad 769 Fig.60 Bonding pad location. 96 Objective specification PCF8833 C191 C144 C143 C96 C95 C48 C47 C0 R64 R95 pad 1 MGU976 ...
Page 97
... C32 1035.694 C33 1035.694 C34 1035.694 C35 1035.694 C36 1035.694 C37 1035.694 C38 1035.694 C39 1030.568 C40 1030.568 C41 1030.568 C42 1030.568 97 Objective specification PCF8833 COORDINATES PAD 9183.592 1030.568 39 9137.128 1030.568 40 9090.664 1030.568 41 9044.200 1030.568 42 8997.736 1030.568 43 8951.272 1030.568 44 8904 ...
Page 98
... C112 1030.568 C113 1030.568 C114 1030.568 C115 1030.568 C116 1030.568 C117 1030.568 C118 1030.568 C119 1030.568 C120 98 Objective specification PCF8833 COORDINATES PAD x y 116 5502.200 1030.568 117 5455.736 1030.568 118 5409.272 1030.568 119 5362.808 1030.568 120 5316.344 1030.568 121 5269 ...
Page 99
... C190 1030.568 C191 1030.568 C192 1030.568 C193 1030.568 C194 1030.568 C195 1030.568 C196 1030.568 C197 1030.568 C198 99 Objective specification PCF8833 COORDINATES PAD x y 194 1763.608 1030.568 195 1717.144 1030.568 196 1670.680 1030.568 197 1624.216 1030.568 198 1577.752 1030.568 199 1531 ...
Page 100
... C268 1030.568 C269 1030.568 C270 1030.568 C271 1030.568 C272 1030.568 C273 1030.568 C274 1030.568 C275 1030.568 C276 100 Objective specification PCF8833 COORDINATES PAD x y 272 +1917.784 1030.568 273 +1964.248 1030.568 274 +2067.912 1030.568 275 +2114.376 1030.568 276 +2160.840 1030.568 277 +2207 ...
Page 101
... C346 1030.568 C347 1030.568 C348 1030.568 C349 1030.568 C350 1030.568 C351 1030.568 C352 1030.568 C353 1030.568 C354 101 Objective specification PCF8833 COORDINATES PAD x y 350 +5656.376 1030.568 351 +5702.840 1030.568 352 +5749.304 1030.568 353 +5795.768 1030.568 354 +5842.232 1030.568 355 +5888 ...
Page 102
... R28 R29 –1030.568 –1030.568 R30 R31 –1030.568 –1030.568 dummy –1030.568 dummy R63 –1030.568 –1030.568 R62 R61 –1030.568 102 Objective specification PCF8833 COORDINATES PAD x y 428 +9394.968 –1030.568 429 +9441.432 –1030.568 430 +9596.664 –1035.694 431 +9649.464 –1035.694 432 +9702.264 –1035.694 433 +9755 ...
Page 103
... V DD2 +1035.694 V DD2 +1035.694 V DD2 +1035.694 V DD2 +1035.694 D7 +1035.694 D3 +1035.694 D6 +1035.694 D2 +1035.694 D5 103 Objective specification PCF8833 COORDINATES PAD x y 506 +8540.664 +1035.694 507 +8487.864 +1035.694 508 +8329.464 +1035.694 509 +8276.664 +1035.694 510 +8223.864 +1035.694 511 +8171.064 +1035.694 512 +8118.264 +1035 ...
Page 104
... Objective specification PCF8833 COORDINATES PAD x y 584 +825.880 +1035.694 585 +773.080 +1035.694 586 +720.280 +1035.694 587 +667.480 +1035.694 588 +614.680 +1035.694 589 +561 ...
Page 105
... V LCDIN1 +1035.694 C5+ +1035.694 C5+ +1035.694 C5+ +1035.694 C5+ +1035.694 C5+ +1035.694 C5+ +1035.694 C5 +1035.694 C5 +1035.694 C5 +1035.694 C5 105 Objective specification PCF8833 COORDINATES PAD x y 662 4375.976 +1035.694 663 4428.776 +1035.694 664 4481.576 +1035.694 665 4534.376 +1035.694 666 4587.176 +1035.694 667 4639.976 +1035.694 668 4798.376 +1035.694 669 4851 ...
Page 106
... Alignment marks (see Fig.62) +1035.694 Alignment circle 1 +1035.694 Alignment circle 2 +1035.694 Alignment circle 3 +1035.694 Alignment circle 4 +1035.694 +1035.694 +1035.694 +1035.694 106 Objective specification PCF8833 COORDINATES PAD x y 740 9753.480 +1035.694 741 9806.280 +1035.694 742 9859.080 +1035.694 743 9911.880 +1035.694 744 9964 ...
Page 107
... Feb 14 3 driver columns: 46.464 all other: 52.800 columns: 28.424 all other: 32.736 15 381 22.93 mm PC8833-1 pitch center x center Fig.62 Alignment circle detail (80 m diameter). 107 Objective specification DIMENSIONS 105.248 95.348 MGU974 80 m MGU975 PCF8833 UNIT ...
Page 108
... Feb 14 3 driver C E Fig.63 Tray details. Table 101 Tray dimensions DIMENSIONS MGU980 108 Objective specification PCF8833 D B MGU979 DESCRIPTION VALUE pocket pitch y direction 4.45 mm pocket width x direction 23.07 mm pocket width y direction 2.47 mm tray width x direction 50.8 mm tray width y direction 50.8 mm number of pockets in ...
Page 109
... Objective specification PCF8833 DEFINITION These products are not Philips Semiconductors ...
Page 110
... Accordingly, Philips Semiconductors assumes no liability for device functionality or performance of the die or systems after third party sawing, handling, packing or assembly of the die the responsibility of the customer to test and qualify their application in which the die is used. 2003 Feb 14 3 driver 110 Objective specification PCF8833 ...
Page 111
... Philips Semiconductors STN RGB - 132 132 2003 Feb 14 3 driver NOTES 111 Objective specification PCF8833 ...
Page 112
Philips Semiconductors – a worldwide company Contact information For additional information please visit http://www.semiconductors.philips.com. For sales offices addresses send e-mail to: sales.addresses@www.semiconductors.philips.com. © Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2003 All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited ...